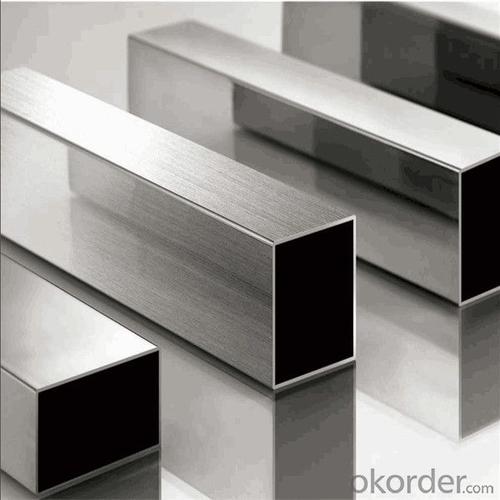
304 316L Stainless Steel Pipe Price (ISO Certified factory direct price )
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 25000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
316 stainless steel pipe
Name | Stainless Steel Seamless & Welded Tube &Pipe | |||||
Items | Square tubes, round tubes, oval pipes, special shaped pipes, empaistic pipes, fittings | |||||
Standard | ASTM A554, A249, A269 and A270 | |||||
Material Grade | 201: Ni 0.8%~1% | |||||
202: Ni 3.5%~4.5% | ||||||
304: Ni 8%, Cr 18% | ||||||
316: Ni 10%, Cr 18% | ||||||
316L: Ni10%~14% | ||||||
430: Cr16%~18% | ||||||
Outer Diameter | 9.53mm--159mm | |||||
Thickness | 0.3mm - 3.0mm | |||||
Length | 6m or as customers' request | |||||
Tolerance | a) Outer Diameter: +/- 0.2mm | |||||
b) Thickness: +/- 0.02mm | ||||||
c) Length: +/- 5mm | ||||||
Surface | 180G, 240G, 320G Satin / Hairline 400G, 600G Mirror finish | |||||
Application | handrail,railing, staircase, weldmesh screen,door,window, balcony,fence,bench,furniture,etc | |||||
Test | Squash test, extended test, water pressure test, crystal rot test, heat treatment, NDT | |||||
Chemical Composition of Material | Material
Composition | 201 | 202 | 304 | 316L | 430 |
C | ≤0.15 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.12 | |
Si | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | |
Mn | 5.5-7.5 | 7.5-10 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤1.00 | |
P | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.040 | |
S | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | |
Cr | 13-15 | 14-17 | 18-20 | 16-18 | 16-18 | |
Ni | 0.7-1.1 | 3.5-4.5 | 8-10.5 | 10-14 | ||
Mo | 2.0-3.0 | |||||
Mechanical Property | Material Item | 201 | 202 | 304 | 316 | |
Tensile Strength | ≥535 | ≥520 | ≥520 | ≥520 | ||
Yield Strength | ≥245 | ≥205 | ≥205 | ≥205 | ||
Extension | ≥30% | ≥30% | ≥35% | ≥35% | ||
Hardness (HV) | <105 | <100 | <90 | <90 | ||
Definition of stainless steel(Adopted form Wikipedia)
In metallurgy, stainless steel, also known as inox steel or inox from French "inoxydable",
is defined as a steelalloy with a minimum of 10.5% to 11% chromium content by mass.
Stainless steel does not readily corrode, rust or stain with water as ordinary steel does,
but despite the name it is not fully stain-proof, most notably under low oxygen, high salinity,
or poor circulation environments. It is also called corrosion-resistant steel or CRES
when the alloy type and grade are not detailed, particularly in the aviation industry.
There are different grades and surface finishes of stainless steel to suit the environment
the alloy must endure. Stainless steel is used where both the properties of steel
and resistance to corrosion are required.
Surface Finish :
Surface finish | Characteristics and application |
No.2B | The surface brightness and flatness of no2B is better than no2D. then through a special surface treatment to improve its mechanical properties, No2B could nearly satisfy comprehensive uses. |
No.3 | Polished with abrasive belt of git#100-#200, have better brightness with discontinuous coarse stria, used as inner and external ornaments for building, electrical appliances and kitchen utensils etc. |
No.4 | Polished with abrasive belt of grit #150-#180,have better brightness with discontinuous coarse stria, but thinner than No3, are used as bathtub buildings inner and external ornaments electrical appliances kitchen utensils and food processing equipment etc. |
HL | Polished with abrasive belt of grit #150-#320 on the NO.4 finish and has continuous streaks, mainly used as buildings ornaments elevators, door of building, frontal plate etc. |
BA | Cold rolled, bright annealed and skin-passed, the product have excellent brightness and good reflexivity like mirror, kitchen apparatus, ornament etc. |
8K | The product have excellent brightness and prefer reflexivity can to be the mirror. |
Mechanical Properties: MaterialY.S(N/MM2)T.S(N/MM2)ElongationHRB304>205>520>40<95304l>175>480>40<90316>205>520>40<90316l>175>480>40<90430>205>450>22<89
Applications: SurfaceApplication2BMedical equipment, Food industry, Construction material, Kitchen utensils.BAKitchen utensils, Electric equipment, Building construction.No.1Chemical tank, pipe.No.4Kitchen utensils, Building construction,Medical equipment.HLBuilding Construction.
|
| ---Packing & Transport--- Packing
Transport
|


- Q: What is the internal lining used for stainless steel pipes?
- The internal lining used for stainless steel pipes can vary depending on the specific application and intended use of the pipes. Some common options for internal linings in stainless steel pipes include epoxy coatings, ceramic linings, and plastic or polymer linings. These linings are used to provide corrosion resistance, enhance the smoothness of the pipe's interior surface, and protect the stainless steel from chemical reactions or wear.
- Q: What is the difference between 304N and 304LN stainless steel pipes?
- The main difference between 304N and 304LN stainless steel pipes lies in their chemical composition and the presence of nitrogen. 304N stainless steel pipes have a higher nitrogen content compared to 304LN stainless steel pipes. Nitrogen enhances the strength and corrosion resistance of stainless steel, making it more suitable for applications in high-stress environments or corrosive conditions. The increased nitrogen content in 304N stainless steel pipes improves their overall performance in terms of strength, hardness, and resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. On the other hand, 304LN stainless steel pipes have a lower nitrogen content but still possess excellent corrosion resistance properties. These pipes are specifically designed for low-temperature applications where toughness is required. The lower nitrogen content in 304LN stainless steel pipes helps maintain good weldability and formability, making them suitable for various fabrication processes. In summary, the difference between 304N and 304LN stainless steel pipes lies in the nitrogen content, which affects their strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for different applications.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for architectural purposes?
- Stainless steel pipes are indeed capable of being utilized for architectural purposes. The architectural applications of stainless steel are facilitated by several properties it possesses. Firstly, its resistance to corrosion is incredibly high, a crucial factor for structures that are exposed to the elements. Moreover, the sleek and modern appearance of stainless steel pipes can impart an aesthetic touch to architectural designs. In addition to this, stainless steel is a formidable and long-lasting material that provides structural integrity and longevity to buildings. Its versatility allows it to be incorporated into a variety of architectural elements, including handrails, balustrades, staircases, and structural supports. All in all, due to their combination of corrosion resistance, aesthetic appeal, and strength, stainless steel pipes are a widely favored choice for architectural purposes.
- Q: Stainless steel seamless steel tube, ordinary seamless steel pipe, which is good?
- The general stainless steel tube is wear-resistant, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance. Plain carbon steel seamless tubes resist pressure better than stainless steel.
- Q: What are the common industry standards for stainless steel pipes?
- The recommended standards for stainless steel pipes differ depending on the intended use and the regulations of each country. Nonetheless, there are several widely recognized and accepted standards, such as those established by the ASTM, ASME, and ISO. The ASTM standards, like ASTM A312 and ASTM A269, provide guidelines for the production and quality control of stainless steel pipes. These standards cover various aspects, including the chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, and tolerances. The ASME standards, particularly ASME B36.19 and ASME B36.10M, specify the dimensions and wall thicknesses of stainless steel pipes for specific applications. Additionally, ASME B31.3 offers guidelines for the design, construction, and maintenance of process piping systems that may incorporate stainless steel pipes. The ISO standards, such as ISO 1127 and ISO 2037, establish international guidelines for the dimensions, tolerances, and surface finishes of stainless steel pipes. These standards ensure that stainless steel pipes can be used interchangeably and are compatible across different countries. Furthermore, specific industries may have their own requirements. For instance, the food and beverage industry often follows the standards set by organizations like 3-A Sanitary Standards, which emphasize the cleanliness and hygiene of stainless steel pipes used in food processing. It is crucial to consult the relevant standards and regulations for each specific application to ensure compliance with industry requirements and to guarantee the safe and efficient use of stainless steel pipes.
- Q: How do you calculate the heat transfer coefficient of stainless steel pipes?
- The heat transfer coefficient of stainless steel pipes can be calculated using various methods, including empirical correlations and theoretical calculations. One commonly used empirical correlation is the Dittus-Boelter equation, which relates the heat transfer coefficient to the Reynolds number and Prandtl number. The Dittus-Boelter equation is given by: Nu = 0.023 * Re^0.8 * Pr^0.4 Where Nu is the Nusselt number, Re is the Reynolds number, and Pr is the Prandtl number. The Nusselt number represents the ratio of convective to conductive heat transfer and is dimensionless. To calculate the Reynolds number, use the following formula: Re = (ρ * v * D) / μ Where ρ is the density of the fluid, v is the velocity of the fluid, D is the hydraulic diameter of the pipe, and μ is the dynamic viscosity of the fluid. The Prandtl number can be determined using the following equation: Pr = μ * Cp / k Where Cp is the specific heat capacity of the fluid and k is the thermal conductivity of the fluid. Once the Reynolds and Prandtl numbers are determined, substitute them into the Dittus-Boelter equation to calculate the Nusselt number. Finally, the heat transfer coefficient can be obtained by multiplying the Nusselt number with the thermal conductivity of the fluid and dividing it by the hydraulic diameter of the pipe: h = (Nu * k) / D Where h is the heat transfer coefficient. It is important to note that these calculations are based on assumptions and empirical correlations, and actual heat transfer coefficients may vary depending on various factors such as pipe roughness, fluid properties, and flow conditions. Therefore, it is recommended to consult relevant heat transfer literature or conduct experimental studies for more accurate results.
- Q: Water and electricity thin wall stainless steel tube 304 material delta 2 what does that mean?
- 304 stainless steel is a universal stainless steel material, antirust performance than the 200 series of stainless steel material stronger.
- Q: What is the difference between 201 and 316 stainless steel pipes?
- The main difference between 201 and 316 stainless steel pipes lies in their chemical composition and respective properties. 201 stainless steel is a lower grade of stainless steel compared to 316. It contains a higher amount of manganese and nitrogen, which gives it improved strength and corrosion resistance compared to other lower grade stainless steels. However, it is not as durable as 316 stainless steel and is more prone to corrosion and rusting. On the other hand, 316 stainless steel is a high-quality grade that contains a higher percentage of chromium and nickel. These elements enhance its corrosion resistance, making it highly resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride environments. 316 stainless steel pipes are also more resistant to high temperatures and have superior strength compared to 201 stainless steel pipes. Therefore, 316 stainless steel pipes are widely used in industries with demanding requirements such as marine, chemical, and medical sectors, where corrosion resistance and durability are crucial. 201 stainless steel pipes, while suitable for general applications, are more commonly used in less demanding environments where cost-effectiveness is a priority.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes resistant to high temperatures?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are highly resistant to high temperatures.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for hydroelectric power plants?
- Hydroelectric power plants can indeed utilize stainless steel pipes. The reason stainless steel is favored for various industrial applications is because of its exceptional corrosion resistance. Within a hydroelectric power plant, the generation of electricity is achieved by the passage of water through turbines. The composition and flow rate of this water can often result in corrosive tendencies. Consequently, stainless steel pipes, which are highly resistant to corrosion, are the ideal conduit for conveying the water in hydroelectric power plants. Furthermore, stainless steel pipes bring forth additional advantages such as superior strength, durability, and the capacity to withstand elevated pressures and temperatures. These properties are vital for ensuring the efficient and dependable operation of the power plant. Moreover, stainless steel pipes maintain their structural integrity over time, thus reducing the need for frequent maintenance and replacement. In addition, stainless steel pipes possess the ability to handle the internal and external pressures that arise during the power generation process. They can effectively endure the high-speed flow of water and resist erosion caused by sediment and debris in the water supply. Consequently, the longevity and efficiency of the hydroelectric power plant are secured. To conclude, stainless steel pipes are an exceptional choice for hydroelectric power plants due to their corrosion resistance, strength, durability, and ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures.
Send your message to us
304 316L Stainless Steel Pipe Price (ISO Certified factory direct price )
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 2 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 25000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords