Structure Steel Equal Angle Bar
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
OKorder is offering Structure Steel Hot Rolled Angle Bar at great prices with worldwide shipping. Our supplier is a world-class manufacturer of steel, with our products utilized the world over. OKorder annually supplies products to European, North American and Asian markets. We provide quotations within 24 hours of receiving an inquiry and guarantee competitive prices.
Product Applications:
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
Product Advantages:
OKorder's Structure Steel Hot Rolled Angle Bar are durable, strong, and resist corrosion.
Main Product Features:
· Premium quality
· Prompt delivery & seaworthy packing (30 days after receiving deposit)
· Corrosion resistance
· Can be recycled and reused
· Mill test certification
· Professional Service
· Competitive pricing
Product Specifications:
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
3.Material: JIS G3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
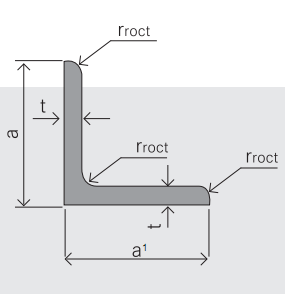
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material Specifications:
Grade | Yield Strength,N/mm² | Extension Strength N/mm² | |||
Thickness of Steel,mm | |||||
≦16 | >16-≦40 | >40-≦100 | >100 | ||
SS330 | ≧205 | ≧195 | ≧175 | ≧165 | 330-430 |
SS400 | ≧245 | ≧235 | ≧215 | ≧205 | 400-510 |
SS490 | ≧285 | ≧275 | ≧255 | ≧245 | 490-610 |
SS540 | ≧400 | ≧390 | - | - | ≧540 |
Packaging & Delivery of Angle Steel
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered byOKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q3: How soon can we receive the product after purchase?
A3: Within three days of placing an order, we will begin production. The specific shipping date is dependent upon international and government factors, but is typically 7 to 10 workdays.
Q4: What makes stainless steel stainless?
A4: Stainless steel must contain at least 10.5 % chromium. It is this element that reacts with the oxygen in the air to form a complex chrome-oxide surface layer that is invisible but strong enough to prevent further oxygen from "staining" (rusting) the surface. Higher levels of chromium and the addition of other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum enhance this surface layer and improve the corrosion resistance of the stainless material.
Q5: Can stainless steel rust?
A5: Stainless does not "rust" as you think of regular steel rusting with a red oxide on the surface that flakes off. If you see red rust it is probably due to some iron particles that have contaminated the surface of the stainless steel and it is these iron particles that are rusting. Look at the source of the rusting and see if you can remove it from the surface.
Images:


- Q: How do steel angles contribute to the overall stability of a structure?
- Steel angles contribute to the overall stability of a structure by providing additional strength and support. They are often used as structural members in construction projects to connect and reinforce different components, such as beams and columns. The angles help distribute and transfer loads, improving the structure's resistance to bending, buckling, and other forces. Additionally, their L-shape design allows them to resist shear and torsional stresses, enhancing the overall stability and integrity of the structure.
- Q: What is the difference between the main keel and the angle steel and the channel steel?
- Light steel keel is made of high-quality continuous hot-dip galvanized sheet and used as raw material and rolled by cold bending technology. It is used for decorative design of non load bearing wall and building roof with plasterboard, decorative gypsum board and other lightweight board. The utility model is suitable for the decoration of the roof of various buildings, the internal and external wall of the building and the basic material of the trellis suspended ceiling. According to the use of ceiling keel and partition keel, in accordance with the form of section V, C, T, L keel. Ceiling keel is divided into: the main keel and vice keel. The main keel is the weight of the weight of the suspended ceiling.
- Q: What are the common thicknesses of steel angles?
- The specific application and industry requirements determine the varying common thicknesses of steel angles. Examples of frequently utilized thicknesses for steel angles are 1/8 inch, 3/16 inch, 1/4 inch, 3/8 inch, and 1/2 inch. These thicknesses find common usage in construction, manufacturing, and structural applications. It is worth noting that thicker steel angles offer enhanced strength and durability, whereas thinner angles are suitable for lighter applications. Ultimately, the decision regarding thickness depends on the specific load-bearing requirements and considerations of the structural design.
- Q: What are the limitations of using steel angles in high-temperature applications?
- One of the limitations of using steel angles in high-temperature applications is their susceptibility to thermal expansion. Steel, like most materials, expands when heated and contracts when cooled. This property can lead to dimensional changes in the steel angles, which may affect their structural integrity and performance. Another limitation is the potential for steel angles to lose their strength and hardness at elevated temperatures. As the temperature increases, the steel can undergo a process called tempering, where its hardness decreases and it becomes more ductile. This can lead to reduced load-bearing capacity and increased susceptibility to deformation or failure under high loads or stresses. Moreover, steel angles are prone to oxidation and corrosion at high temperatures. When exposed to oxygen and moisture in the air, steel can form iron oxide or rust. This can weaken the steel angles and compromise their structural integrity, especially in environments with high humidity or aggressive chemical agents. Furthermore, steel angles may also experience a phenomenon called creep when subjected to high temperatures and constant loads. Creep refers to the gradual deformation or elongation of a material under a constant stress over time. This can result in permanent deformation and compromise the structural stability of the steel angles. Lastly, the design and fabrication of steel angles for high-temperature applications require careful consideration of the material's thermal conductivity. Steel has relatively high thermal conductivity, which means it can transfer heat quickly. This property can result in uneven heating and cooling of the steel angles, leading to potential stress concentrations or thermal gradients that could affect their performance. Considering these limitations, it is important to carefully evaluate the suitability of steel angles for high-temperature applications and consider alternative materials or design modifications to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Q: How do you design connections for steel angles to steel beams?
- Designing connections for steel angles to steel beams involves several steps and considerations. Here is a general outline of the process: 1. Determine the loads: The first step is to determine the loads that will act on the connection. This includes vertical loads, horizontal loads, and any applied moments. The loads will be used to determine the strength requirements for the connection. 2. Select the appropriate steel angles and beams: Based on the loads and the desired design criteria, select the appropriate steel angles and beams that will be used in the connection. Consider factors such as the material grade, size, and shape of the angles and beams. 3. Analyze the connection: Analyze the connection to determine the required connection strength. This involves calculating the shear, moment, and axial forces that will act on the connection. Use appropriate structural analysis methods and consider both the service loads and the ultimate strength requirements. 4. Determine the connection type: Based on the analysis, select the appropriate connection type. Common connection types for steel angles to steel beams include bolted connections, welded connections, and a combination of both. Consider factors such as the available space, ease of construction, and the structural requirements. 5. Design the connection: Design the connection to meet the required strength and performance criteria. This involves determining the number, size, and layout of bolts or welds, as well as any additional reinforcement or stiffeners that may be required. Consider factors such as the connection's resistance to shear, moment, and axial forces, as well as any specific design codes or standards that need to be followed. 6. Detailing and fabrication: Provide detailed drawings and specifications for the connection, including the dimensions, tolerances, and material specifications. Coordinate with fabricators and contractors to ensure that the connection can be accurately fabricated and installed. 7. Quality control and inspection: During fabrication and construction, perform quality control checks and inspections to ensure that the connection is being fabricated and installed correctly. This may include visual inspections, non-destructive testing, and load testing if required. It is essential to consult with a structural engineer or a professional experienced in steel connection design to ensure that the connection is designed safely and in compliance with applicable building codes and standards.
- Q: How do you store steel angles?
- Steel angles can be stored in a variety of ways depending on the available space and the quantity of angles. Here are a few common methods: 1. Vertically: One option is to store steel angles vertically by leaning them against a wall or using a storage rack. This method is suitable for smaller quantities as it allows easy access to each angle. It is important to ensure that the angles are stable and securely positioned to prevent any accidents. 2. Horizontally: Another option is to store steel angles horizontally, especially if you have a larger quantity. This can be done by stacking them on a pallet or using a storage rack with compartments. When stacking, it is crucial to distribute the weight evenly and use spacers between the angles to avoid deformation. 3. Bundled: If you have a large number of steel angles, bundling them together can be a convenient storage method. This is achieved by tying the angles together with steel strapping or using banding equipment. Bundling helps to keep the angles organized and prevents them from shifting or falling during storage or transportation. Regardless of the storage method chosen, it is important to consider the following points: - Provide a clean and dry storage area to prevent rust or corrosion. - Ensure the storage area is well-ventilated to avoid moisture buildup. - Keep the angles away from direct sunlight and extreme temperature fluctuations. - Regularly inspect the angles for any signs of damage or corrosion. - Use appropriate lifting equipment and follow safety guidelines when moving or stacking steel angles.
- Q: How do you determine the load capacity of a steel angle?
- The load capacity of a steel angle is determined by calculating its moment of inertia and considering factors such as material strength, dimensions, and the type of loading it will be subjected to. Additionally, engineering standards and codes provide guidelines for determining load capacities based on these calculations.
- Q: What are the safety considerations when working with steel angles?
- When working with steel angles, it is crucial to prioritize safety. Some key safety considerations include wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots to protect against potential injuries. Additionally, it is important to handle steel angles with care and use proper lifting techniques to avoid strain or muscle injuries. Adequate training and knowledge of the equipment being used, such as angle grinders or welding tools, is essential to prevent accidents. Finally, maintaining a clean and organized work area can help minimize tripping hazards and ensure a safer working environment.
- Q: How do you determine the shear capacity of a steel angle?
- To determine the shear capacity of a steel angle, several factors need to be considered. The shear capacity is the maximum load that the angle can sustain without failure in shear. The first step in determining the shear capacity is to identify the properties of the steel angle, such as the material grade and dimensions. The grade of the steel determines its strength properties, which are crucial for calculating the shear capacity. The dimensions of the angle, including the length, width, and thickness, will also play a significant role in the calculations. Next, it is necessary to determine the critical shear area of the angle. This area represents the portion of the angle that will experience the highest shear stress during loading. The critical shear area can be calculated by considering the location of the applied load and the geometry of the angle. Once the critical shear area is determined, the next step is to calculate the shear stress acting on this area. The shear stress is calculated by dividing the applied load by the area. It is important to ensure that the shear stress does not exceed the allowable shear stress for the specific grade of steel being used. The allowable shear stress is typically provided by design codes or standards. Finally, the shear capacity of the steel angle can be calculated by multiplying the shear stress by the critical shear area. This calculation provides the maximum load that the angle can sustain without failure in shear. It is important to note that the shear capacity of a steel angle may be influenced by other factors such as the presence of holes or welds, which can weaken the structure. In such cases, additional calculations or considerations may be required. Overall, determining the shear capacity of a steel angle involves considering the properties of the steel, calculating the critical shear area, determining the shear stress, and ensuring that it does not exceed the allowable shear stress for the material grade.
- Q: How do steel angles perform in chemical industry applications?
- Steel angles are commonly used in chemical industry applications due to their excellent strength, durability, and corrosion resistance. They can withstand harsh chemical environments, making them ideal for supporting structures, platforms, and equipment in chemical plants. Additionally, steel angles can be easily welded, providing flexibility in design and construction.
Send your message to us
Structure Steel Equal Angle Bar
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























