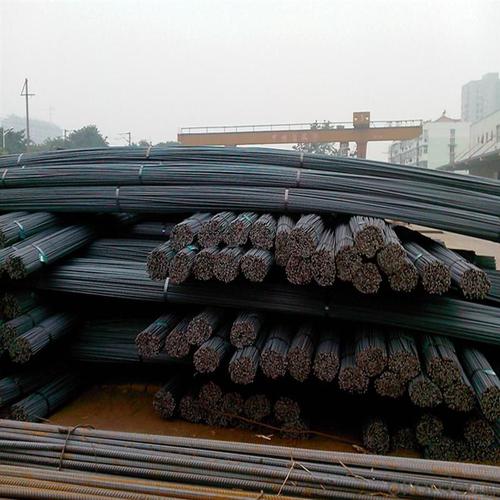
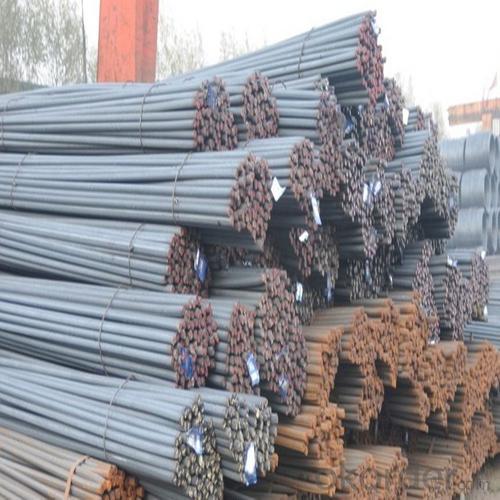
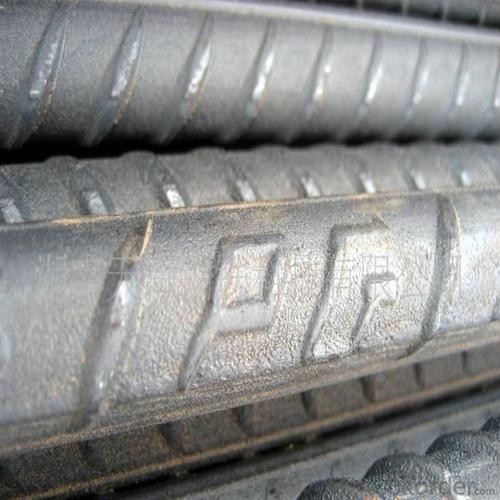
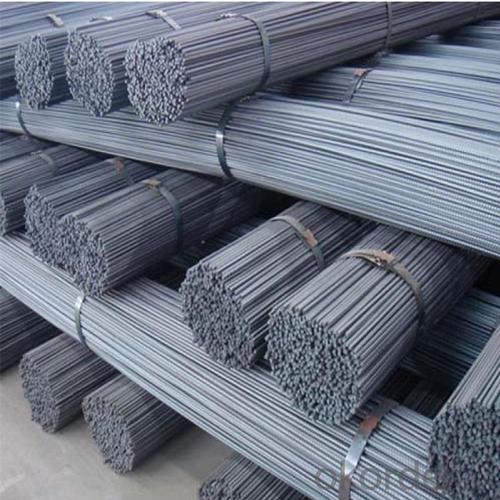
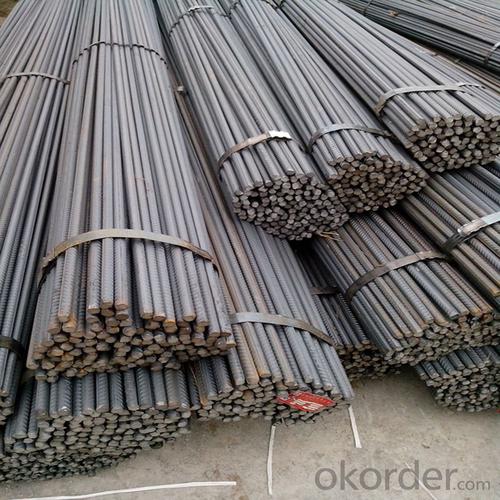
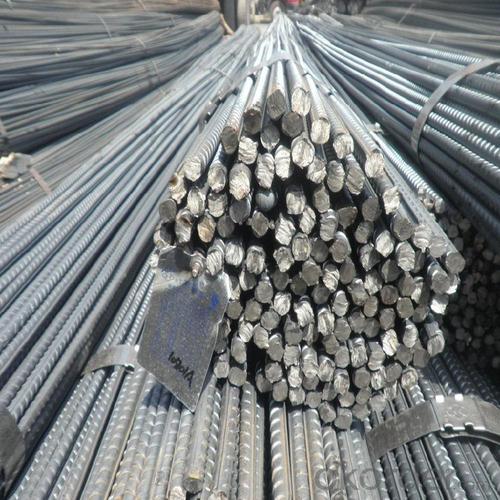
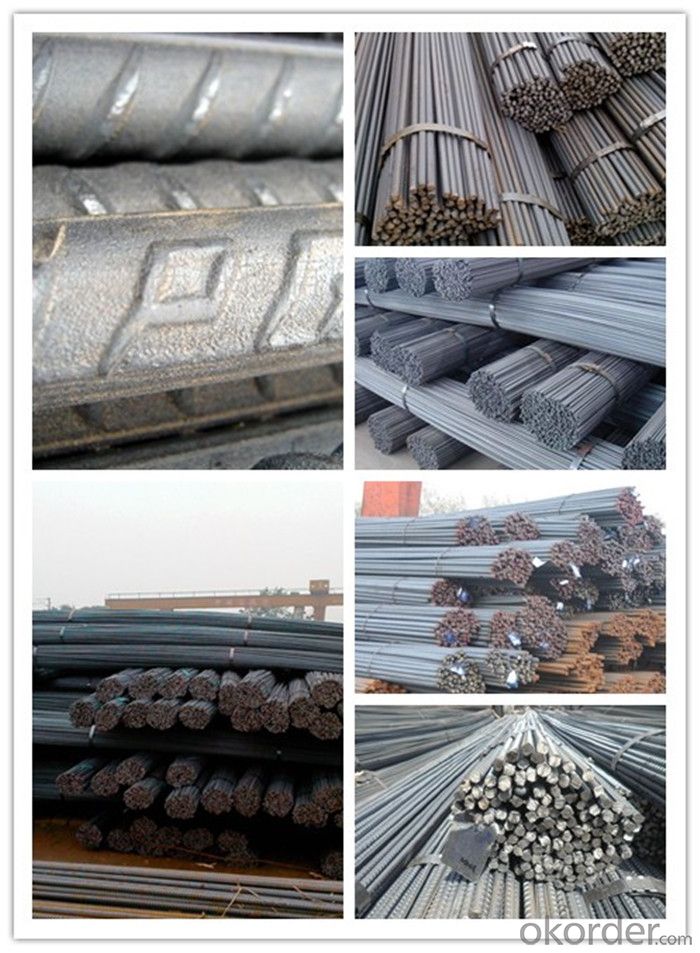
Steel Rebar Size for Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Steel Rebar Size for Construction
Description of Steel Rebar Size:
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm rounds reinforcing steel bar
10m- 40 rods reinforcing Steel Rebar Size
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of Steel Rebar Size:
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
Product Show of Steel Rebar Size:
Workshop

Company Information:
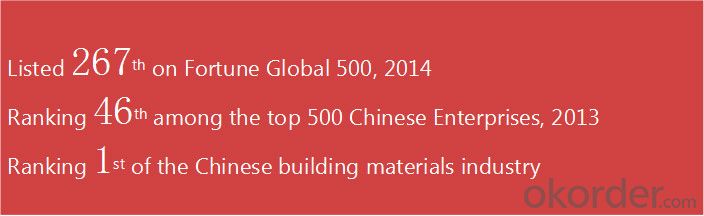
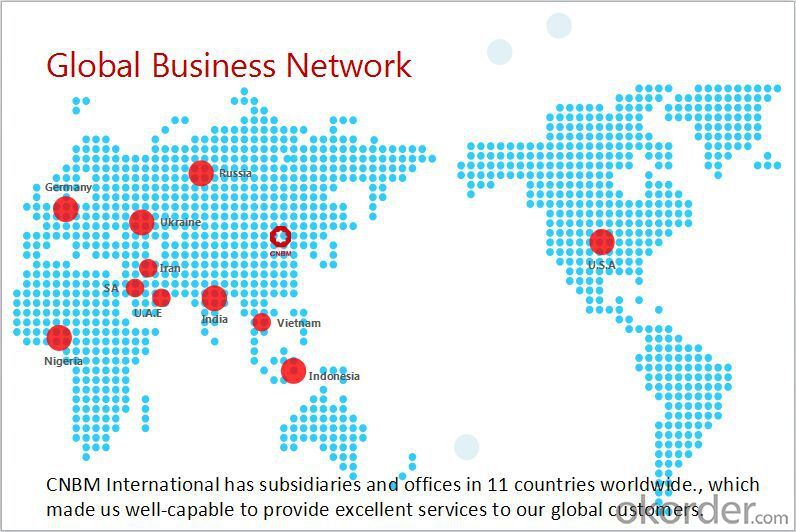
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
FAQ:
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
Contact Us:

- Q: What are the factors that determine the cost of special steel?
- There are several factors that determine the cost of special steel. These include the raw material costs, manufacturing processes and techniques involved, the complexity of the steel composition, the market demand and supply, and any additional treatments or finishes required. Other factors such as transportation costs, import/export taxes, and industry regulations may also influence the overall cost.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the mining equipment manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the mining equipment manufacturing industry. Special steel, often known as alloy steel, offers improved strength, durability, and resistance to wear and corrosion compared to standard steel. These properties make it well-suited for the harsh and demanding conditions encountered in mining operations. Special steel can be utilized in various mining equipment components, such as drill bits, crushers, conveyor systems, and excavator buckets, to enhance their performance and prolong their lifespan.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the power generation equipment industry?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the power generation equipment industry by offering enhanced performance, durability, and reliability. Power generation equipment, such as turbines, generators, and transformers, operate under severe conditions including high temperatures, pressure, and corrosive environments. Special steel, with its unique properties and characteristics, addresses these challenges and contributes significantly to the industry. One of the key advantages of special steel in power generation equipment is its ability to withstand high temperatures. Special steel alloys, such as heat-resistant steels, are designed to perform under extreme conditions, enabling power plants to operate at elevated temperatures without compromising efficiency or safety. These steels maintain their strength, structural integrity, and resistance to creep and fatigue even at the highest operating temperatures, ensuring the reliability and longevity of the equipment. Furthermore, special steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, which is essential in power generation equipment due to the presence of corrosive substances like water, steam, and chemicals. Stainless steel, for instance, is widely used in power plants for its exceptional resistance to corrosion, preventing equipment degradation and minimizing maintenance costs. By using special steel, power generation companies can reduce downtime and enhance overall efficiency. Special steel also contributes to the power generation equipment industry by providing exceptional strength and mechanical properties. This is particularly important for large-scale equipment such as turbines and generators, which are subjected to high mechanical loads. High-strength special steel allows these components to withstand the stress and pressure, ensuring their safe and reliable operation over an extended period. Moreover, special steel's unique properties, such as high hardness and wear resistance, make it suitable for critical components like blades and rotors, reducing the risk of failure and enhancing overall performance. In summary, special steel is an indispensable material in the power generation equipment industry. Its ability to withstand high temperatures, resist corrosion, and provide exceptional strength and mechanical properties ensures the reliability, durability, and efficiency of power plants. By utilizing special steel, power generation companies can enhance their equipment's performance and reduce maintenance costs, ultimately contributing to the sustainable and reliable production of electricity.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the renewable energy sector?
- Indeed, the renewable energy sector can effectively utilize special steel. This type of steel, also referred to as alloy steel, offers improved qualities such as exceptional strength, longevity, and resistance to corrosion, rendering it suitable for a diverse range of applications within renewable energy technologies. Within the realm of wind energy, special steel is employed for the production of wind turbine components. Wind turbine towers necessitate materials that are both robust and lightweight in order to withstand the dynamic loads and harsh environmental conditions they encounter. Special steel alloys, including high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel, provide the requisite strength-to-weight ratio, thereby ensuring the structural integrity of wind turbine towers. Furthermore, special steel proves advantageous in the field of solar energy. Concentrated solar power (CSP) plants rely on mirrors or lenses to concentrate sunlight, generating intense heat for the purpose of electricity generation. In the construction of these components, special steel alloys possessing high thermal conductivity and the ability to withstand high temperatures are employed. This ensures efficient energy capture and durability. In addition, special steel plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of equipment for hydroelectric power generation. Turbine components, such as blades, shafts, and runners, necessitate materials with exceptional strength and resistance to erosion and cavitation. Special steel alloys, including stainless steel and tool steel, exhibit these characteristics, guaranteeing the longevity and reliability of hydroelectric power systems. In summary, special steel finds widespread application within the renewable energy sector. Its qualities, such as high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, make it suitable for use in wind energy, solar energy, and hydroelectric power generation. Through the utilization of special steel, the renewable energy sector can enhance the performance, efficiency, and lifespan of various renewable energy technologies.
- Q: What are the different international trade regulations for special steel?
- The different international trade regulations for special steel vary depending on the specific country and region. These regulations may include import and export restrictions, tariffs, quotas, anti-dumping measures, quality standards, labeling requirements, and intellectual property rights protection. Additionally, special steel may be subject to specific regulations related to its use in certain industries such as aerospace or automotive. It is important for businesses involved in international trade of special steel to stay updated on these regulations to ensure compliance and smooth operations.
- Q: What are the different surface treatments applied to special steel?
- There are several different surface treatments that can be applied to special steel to enhance its properties and improve its performance. Some of the commonly used surface treatments include: 1. Heat treatment: This is a process that involves heating the steel to a specific temperature and then cooling it at a controlled rate. Heat treatment can be used to improve the hardness, strength, and toughness of the steel, as well as to enhance its resistance to wear and corrosion. 2. Coating: Coating the surface of special steel with a protective layer is another common surface treatment. This can be done using various methods such as electroplating, hot-dip galvanizing, or powder coating. Coatings can provide additional resistance to corrosion, improve the appearance of the steel, and increase its lifespan. 3. Nitriding: Nitriding is a process that involves diffusing nitrogen into the surface of the steel, typically at high temperatures. This forms a hard surface layer that improves the wear resistance and fatigue strength of the steel, while maintaining the core toughness. 4. Shot peening: Shot peening is a mechanical surface treatment that involves bombarding the steel surface with small spherical particles, typically made of steel or ceramic. This process induces compressive stresses in the surface layer, which improves the fatigue strength and resistance to stress corrosion cracking. 5. Passivation: Passivation is a chemical treatment that is used to remove impurities and contaminants from the surface of the steel, typically by immersing it in an acid solution. This process helps to restore the natural corrosion resistance of stainless steel by forming a protective oxide layer on the surface. 6. Electro-polishing: Electro-polishing is an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material from the surface of the steel. This treatment can improve the surface finish, remove micro-roughness, and enhance the corrosion resistance of the steel. These are just a few examples of the various surface treatments that can be applied to special steel. The choice of treatment depends on the specific requirements of the application and the desired properties of the steel.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface cleaning for special steel?
- There are several different methods of surface cleaning for special steel, including mechanical methods such as abrasive blasting or grinding, chemical methods like pickling or passivation, and electrochemical methods such as electrocleaning or electropolishing. Each method has its own advantages and is chosen based on the type of contamination or surface condition that needs to be addressed.
- Q: How does special steel perform in terms of high-temperature strength?
- Special steel typically performs very well in terms of high-temperature strength. It has excellent resistance to thermal fatigue, oxidation, and creep, allowing it to withstand extreme heat conditions without losing its structural integrity or mechanical properties. This makes special steel a preferred choice in applications where high-temperature strength is crucial, such as in the aerospace, power generation, and petrochemical industries.
- Q: What are the properties of low alloy steel?
- Low alloy steel possesses a combination of improved strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance compared to regular carbon steel. It contains a small amount of alloying elements (such as manganese, nickel, chromium, or molybdenum) that enhance its mechanical properties. Additionally, low alloy steel has the advantage of being more cost-effective than high alloy steels, making it a popular choice in various industries.
- Q: What are the different high-pressure grades of special steel?
- There exist several distinct varieties of special steel that are designed to withstand high pressures, each possessing its own unique characteristics and uses. Some frequently employed high-pressure grades of special steel encompass the following: 1. 4130 steel: This particular grade of steel is renowned for its exceptional strength, toughness, and resistance to heat. It finds considerable application in the fabrication of high-pressure tubing and components for the oil and gas industry. 2. 4340 steel: Distinguished by its extraordinary strength and toughness, this grade of steel is commonly utilized in the production of critical components like high-pressure valves, gears, and other crucial parts in industries such as aerospace, defense, and automotive. 3. 316 stainless steel: Highly resistant to corrosion and boasting excellent high-temperature properties, this stainless steel grade is frequently employed in high-pressure scenarios like pipelines, heat exchangers, and pressure vessels within the chemical and petrochemical industries. 4. 17-4 PH stainless steel: Offering a combination of high strength, superb corrosion resistance, and good toughness, this stainless steel grade often finds application in high-pressure pump components, turbine blades, and other vital parts within industries like power generation and aerospace. 5. F22 steel: Classified as a low-alloy steel with remarkable high-temperature strength and exceptional resistance to creep, this grade of steel is commonly used in high-pressure and high-temperature environments such as boilers, pressure vessels, and piping systems found in power plants and refineries. The aforementioned examples represent just a small selection of the available high-pressure grades of special steel. The appropriate grade choice is contingent upon the specific requirements of the application, encompassing factors such as pressure, temperature, corrosion resistance, and mechanical properties.
Send your message to us
Steel Rebar Size for Construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



































