Structural Steel Angles
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Structural Steel Angles
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Length:6m,9m,12m
3.Material:GBQ235B,Q345BorEquivalent;ASTMA36;EN10025,S235JR,S355JR;JISG3192,SS400;SS540.
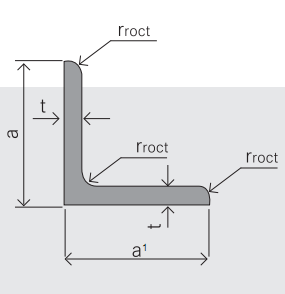 .
.
4.Sizes:
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material details:
Alloy No | Grade | Element (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 0.12—0.20 | 0.3—0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.3 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Alloy No | Grade | Yielding strength point( Mpa) | |||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Q235 | B | 235 | 225 | 215 | 205 | ||
Alloy No | Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) | Elongation after fracture (%) | ||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
| ≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | |||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 375--500 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | |
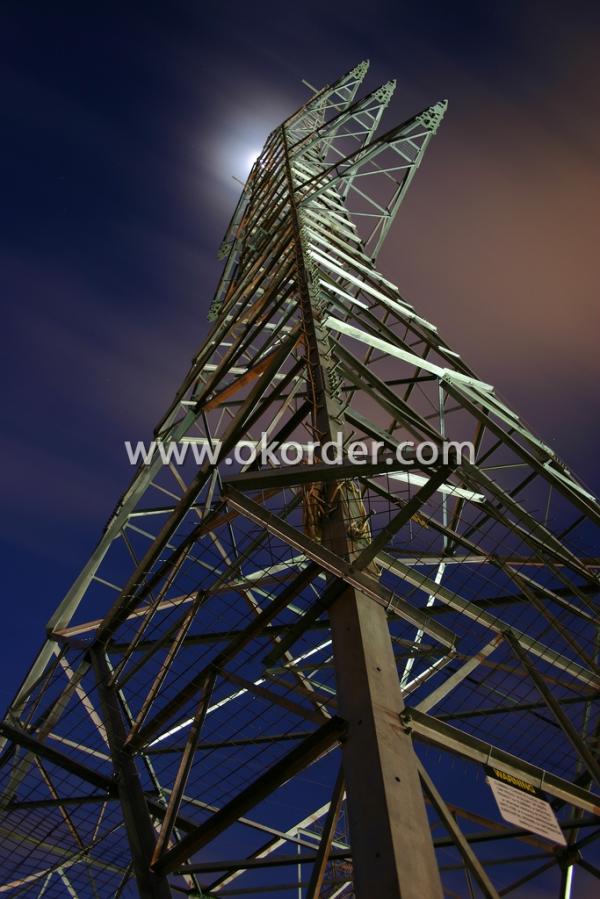
Usage & Applications of Structural Steel Angles
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.

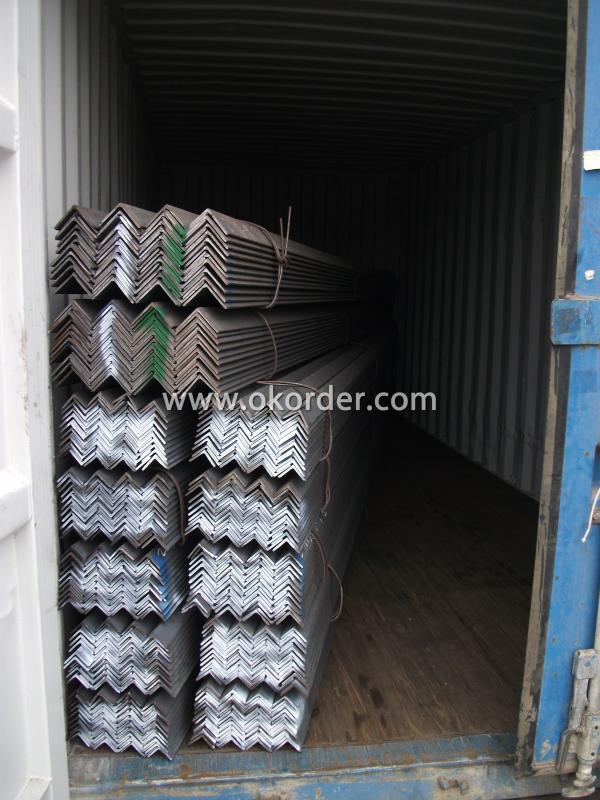
Packaging & Delivery of Structural Steel Angles
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.

- Q: Can steel angles be used in residential construction?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in residential construction. Steel angles are versatile structural elements that are commonly used in various construction applications, including residential buildings. They are often used for framing, reinforcing, and providing structural support in walls, roofs, and floors. Steel angles are preferred in residential construction due to their strength, durability, and ability to withstand heavy loads. They can be easily welded, bolted, or screwed into place, making them suitable for a wide range of construction projects. Additionally, steel angles can be galvanized or coated to enhance their resistance to corrosion, ensuring their longevity. Overall, steel angles are a reliable and cost-effective choice for residential construction.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in load-bearing columns?
- Yes, steel angles can be used in load-bearing columns. Steel angles are commonly used in construction as structural members to provide stability and support for vertical loads. They are able to handle high compressive forces and are often used to reinforce and strengthen load-bearing columns in buildings and other structures.
- Q: How do you prevent steel angles from rusting?
- There are several methods to prevent steel angles from rusting: 1. Protective Coatings: Applying a protective coating on the surface of steel angles is an effective way to prevent rust formation. Common coating options include paint, epoxy, enamel, and galvanized coatings. These coatings act as a barrier, preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the steel surface, thus minimizing the chances of rusting. 2. Rust Inhibitors: Rust inhibitors are chemical compounds that can be applied to steel angles to prevent rust formation. These inhibitors work by either forming a protective layer on the steel surface or by actively inhibiting the corrosion process. Rust inhibitors can be applied as sprays, coatings, or even added to the steel during the manufacturing process. 3. Proper Storage and Handling: One of the simplest ways to prevent rust is to store and handle steel angles properly. This includes keeping them in a dry environment, preferably indoors or under a protective covering, to avoid exposure to moisture and humidity. Additionally, handling steel angles with clean, dry gloves can prevent the transfer of moisture from hands, which can accelerate the rusting process. 4. Regular Maintenance: Regular inspection and maintenance of steel angles can help identify and address any signs of rust formation at an early stage. Promptly addressing any rust spots by removing them with wire brushes or sandpaper and applying touch-up coatings can prevent further corrosion. 5. Dry Storage and Proper Ventilation: If steel angles are stored outdoors, it is crucial to ensure they are placed in a well-ventilated area to promote air circulation and prevent the accumulation of moisture. Furthermore, covering the angles with a waterproof tarp or plastic wrap can provide an additional layer of protection against rain, snow, and other weather elements. By implementing a combination of these preventive measures, steel angles can be safeguarded against rust formation, ensuring their longevity and structural integrity.
- Q: What are the different types of steel angles used in manufacturing industries?
- There are several types of steel angles used in manufacturing industries, including equal angles, unequal angles, L-shaped angles, and structural angles. These angles are commonly used in construction, fabrication, and other industrial applications for providing structural support and stability.
- Q: Are steel angles available in pre-galvanized form?
- Steel angles are indeed available in a pre-galvanized state. Before being shaped into angles, these steel angles have been coated with a layer of zinc. This particular coating serves as a shield against corrosion, which makes pre-galvanized steel angles highly suitable for outdoor and high-moisture environments. Moreover, the pre-galvanized coating enhances the aesthetics of the steel angles, imparting a shiny and metallic look. Due to their strength, durability, and ability to resist corrosion, pre-galvanized steel angles find wide usage in construction, infrastructure projects, and various industrial applications.
- Q: What is the maximum deflection for a steel angle beam?
- The maximum deflection for a steel angle beam depends on various factors such as the span length, load applied, and the properties of the steel angle beam itself. To determine the maximum deflection, one must consider the beam's moment of inertia, elastic modulus, and the applied load. By using appropriate formulas and calculations, engineers can determine the precise maximum deflection for a steel angle beam in a given scenario. It is important to note that the maximum deflection should always be within acceptable limits to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the beam.
- Q: What is the typical density of steel angles?
- Steel angles can have varying densities depending on the particular steel type and grade employed. On average, their density falls within the range of 7.7 to 8.1 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³), or equivalently 7700 to 8100 kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). In comparison to other substances, steel angles possess a notably high density, imparting strength and durability for a multitude of structural and construction purposes.
- Q: What are the design considerations for incorporating steel angles into a structure?
- When incorporating steel angles into a structure, several design considerations need to be taken into account. First and foremost, the load-bearing capacity of the steel angles must be carefully assessed to ensure they can support the intended loads. The dimensions and thickness of the angles should be determined based on the structural requirements and anticipated stress levels. Additionally, the connection details between the steel angles and other structural elements need to be carefully designed to ensure they provide sufficient strength and rigidity. Considerations should include the type of fasteners, welding techniques, and any additional reinforcement required to achieve the desired structural integrity. Furthermore, factors such as corrosion protection, fire resistance, and durability should also be considered during the design process. Appropriate measures should be taken to prevent rust and corrosion on the steel angles, such as applying protective coatings or using stainless steel. Fire-resistant coatings or fireproofing materials may also be necessary, depending on the building's fire safety requirements. Lastly, aesthetics and architectural considerations may come into play when incorporating steel angles into a structure. The design should take into account the desired visual appearance, whether the angles will be exposed or concealed, and how they will integrate with the overall architectural style. In conclusion, the design considerations for incorporating steel angles into a structure involve assessing load-bearing capacity, connection details, corrosion protection, fire resistance, durability, and aesthetic integration.
- Q: What does L50*4 angle mean in CAD?
- Angle called angle, the steel strip is perpendicular to each other on both sides into the corner. There are equal angles and unequal angles. The two sides of an equal angle steel are equal in width. The specifications are expressed in millimeters of edge width * edge width * edge thickness. Such as "30 x 30 x 3", that is 30 mm width equal angle, edge thickness of 3 mm.
- Q: Are steel angles resistant to pests or insects?
- Pests and insects pose a threat to steel angles as they lack resistance against them. Unlike treated wood and other materials, steel angles do not possess innate abilities to repel or deter pests and insects. Nevertheless, when combined with other pest control methods, steel angles can still serve as an effective solution to prevent damage caused by pests or insects. One approach is to seal off any gaps or openings surrounding the steel angles, thus preventing pests or insects from infiltrating the area. Moreover, conducting regular inspections and maintenance is crucial in promptly identifying and resolving any pest or insect-related concerns before they escalate into significant issues.
Send your message to us
Structural Steel Angles
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























