Fire Resistant PU Coated Fiberglass Fabrics
- Loading Port:
- Ningbo
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 500 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 300000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description: PU coated fabric is fiberglass cloth coated with flame retarded PU (polyurethane) on one-sided or double-sided surface. PU coating imparts fiberglass cloth good weave setting (high stability) and water resistance properties. PU coated fiberglass cloth can withstand a continuous working temperature of 550℃ and a short duration working temperature of 600℃. Compared with basic woven glass fiber fabric, It has many good features such as good air gas sealing, fire resistant, abrasion resistance, oils, solvents resistance chemical resistant ability, no skin irritation, halogen free. Can be used in fire and smoke applications, such as welding blanket, fire blanket, fire curtain, fabric air distribution ducts, fabric duct connector. We can offer polyurethane coated fabric with different colors, thickness, widths.
Features: Fire Resistant, Water Resistant, Abrasion Resistance
Application: Fabric Expansion Joint, Flexible Connector, Fireproof Curtain, Welding Curtain, Smoke Curtain, Welding Blanket, Fire Blanket, Insulation Cover
PRICE: USD3 per square meter
UNIT: square meter
MOQ: 500square meters
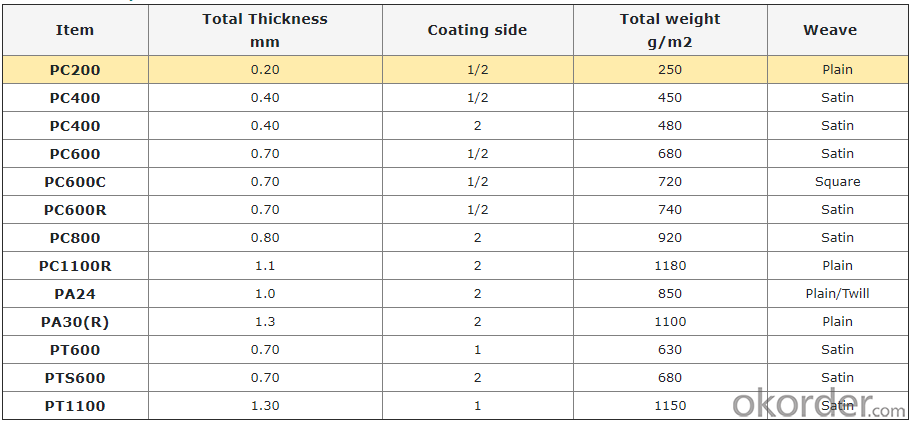
Weight: 210gsm-1800gsm
Width: 1m-2m or customized
Yarn Type: E-glass
Standing temperature -50℃-550℃
Product name: PU coated fiberglass fabric
Coating/Finish/Surface Treatment: PU coated
Roll length: 50 meter or customized
Color: Grey, Red, White, Green, Blue, Yellow, or customized
Weave Type: twill woven
Alkali content: alkali free
Processing service: cutting
Material: fiberglass PU
Thickness: 0.2mm to 3mm
Size: can be customized
Supply ability: 300000 meters per month
Packaging: PU coated fiberglass fabric rolls packed in cartons loaded on pallets or according to customers’ requirements
Lead time: 7-30 days
- Q: Is fiberglass fabric resistant to chemicals in food processing?
- Yes, fiberglass fabric is generally resistant to chemicals in food processing.
- Q: Which is more durable, stone cotton or glass cloth?
- No data connection, I design a variety of heating process, with some experience. You say, 160 degrees brittleness is generally a temperature measurement point and the heat source has a certain distance to show an illusion. The surface of the heat source may have reached a high temperature, and the heating medium is very low. If it is 160 degrees hot air heating, never crack. Welcome to the heating problem.
- Q: What are the environmental impacts of using fiberglass fabric?
- The use of fiberglass fabric can have several environmental impacts. Firstly, the production of fiberglass fabric involves the extraction of raw materials, such as silica sand, which can have detrimental effects on the environment. The extraction process can disrupt local ecosystems, contribute to deforestation, and result in the release of harmful pollutants into the air and water. Furthermore, the manufacturing process of fiberglass fabric requires a significant amount of energy, often derived from non-renewable sources. This energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and exacerbates climate change. Additionally, the production process may also generate toxic byproducts, such as formaldehyde and volatile organic compounds, which can have harmful effects on human health and the environment if not properly managed. Another environmental concern related to fiberglass fabric is its end-of-life disposal. Fiberglass is not biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a long time. Improper disposal of fiberglass fabric, such as sending it to landfills, can lead to the release of microplastics into the soil and water, posing a threat to wildlife and ecosystems. Moreover, fiberglass fabric is often coated with resins or chemicals to improve its performance and durability. These coatings may contain harmful substances, such as heavy metals or flame retardants, which can leach into the environment during use or disposal, potentially contaminating soil, water, and air. Overall, the environmental impacts of using fiberglass fabric include habitat destruction, energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, generation of toxic byproducts, poor end-of-life disposal, and contamination risks. It is essential to consider these impacts and explore alternative materials or manufacturing processes that are more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- Q: Is fiberglass fabric resistant to chemicals used in wastewater treatment?
- Fiberglass fabric exhibits remarkable resistance to the chemicals employed in wastewater treatment. Its outstanding chemical resistance has earned fiberglass a reputation as an optimal material for scenarios where exposure to diverse chemicals is probable. It has the capacity to endure a broad spectrum of corrosive substances, such as acids, alkalis, and solvents, commonly encountered in wastewater treatment processes. Due to the non-reactive quality of fiberglass fabric, it remains unaffected and undamaged when exposed to these chemicals, making it a dependable choice for implementation in wastewater treatment facilities. Additionally, fiberglass fabric also offers resistance to UV radiation, moisture, and fluctuations in temperature, which further bolsters its durability and suitability for such environments.
- Q: Can fiberglass fabrics be used for gasketing or sealing purposes?
- Yes, fiberglass fabrics can be used for gasketing or sealing purposes. Fiberglass fabrics are known for their high temperature resistance, chemical resistance, and excellent electrical insulation properties. These characteristics make them ideal for applications where gasketing or sealing is required, such as in industrial equipment, automotive engines, and electrical enclosures. Fiberglass fabrics can be used to create gaskets or seals that are able to withstand high temperatures, prevent leaks, and provide a reliable barrier against moisture, chemicals, and gases. The fabrics can be easily cut or molded into various shapes and sizes, allowing for customized gaskets or seals to fit specific requirements. Additionally, fiberglass fabrics are lightweight and have a long lifespan, making them a cost-effective choice for gasketing or sealing applications.
- Q: What are the environmental considerations of using fiberglass fabric?
- Using fiberglass fabric comes with various environmental considerations. To begin with, the extraction of raw materials like silica sand, limestone, and soda ash for fiberglass fabric production can harm ecosystems and contribute to habitat destruction. Moreover, the manufacturing process itself requires a substantial amount of energy, usually sourced from non-renewable sources, resulting in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Furthermore, fiberglass fabric is non-biodegradable and can persist in the environment for a considerable period if not disposed of properly. This can result in landfill overcrowding, generating more waste and occupying valuable space. Additionally, certain applications of fiberglass fabric, such as insulation or boat building, may release microscopic glass fibers into the air. Inhaling these fibers can pose health risks, including respiratory issues and lung damage, for workers involved in manufacturing or installing fiberglass products. On a positive note, fiberglass fabric is highly durable and long-lasting, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. It also exhibits resistance to moisture, chemicals, and fire, contributing to the safety and longevity of structures and products in which it is utilized. To address the environmental impacts associated with fiberglass fabric, it is crucial to consider sustainable alternatives and practices. This may involve utilizing recycled fiberglass materials, reducing energy consumption during production, improving waste management and recycling programs, and promoting proper safety measures to safeguard workers from potential health hazards linked to fiberglass. Furthermore, exploring alternative materials with lower environmental footprints and greater eco-friendliness could be considered.
- Q: Can fiberglass fabric be used for insulation in wineries?
- Certainly, insulation in wineries can be achieved with the utilization of fiberglass fabric. This particular type of fabric is highly favored for its remarkable thermal qualities and long-lasting nature. By effectively trapping and preserving heat, it significantly aids in maintaining the ideal temperature conditions within winery premises. Furthermore, fiberglass fabric possesses the vital characteristic of being resistant to mold, mildew, and moisture, which is particularly crucial in winery settings where humidity levels tend to be elevated. Moreover, it boasts the advantage of being simple to install and can be tailored to meet specific insulation requirements. In summary, fiberglass fabric represents a dependable and effective choice for winery insulation purposes.
- Q: What are the different dyeing options available for fiberglass fabric?
- Fiberglass fabric offers various dyeing options, each with its own advantages and factors to consider. 1. Pigment dyeing: To achieve color, pigments are added to the fabric, bonding with the fibers. This method provides a wide range of color choices and is relatively straightforward. However, it may not deeply or uniformly penetrate the fabric, and the color may fade over time due to sunlight and other environmental factors. 2. Solution dyeing: Color is added to the liquid before it becomes fibers. This results in a more permanent and fade-resistant color, as the dye is integrated throughout the entire fabric. However, it limits color options since dye must be added during manufacturing. 3. Disperse dyeing: Commonly used for synthetic fibers like fiberglass, disperse dyeing involves dispersing dye in a carrier liquid, then applying it to the fabric through immersion, padding, or spraying. It offers good color fastness and vibrant, uniform colors. However, it requires high temperatures and pressure for proper dye penetration. 4. Sublimation dyeing: This heat transfer process converts dye from solid to gas and back to solid on the fabric, directly bonding with the fibers. It results in vibrant, long-lasting colors and allows for intricate patterns and designs. However, it requires specialized equipment and is typically more suitable for large-scale production. It's important to note that the available dyeing options may vary depending on the specific type and composition of fiberglass fabric. Additionally, when choosing a dyeing method, factors like desired color, durability, and application requirements should be considered.
- Q: Can fiberglass fabric be used for making window screens?
- Certainly, window screens can indeed be made using fiberglass fabric. Fiberglass, being a lightweight and durable material, possesses resistance against tears, corrosion, and the harmful effects of UV rays. This outstanding quality makes it an excellent choice for crafting window screens. Moreover, its high flexibility enables effortless installation and removal. In addition to these benefits, fiberglass fabric boasts a fine mesh structure that effectively blocks insects while still permitting airflow and maintaining visibility. All in all, fiberglass fabric is widely favored and considered a dependable option for producing window screens.
- Q: What are the different weight options for fiberglass fabric?
- Fiberglass fabric comes in various weight options, which determine its thickness and density. Manufacturers and intended applications can influence the weight options available. Fiberglass fabric weight is typically measured in ounces per square yard (oz/yd²) or grams per square meter (g/m²). Different weight options for fiberglass fabric exist, depending on the manufacturer and intended use. Common weight options include 1.5 oz/yd², 3 oz/yd², 6 oz/yd², 9 oz/yd², and 18 oz/yd². These weights indicate the number of fiberglass strands per unit area, with higher weights indicating a denser fabric. Lighter weight fiberglass fabrics, like 1.5 oz/yd², find application in projects requiring flexibility and a smooth finish, such as surfboards, model airplanes, and lightweight structures. The automotive industry also commonly utilizes them for interior parts or as reinforcement in composite materials. Medium weight fiberglass fabrics, ranging from 3 oz/yd² to 9 oz/yd², serve general-purpose applications, including boat building, mold making, and repairing or reinforcing structures. These weight options strike a balance between flexibility and strength, making them suitable for a wide range of projects. Heavier weight fiberglass fabrics, such as 18 oz/yd², come into play when maximum strength and durability are necessary. They find common use in industrial applications like tank and pipe wrapping, as well as in the construction industry for reinforcing concrete or other structural elements. It is important to consider that the weight of fiberglass fabric is just one factor to contemplate when choosing the appropriate fabric for a specific application. Other factors, like weave pattern, resin compatibility, and intended use, should also be taken into account to ensure the desired performance and outcome.
Send your message to us
Fire Resistant PU Coated Fiberglass Fabrics
- Loading Port:
- Ningbo
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 500 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 300000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























