Stainless Steel 304 sheet with competitive pricing
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Stainless steel 304 sheet
Company advantage of stainless steel:
-Top Equipments, Leading In The Industry.
- Professional Team, Leading Innovation.
- Huge Supply Capacity Advantage, Timely and Effective Delivery.
- Modern Logistic, Fact and Convenient.
- Precise Manufacturing, Exquisite Products.
- Serve People, Create Value.
- Dimensional Network, Powerful Expansion.
Product Information of stainless steel sheet:
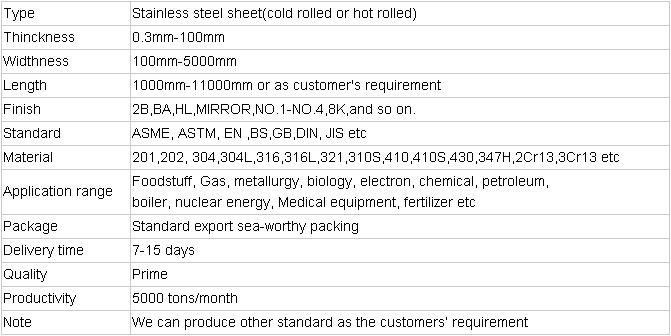
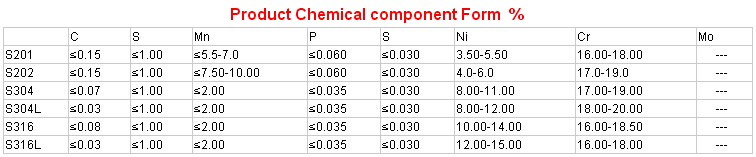
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for exhaust systems?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for exhaust systems. Stainless steel is a popular material for exhaust systems due to its high resistance to corrosion and heat. It can withstand the extreme temperatures and harsh conditions that exhaust systems are subjected to, making it a durable and long-lasting option. Stainless steel pipes also have the advantage of being lightweight, which can help improve the performance of the exhaust system. Additionally, stainless steel pipes can be easily bent and shaped, allowing for customization to fit different vehicle models and configurations. Overall, stainless steel pipes are a reliable choice for exhaust systems, providing excellent performance and longevity.
- Q: How do you protect stainless steel pipes from internal corrosion?
- One effective way to protect stainless steel pipes from internal corrosion is by utilizing a corrosion inhibitor. Corrosion inhibitors are chemicals that can be added to the fluid flowing through the pipes to create a protective layer on the inner surface of the pipe. This layer acts as a barrier, preventing the corrosive agents in the fluid from coming into direct contact with the stainless steel. There are various types of corrosion inhibitors available, and the selection depends on the specific application and the fluid being transported. Some common corrosion inhibitors include organic inhibitors, which form a protective film on the pipe surface, and inorganic inhibitors, which react with the corrosive agents to form less harmful compounds. Another method to protect stainless steel pipes from internal corrosion is by using cathodic protection. Cathodic protection involves connecting the stainless steel pipe to a sacrificial anode made of a more reactive metal, such as zinc or aluminum. This creates a galvanic cell, where the anode corrodes instead of the stainless steel pipe. By sacrificing the anode, the pipe is effectively protected from internal corrosion. Regular maintenance and inspection are also crucial in preventing internal corrosion. It is essential to monitor the condition of the pipes, identify any signs of corrosion or damage, and promptly address any issues. Flushing the pipes with clean water or appropriate cleaning solutions can help remove any deposits or contaminants that could contribute to corrosion. Furthermore, maintaining proper fluid composition and pH levels is vital to prevent internal corrosion. In some cases, adjusting the fluid's pH or adding corrosion inhibitors specific to the fluid being transported can significantly reduce the risk of corrosion. Overall, a combination of corrosion inhibitors, cathodic protection, regular maintenance, and appropriate fluid management can effectively protect stainless steel pipes from internal corrosion, ensuring their longevity and optimal performance.
- Q: What are the different types of stainless steel pipe tees?
- There are several different types of stainless steel pipe tees, each designed for specific applications and requirements. 1. Equal Tee: This type of tee has three outlets of the same size, forming a 90-degree angle. It is commonly used to branch off or combine flow in a pipeline with equal diameters. 2. Reducing Tee: As the name suggests, a reducing tee has one outlet smaller than the other two. It is used to connect pipes of different sizes, allowing for a smooth transition in the flow of fluids or gases. 3. Barred Tee: This tee has a bar welded across the branch opening, providing additional support and reinforcement. It is commonly used in high-pressure or high-temperature applications to prevent stress concentration and potential failure. 4. Lateral Tee: A lateral tee has one outlet at a 45-degree angle, allowing for a branch connection at a different direction. It is often used in situations where a pipeline needs to be diverted or connected at an angle. 5. Cross Tee: A cross tee has four outlets forming a cross-shaped configuration. It is used when there is a need to split or combine flow in multiple directions, commonly found in complex piping systems. 6. Unions and Socket Weld Tee: These types of tees have sockets or unions at the branch connection, allowing for easy disassembly and maintenance. They are often used in applications where regular inspection, cleaning, or replacement is required. 7. Threaded Tee: Threaded tees have threaded branch connections, which can be screwed onto the pipe without the need for welding. They are commonly used in low-pressure applications or when frequent disassembly is required. Each type of stainless steel pipe tee offers specific advantages and is selected based on the requirements of the particular piping system, such as flow rates, pressure, temperature, and compatibility with the fluids or gases being transported.
- Q: How can stainless steel and copper pipe be welded?
- Prepare a brass wire cleaning flux of base metal 3/4 stainless steel tube 5/8 copper rust (specific parent material specification is not clear to me) welding tools
- Q: What is the difference between 304Cb and 316Cb stainless steel pipes?
- The main difference between 304Cb and 316Cb stainless steel pipes lies in their composition and corrosion resistance. 304Cb stainless steel contains a higher amount of chromium and nickel, which provides excellent resistance to corrosion and oxidation in various environments. On the other hand, 316Cb stainless steel contains additional molybdenum, which enhances its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, particularly in chloride-rich environments such as marine or coastal areas. Overall, while both grades offer good corrosion resistance, 316Cb stainless steel pipes are more suitable for applications in aggressive environments where higher resistance to corrosion is required.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for underground heating systems?
- Indeed, underground heating systems can employ stainless steel pipes as they possess suitability. The reason lies in the fact that stainless steel exhibits remarkable resistance against corrosion and can endure the severe circumstances of subterranean burial. Moreover, this material showcases durability, longevity, and the ability to withstand elevated temperatures and pressures, rendering it an exemplary option for heating systems. Not only that, but stainless steel pipes also offer ease in installation and maintenance, thereby furnishing a dependable and effective resolution for underground heating systems.
- Q: What are the standard sizes for stainless steel pipes?
- The standard sizes for stainless steel pipes can vary depending on the industry and application. However, there are some commonly used standard sizes that are widely available. In general, stainless steel pipes are produced in nominal sizes ranging from 1/8 inch to 72 inches in diameter. These sizes are typically classified using the Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) system, which refers to the approximate internal diameter of the pipe. The NPS sizes commonly used for stainless steel pipes range from NPS 1/8 to NPS 36. Additionally, stainless steel pipes are available in various schedules, which indicate the wall thickness of the pipe. The most commonly used schedules for stainless steel pipes are Schedule 5, Schedule 10, Schedule 40, and Schedule 80. It's important to note that these standard sizes may vary slightly depending on the country or region. Therefore, it is advisable to consult the relevant standards and regulations specific to your location or consult with a supplier to determine the exact standard sizes available for stainless steel pipes in your area.
- Q: What is the hardness of stainless steel pipes?
- The hardness of stainless steel pipes can vary depending on the specific grade and treatment of the steel. Stainless steel pipes have a range of hardness levels, usually measured using the Rockwell scale or the Brinell scale. The hardness of stainless steel pipes is typically higher than that of other types of steel due to the alloying elements, such as chromium and nickel, which provide increased resistance to corrosion and wear. Generally, stainless steel pipes have a hardness level that falls within the range of 75 to 180 on the Rockwell scale or 150 to 300 on the Brinell scale. However, it's important to note that the hardness can also be influenced by factors such as heat treatment, welding, and cold working processes.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be painted or coated?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be painted or coated. However, it is important to choose the appropriate type of paint or coating that is specifically designed for use on stainless steel surfaces. This is because stainless steel has a smooth and non-porous surface, which can make it challenging for paint or coatings to adhere properly. Additionally, stainless steel pipes may be exposed to harsh environmental conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive substances, so it is crucial to select a paint or coating that is resistant to these factors. By using the right type of paint or coating and following proper surface preparation techniques, stainless steel pipes can be effectively painted or coated to enhance their appearance or provide additional protection against corrosion.
- Q: What are the common joining methods for stainless steel pipes?
- The common joining methods for stainless steel pipes include welding, threaded connections, and flanged connections. Welding is the most common and widely used method for joining stainless steel pipes. It involves melting the ends of the pipes and fusing them together using a welding electrode. The weld can be made using various types of welding techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding, MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding, or Stick welding, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Threaded connections are another popular joining method for stainless steel pipes, especially for smaller diameter pipes. This method involves threading the ends of the pipes and using threaded fittings to connect them. Threaded connections provide a secure and leak-proof joint, and they are relatively easy to install and disassemble when necessary. Flanged connections are used for larger diameter stainless steel pipes or when there is a need for easy disassembly and reassembly. This method involves attaching flanges to the ends of the pipes and connecting them using bolts and gaskets. Flanged connections provide a rigid and reliable joint, and they are commonly used in industrial applications where frequent maintenance or replacement is required. It is important to note that the choice of joining method for stainless steel pipes depends on various factors such as the pipe diameter, pressure and temperature requirements, accessibility, and the specific application. Consulting with a qualified engineer or professional is recommended to ensure the most appropriate joining method is selected for a specific project.
Send your message to us
Stainless Steel 304 sheet with competitive pricing
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 m.t
- Supply Capability:
- 1000000 m.t/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























