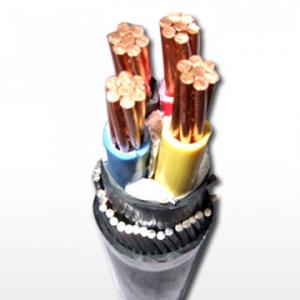
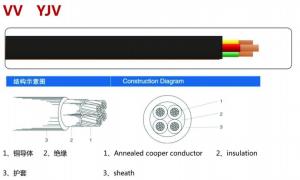
cross linked polyethylene insulated fire-resistant cables
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Q: How would I go about stripping 4 gauge power battery cable for my amp? oh and how would i screw the fuse holder down? with what kind of screws? thank you!
- I use a knife to strip that wire, just be careful not to nick the wire. Drill a hole and use sheet metal screws to screw the fuse holder down.
- Q: I know there is problem in the CPU, please suggest what is the problem and how much it is going to cost me?
- Power cable into CPU? I guess you must possibly still have some of those dual power connector Power Supply? Those one where you can connect both the Power to the monitor and the input power to the CPU? If this is the case, your Power supply is possibly dying slowly. You need to change the poer supply. However, if that is not the kind of power supply that you have, I guess what you are pssibly talking about is that your monitor data communication cable which you connect to the CPU so that the data can be transmitted through to your monitor? If this is the case, then your monitor is not having any problem, it is just responding to the fact that it is properrly connected. Put on your system and see if your monitor do come on... If it comes on then everything is fine.... Now finally, if all these is not the case, then it mean you have not put your question properly. Rephrase your question so that you can have an answer... except ofcourse you are just trying to fool around...
- Q: I need to select a power cord for a computer and other appliances (like a printer). Power cords usually have their amps and voltage (capacities?) imprinted on the outside. What is the rule of thumb for selecting a power cord and why?For example, if my printer has the following requirements:Power Source AC 120V 50/60 HzPower Consumption - 5W-350WWhat amp/voltage type of power cord will do the job?I am of course concerned about overloading the cord with too much electric requirements.(People who actually know this matter SPECIFICALLY only need to reply; please excuse if the electric language is not used right.)
- The power cables themselves don't have much bearing on Power Source AC 120V 50/60 Hz (Your typical household outlet) You couldn't acciddentally plug it into a 220 line anyway. Power Consumption - 5W-350w -- How many watts of power it draws from the socket. Typically the thicker guaged wire is better to use, as it has less impedance or so I've been told.
- Q: My friend I were going to play his second Xbox 360 n his living room. Went to turn it on and the RROD turned up with three lights. So we took this one and hooked it up to the cables in his room. And guess what? No RROD... So, I am lead to belive that the Xbox 360's power cable is the one that causes the RROD. Only problem is that most people can' test this due to not having a second power cable. So post your ideas about this idea. Could Microsoft be lying to us by saying that the malfunction is inside there console. I'm only 14 and i figured this out. So, how is it that no one else has??
- Nope nothing new, there are like 5 types of RROD which is why they ask you to check the ligt on the power cable. if its green then its the consle but if its red then its the power cord. it might have been Red or you might have had the 1 time only problem which i had
- Q: difference between power and control cable?
- Sorry, but what is the context? It's difficult to answer without more detail.
- Q: Low voltage power cable telemetry insulation resistance, the number should be used to shake the table? The More
- ZR-KVVRP-500 is mainly used for transmission control, measurement signals and other cables. ZR: Control cable KVVRP: PVC insulation 500: Rated voltage 500 V or less 1 × 2: Two core 1.5: Wire diameter
- Q: best buy geeks advised me to buy wd320sata h/d to replace seagate barracuda 7200 h/d....... cannot connect .... no sata connector on motherboard that i can find....... instructions says need power cord. any suggestions????????? please and thank you.........
- The SATA specification demands 7 pins to flow archives. Conveying potential to gadgets demands heavily greater desirable potential throughput than conveying archives. potential adapters have been redesigned for SATA gadgets from usual Molex to make it as common to plug and unplug because of the fact the recent SATA archives cables. The redecorate made the pins smaller. With electrical energy bypass with the aid of potential conduits, travelling electrons inevitably hit the molecules of the conduit itself, which excites the molecules and the molecules launch this further potential as warmth. once you're attempting to maintain an identical bypass of electrons over the years yet shrink the actual length of the conduit (as develop into finished with the SATA potential spec), an identical variety of electrons could desire to bypass interior the path of the conduit over the years yet with the aid of a smaller pipe. This focused 'site visitors' leads to greater collisions, ensuing in greater desirable warmth output from the steel conduit. with the intention to have the smaller pipe and an identical quantity of site visitors without overheating the steel conduit to the factor the place it burns the plastic housing, you may desire to have greater of the smaller pipes turning in that site visitors. think of of it like highway site visitors. in case you may desire to make a highway smaller, the site visitors that already traverses that highway will now could desire to deal with one yet another for that narrower thoroughfare. with the intention to maintain site visitors shifting and forestall site visitors jams, you may desire to construct further roads to accommodate that exact same site visitors quantity. only area of this analogy that would not correlate is that electrons do no longer decelerate once you're piping them with the aid of a smaller conduit.
- Q: I have a 2003 Honda Accord. I'm trying to put an amp and sub in it. My problem is, I'm not sure how to get the power cable from the batter to the inside of the car. I know it needs to go through the firewall, but I need to know exactly where. I couldn't find any unoccupied holes. I also need to know where the other side of the hole will be so that I can grab the wire from the other side. Pictures would be really great if you have them.
- The best place to run a wire through the firewall is through the firewall connector. Take the firewall connector apart, and look for an empty connection port. Take your power supply wire and hook it up to the engine compartment side, then take another wire (to lead to the radio), and hook it up top the corresponding port in the interior side of the connector. This will be the best way to make your connection. If you can't do this, then drill a hole in the firewall, install a grommet to protect the wires from the firewall. Again, the firewall connector will be your best bet, and people will be asking where did you take it to get it installed. This is how a professional would do it.
- Q: what does it mean by 4 core cable, 35 mm. can it be used for DC and AC as well. can it be used for a 3 phase AC. what are its advantages and disadvantages? is one core means one phase? can we use 2 core cable for 3 phase AC? am really confused please explain.
- A 4 core cable has 4 conductors in an overall sheath. The 35 mm indicates the area of each conductor's copper is 35 square mm. You can use the 4 core cable for 3-phase power (3 wires with a spare or ground). You cant use a 2-core cable for three phase service, unless you are using three 2-core cables with the 2 wires connected in parallel to provide one of the phases. It can be used for AC or DC. TexMav
- Q: i am going to establish a new power cable manufacturing business. i want to ask you what should i name to my business or what brand name should i adopt that is appopriate.
- follow the suggestions. Good Luck
Send your message to us
cross linked polyethylene insulated fire-resistant cables
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords