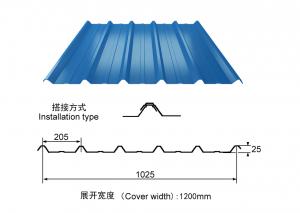
PRE-PAINTED GALVANIZED STEEL SHEET
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
PRE-PAINTED GALVANIZED STEEL SHEET
THICKNESS:0.18mm-1.5mm
WIDTH:900mm-1250mm
COATING MASS:Z30-Z275
PAINT:PE、HP、HDP、PVDF、SMP、MATT、PVDF
COLOR:RAL Scale
COIL INNER DIAMETER:508mm/610mm
COIL WEIGHT:3mt-7mt
BASE MATERIAL:Hot-dip GALVANIZED Steel
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for cladding?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for cladding.
- Q: What are the different sheet metal rolling techniques for steel sheets?
- Steel sheets can be rolled using different techniques, including hot rolling, cold rolling, and roll forming. Hot rolling involves heating steel sheets above their recrystallization temperature and passing them through rollers to reduce thickness. This method is commonly used to produce steel sheets with consistent thickness and improved mechanical properties. In contrast, cold rolling rolls steel sheets at room temperature. This process creates thinner and smoother sheets with higher dimensional accuracy. Cold-rolled steel is often used for applications that require a high-quality surface finish, such as automotive body panels and appliances. Roll forming is a continuous bending process where a long strip of steel is gradually shaped into a desired profile using rollers. This technique is suitable for producing steel sheets with complex shapes and profiles, like corrugated roofing or C-channel beams. Roll forming offers excellent precision and repeatability, making it a popular choice for mass producing steel sheets with consistent dimensions. Ultimately, the choice of rolling technique depends on the specific requirements of the application. Hot rolling is ideal for achieving uniform thickness and improved mechanical properties. Cold rolling is preferred for applications that demand high-quality surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Roll forming is suitable for creating steel sheets with complex shapes and profiles.
- Q: Are the steel sheets available in different thickness tolerances?
- Yes, steel sheets are available in different thickness tolerances. Steel manufacturers produce sheets with varying thicknesses to cater to different applications and requirements. These thickness tolerances are specified by industry standards and can vary depending on the type of steel and the intended use. For example, in the construction industry, steel sheets with tighter tolerances may be required to ensure structural integrity, while in manufacturing processes, such as automotive or aerospace, specific tolerances may be necessary to meet design specifications. By offering steel sheets in different thickness tolerances, manufacturers provide customers with options to choose the most suitable product for their specific needs.
- Q: What are the environmental considerations of using steel sheets?
- Some of the environmental considerations of using steel sheets include the extraction and processing of raw materials, energy consumption during manufacturing, and the potential for air and water pollution. Additionally, the disposal of steel sheets at the end of their life cycle can contribute to waste management challenges. However, steel is also a highly recyclable material, and its use in construction and other industries can contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.
- Q: Are the steel sheets suitable for automotive applications?
- Yes, steel sheets are commonly used in automotive applications due to their high strength, durability, and formability. They provide structural support, enhance crash safety, and can be easily shaped into various automotive components, making them suitable for the automotive industry.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in construction?
- Certainly, construction can definitely make use of steel sheets. Due to their strength, durability, and versatility, steel sheets are commonly employed in construction ventures. They find application in diverse areas such as roofing, walls, flooring, and structural components. Steel sheets possess a remarkable tensile strength, rendering them capable of enduring heavy loads and extreme weather conditions. Moreover, steel sheets exhibit fire-resistance, termite-resistance, and a long lifespan, making them a dependable option for construction projects. Additionally, steel sheets offer ease of fabrication, enabling customization and flexibility in design. In summary, steel sheets serve as an outstanding option for construction, ensuring structural integrity, durability, and design adaptability.
- Q: What is the typical impact resistance of a steel sheet?
- The typical impact resistance of a steel sheet varies depending on the specific grade and thickness of the steel. However, steel sheets are known for their high impact resistance compared to other materials. They can withstand substantial force without breaking or deforming, making them suitable for applications requiring durability and protection against impacts.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for manufacturing musical instruments?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for manufacturing musical instruments. Steel is a versatile material that can be shaped and tuned to produce various sounds. It is commonly used in instruments like steel guitars, steel drums, and some percussion instruments.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for staircases?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for staircases. Steel sheets are often used in the construction of staircases due to their durability, strength, and resistance to wear and tear. They can be molded and shaped into various designs to create aesthetically pleasing staircases while providing a sturdy and long-lasting structure.
- Q: How are steel sheets coated for corrosion resistance?
- Galvanization is a common technique for protecting steel sheets from corrosion. It involves adding a layer of zinc to the surface of the steel sheet. There are two ways to do this: hot-dip galvanization and electro-galvanization. During hot-dip galvanization, the steel sheet is dipped into a bath of molten zinc. The zinc adheres to the steel through a metallurgical reaction. This creates a protective barrier that prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the steel, thus stopping corrosion. Electro-galvanization, on the other hand, uses an electric current. The steel sheet is placed in a zinc electrolyte solution, and the electric current causes the zinc ions to be attracted to the steel surface. This forms a thin layer of zinc coating. This method is usually used for thinner steel sheets or when a precise coating thickness is needed. Both hot-dip galvanization and electro-galvanization effectively protect steel sheets from corrosion. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial layer, meaning it corrodes before the steel underneath. This prolongs the lifespan of the steel sheet and prevents rust. Additionally, the zinc coating can also provide a decorative finish, making it suitable for practical and aesthetic purposes. In conclusion, galvanization is a widely used and effective method for enhancing the corrosion resistance and durability of steel sheets.
Send your message to us
PRE-PAINTED GALVANIZED STEEL SHEET
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords