hot rolled steel sheet DIN 17100 in Good Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Rolled to its final dimensions while it’s hot enough to scale, our hot-rolled steel is an amalgamation of the various qualities of steel. It can be in the form of plates, sheets and coils. Our Hot-Rolled Steel Sheets and Coils are applied to a wide range of uses such as automobile, electrical appliance, machinery manufacturing, container manufacturing, shipbuilding, bridge, pipeline, and receive high acclaim from our customers for its excellent quality.
Description:
Product: | Hot Rolled Steel Coils/Sheets |
Material: | Q195,Q235,A36,SS400,S235JR,Q345,ST37-2, CCSB etc |
Standard : | JIS G3002 GB/T251B |
Technique: | hot rolled |
Thickness | 1.2mm to 200mm |
Tolerance of thickness: | :+/-0.03mm |
Width: | 750mm-2000mm |
Tolerance of width: | :+/-5.00mm (aiming to +/-2.00mm) |
Normal width: | 914mm, 1000mm, 1200mm, 1219mm, 1250mm,1500mm |
Length: | According to requirement |
Coil ID: | 508mm-610mm |
Coil Weight: | 10-25 Metric Tons |
Surface: | Black, Chromate, fingerprint resistant treatment, slight oiled or non-oiled, dry |
Port of Loading: | Tianjin/Shanghai port |
Packaging Details: | Standard export packing or according to the clients required |
Delivery Time | Within 30 days after received 30% deposit or workable L/C |
Payment Terms: | L/C,T/T |
Image:


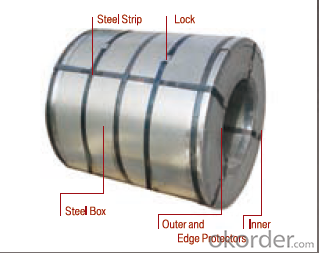
We can ensure that stable quality standards are maintained, strictly meeting both market requirements and customers’ expectations. Our products enjoy an excellent reputation and have been exported to Europe, South-America, the Middle-East, Southeast-Asia, Africa and Russia etc.. We sincerely hope to establish good and long-term business relationship with your esteemed company.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for earthquake-prone regions?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for earthquake-prone regions. Steel is known for its strength and durability, making it an excellent choice for construction in areas prone to seismic activity. Steel sheets can absorb and distribute the forces generated during an earthquake, reducing the risk of structural damage and collapse. Additionally, steel structures can be designed to flex and bend, allowing them to withstand the shaking caused by earthquakes without significant damage.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for sound insulation?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for sound insulation. They have high mass and density, which helps to block sound waves and reduce noise transmission. Additionally, steel sheets can be combined with other sound-absorbing materials, such as acoustic foam or insulation, to enhance their soundproofing capabilities.
- Q: What is the average weight of steel sheets per square foot?
- The average weight of steel sheets per square foot can vary depending on the specific type and thickness of the steel. However, as a rough estimate, it is typically around 40 to 50 pounds per square foot.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for playground equipment?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for playground equipment. Steel is a highly durable and strong material that can withstand heavy use and harsh weather conditions, making it suitable for playground structures such as climbing frames, slides, and swings. Additionally, steel sheets can be shaped and formed into various designs, offering flexibility in creating engaging and safe play structures for children.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in marine environments?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used in marine environments. However, it is important to use corrosion-resistant steel grades or apply protective coatings to prevent rusting and degradation caused by exposure to saltwater and other harsh marine conditions.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for agricultural equipment?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for agricultural equipment due to their durability, strength, and resistance to harsh environmental conditions typically encountered in agricultural settings. They provide excellent protection against impact, corrosion, and wear, making them ideal for manufacturing various agricultural machinery and implements such as plows, cultivators, and seeders. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily formed and welded to create custom components, ensuring versatility in design and functionality for agricultural equipment.
- Q: Are the steel sheets resistant to chemical spills?
- In general, steel sheets possess resistance against chemical spills. Steel is famous for its durability and capacity to endure different environmental conditions, including chemical exposure. The non-reactive properties of steel make it extremely resistant to corrosion, thereby providing effective protection against chemical spills. Nevertheless, the ability of steel sheets to resist chemical spills may vary depending on the type and concentration of the chemicals. To ensure the highest level of resistance, it is advisable to seek advice from experts or refer to specific steel grades and their compatibility with different chemicals.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for chimneys and flue systems?
- No, steel sheets are not suitable for chimneys and flue systems as they can corrode and deteriorate rapidly due to the high temperatures and corrosive gases generated by the combustion process. It is recommended to use materials specifically designed for chimneys and flue systems, such as stainless steel or ceramic.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for manufacturing furniture?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for manufacturing furniture. Steel is a durable and versatile material that can be easily shaped and welded into various furniture designs. It is commonly used in the manufacturing of tables, chairs, and storage units due to its strength and ability to withstand heavy use.
- Q: Can the steel sheets be used for metal stamping?
- Yes, steel sheets are commonly used for metal stamping due to their high strength and durability.
Send your message to us
hot rolled steel sheet DIN 17100 in Good Quality
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords