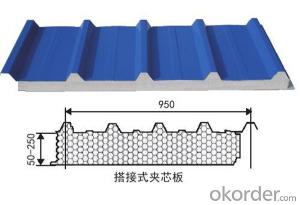
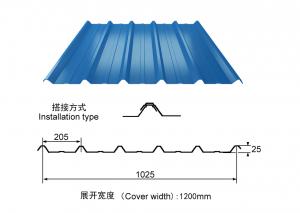
Corrugated color coated Galvanized steel from China, CNBM, fast delivery
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1) AVAILABLE DESIGNATION OF (Prepainted galvanized steel coils) printed PPGI coils
Quality Q/BQB 440-2003 JIS G3312-1994 EN 10326-2004 ASTM A653-02a
EN 10327-2004 (BASE PLATE)
(BASE PLATE)
Commercial Steel TDC51D CGCC DX51D+Z/AZ CS Type A/B/C
Forming Steel (TSt01,TSt02,TSt03) CGCD1 FS Type A, Type B
Drawing TDC52D /TDC53D - DX52D+Z/AZ DDS TYPE A/C
Steel DX53D+Z/AZ
Structural TS280GD(TStE28) CGC400 S280D+Z/AZ SS275
Steel TS350GD(TStE34) CGC440 S350D+Z/AZ SS340 Class1
2) OUR SPECIFICATION OF (Prepainted galvanized steel coils) printed PPGI coils
Available Size:
Manufacturer Thickness Width Length of plate Inner diameter of coil
JIANGSU HUIYE STEEL SHEET CO.,LTD 0.2-1.2mm 800/914/1000/1200/1219/1250mm 1000-6000mm 508mm/610mm
Coated Mass OF (Prepainted galvanized steel coils) printed PPGI coils:
Base plate Available Coated Mass(g/m^2)
Galvanized Steel 80, 100, 120, 160, 180
Galvalume Steel 50, 70, 150
Available Painting OF (Prepainted galvanized steel coils) printed PPGI coils:
Category of Painting Item Code
Polyester PE
High-durability polyester HDP
Silicon modified polyesters SMP
Polyvinylidene fluoride PVDF
Easy-Cleaning —
Painting Thickness Top side: 20+5microns;
Bottom side: 5~7microns.
Color System Produce according to RAL Color System or as per buyer’s color sample.
Painting structure Top surface Bottom surface
Primer coating No coating 1/0
Primer coating Primer coating 1/1
Primer coating + Finish coating No coating 2/0
Primer coating + Finish coating Primer coating or single back coating 2/1
Primer coating + Finish coating Primer coating + Finish back coating 2/2
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for construction purposes?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for construction purposes. They are commonly used in various construction applications such as roofing, wall cladding, flooring, and structural components due to their durability, strength, and resistance to fire and corrosion.
- Q: Are the steel sheets suitable for automotive body repairs?
- Indeed, automotive body repairs can be effectively carried out using steel sheets. Given its exceptional strength and durability, steel is widely utilized in the automotive sector. This material exhibits remarkable resistance to impact and contributes significantly to the structural integrity of the vehicle's body. Consequently, steel sheets are frequently employed in the restoration of impaired or dented body panels, facilitating a flawless repair that reinstates the vehicle's original form and robustness. Moreover, steel sheets can be effortlessly manipulated and molded to correspond precisely to the unique contours of the vehicle, guaranteeing a meticulous and precise restoration.
- Q: Are the steel sheets suitable for food-grade applications?
- Yes, steel sheets can be suitable for food-grade applications. Stainless steel in particular is commonly used in the food industry due to its excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and ease of cleaning. It is non-reactive and does not release any harmful substances into food, making it a safe choice for food storage, processing, and transportation. Additionally, stainless steel is resistant to high temperatures and can withstand rigorous cleaning and sanitization processes, making it ideal for use in food-grade applications. However, it is important to ensure that the steel sheets meet the necessary food-grade standards and regulations before using them in any food-related setting.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for manufacturing shipping containers?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for manufacturing shipping containers. Steel is a common material choice for shipping containers due to its strength, durability, and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. Steel sheets are used to construct the walls, floors, and roofs of shipping containers, providing a secure and reliable structure for transportation and storage purposes.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for stairs and handrails?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for stairs and handrails. Steel is a durable and sturdy material that is commonly used in construction, including for stairs and handrails. It provides strength, stability, and a modern aesthetic to these structures.
- Q: What is the process of applying insulation materials to steel sheets?
- The process of applying insulation materials to steel sheets typically involves preparing the steel surface, applying an adhesive or bonding agent, and then affixing the insulation material to the steel using pressure or other mechanical means. This ensures a secure and effective insulation layer on the steel sheets.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in the construction of bridges?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used in the construction of bridges. Steel sheets are commonly used as structural components for various types of bridges due to their high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. They provide excellent load-bearing capacity and can be easily fabricated and assembled, making them a popular choice in modern bridge construction.
- Q: Are steel sheets non-magnetic?
- No, steel sheets are generally magnetic.
- Q: What are the standard dimensions of steel sheets?
- The standard dimensions of steel sheets vary depending on the specific type and application. However, common standard dimensions for steel sheets range from 4 feet by 8 feet to 5 feet by 10 feet, with thicknesses typically ranging from 16 gauge (0.0598 inches) to 10 gauge (0.1345 inches).
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for staircases?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for staircases. Steel sheets are often used in the construction of staircases due to their durability, strength, and resistance to wear and tear. They can be molded and shaped into various designs to create aesthetically pleasing staircases while providing a sturdy and long-lasting structure.
Send your message to us
Corrugated color coated Galvanized steel from China, CNBM, fast delivery
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords