Hot Rolled Steel Angle Euqal Angle Bar Uneuqal Angle Bar Made In China
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
OKorder is offering Hot Rolled Steel Angle Euqal Angle Bar Uneuqal Angle Bar Made In China
at great prices with worldwide shipping. Our supplier is a world-class manufacturer of steel, with our products utilized the world over. OKorder annually supplies products to European, North American and Asian markets. We provide quotations within 24 hours of receiving an inquiry and guarantee competitive prices.
Product Applications:
Hot Rolled Steel Angle Euqal Angle Bar Uneuqal Angle Bar Made In China are ideal for structural applications and are widely used in the construction of buildings and bridges, and the manufacturing, petrochemical, and transportation industries.
Product Advantages:
OKorder's Hot Rolled Steel Angle Euqal Angle Bar Uneuqal Angle Bar Made In China
are durable, strong, and resist corrosion.
Main Product Features:
· Premium quality
· Prompt delivery & seaworthy packing (30 days after receiving deposit)
· Corrosion resistance
· Can be recycled and reused
· Mill test certification
· Professional Service
· Competitive pricing
Product Specifications:
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
3.Material: JIS G3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
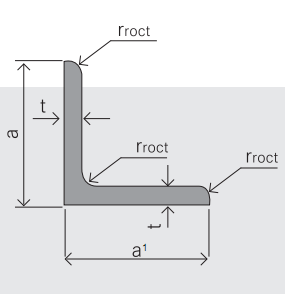
Name | Stainless Steel Angles | ||||||
Standard | ASTM A554, A312, A249, A269 and A270 | ||||||
Material Grade | 304,316,201,202, 316L,430 | ||||||
Length | 6m or as customers' request | ||||||
Tolerance | a) thickness: +/-0. 15mm | ||||||
b) Length:+/-4. 5mm - 0mm | |||||||
Surface | 180G, 320G, 400G Satin / Hairline(Matt Finish, Brush, Dull Finish) 400G, 500G, 600G or 800G Mirror finish | ||||||
Application | Decoration construction, upholstery, industry instruments | ||||||
Test | Squash test, Extended test, Water pressure test, Crystal rot test, Heat treatment, NDT | ||||||
Chemical Composition of Material |
Composition
Material | 201 | 202 | 304 | 316L | 430 | |
C | ≤0.15 | ≤0.15 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.08 | ≤0.12 | ||
Si | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤1.00 | ||
Mn | 5.5-7.5 | 7.5-10 | ≤2.00 | ≤2.00 | ≤1.00 | ||
P | ≤0.06 | ≤0.06 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.040 | ||
S | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 | ||
Cr | 16-18 | 17-19 | 18-20 | 16-18 | 16-18 | ||
Ni | 3.5-5.5 | 4-6 | 8-10.5 | 10-14 | |||
Mo | 2.0-3.0 | ||||||
Mechanical Property | Material Item | 201 | 202 | 304 | 316L | ||
Tensile Strength | ≥535 | ≥520 | ≥520 | ≥520 | |||
Yield Strength | ≥245 | ≥205 | ≥205 | ≥205 | |||
Extension | ≥30% | ≥30% | ≥35% | ≥35% | |||
Hardness (HV) | <253 | <253 | <200 | <200 | |||
FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered byOKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q3: How soon can we receive the product after purchase?
A3: Within three days of placing an order, we will begin production. The specific shipping date is dependent upon international and government factors, but is typically 7 to 10 workdays.



- Q: Can steel angles be used in the construction of industrial platforms?
- Yes, steel angles can definitely be used in the construction of industrial platforms. Steel angles are commonly used in construction projects due to their high strength and durability. These angles can be easily welded or bolted together to create a strong and stable platform structure. They are particularly useful in industrial settings where heavy loads and constant foot traffic are expected. Steel angles provide support and stability to the platform, ensuring it can withstand the weight and movement of equipment, machinery, and workers. Additionally, steel angles are resistant to corrosion, making them suitable for use in various environments, including industrial settings where exposure to chemicals, moisture, and extreme temperatures is common. Overall, steel angles are a reliable and cost-effective choice for constructing industrial platforms.
- Q: Are steel angles affected by vibration?
- Yes, steel angles can be affected by vibration. Vibrations can cause the steel angles to experience fatigue and structural damage over time, potentially leading to failure if not properly addressed. It is important to consider and mitigate the effects of vibration when designing, installing, and maintaining steel angles in various applications to ensure their longevity and structural integrity.
- Q: How do you calculate the maximum allowable deflection for a steel angle beam?
- The maximum allowable deflection for a steel angle beam can be calculated using the formula for deflection in beams, which is based on the beam's length, material properties, and the applied load. The calculation involves determining the moment of inertia of the beam, the modulus of elasticity of the steel, and the applied load. By plugging these values into the formula, the maximum allowable deflection can be determined.
- Q: What are the standard dimensions for equal leg steel angles?
- The dimensions of equal leg steel angles differ based on the industry and country. Generally, these dimensions are determined by the length of each leg and the thickness of the angle. Leg lengths commonly range from 20mm to 200mm, while thicknesses range from 3mm to 20mm. These measurements are typically expressed in millimeters and can be further adjusted to suit specific project needs. To ascertain the precise dimensions for equal leg steel angles in a given situation, it is crucial to refer to industry standards and specifications.
- Q: How are steel angles installed?
- Steel angles are typically installed using a few simple steps. First, you will need to mark the desired location for the angle on the surface or structure where it will be installed. Next, using a level and measuring tape, ensure that the angle is aligned correctly and mark the positions for the screw or bolt holes. Once the markings are made, you will need to pre-drill the holes using a drill bit that is slightly smaller than the diameter of the screws or bolts you will be using. This will prevent the steel angle from cracking or splitting during installation. After pre-drilling the holes, place the steel angle back in position and align the holes with the markings on the surface. Use a wrench or screwdriver to tighten the screws or bolts securely, making sure the angle is firmly attached. It is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and recommendations for the specific type and size of steel angle being installed. Additionally, ensure that the surface or structure where the angle is being installed is able to support the weight and load that will be applied to it. Overall, steel angles are relatively simple to install and provide excellent structural support in various applications such as construction, manufacturing, and DIY projects.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for machinery frames?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for machinery frames. Steel angles are commonly used in construction and manufacturing industries due to their strength and versatility. They are often used to provide structural support and stability in various applications, including machinery frames. Steel angles offer a cost-effective solution as they are readily available and can be easily fabricated to meet specific design requirements. Additionally, steel angles provide excellent load-bearing capacity and resistance to deformation, making them suitable for supporting heavy machinery and equipment. Their rigid and durable nature ensures the stability and longevity of machinery frames, making them a reliable choice in industrial settings.
- Q: How do you protect steel angles from abrasive wear?
- One way to protect steel angles from abrasive wear is by applying a protective coating or finish, such as paint or a specialized protective coating. This ensures that the steel surface is shielded from direct contact with abrasive materials, reducing the risk of wear and tear. Additionally, using rubber or plastic covers or linings on the steel angles can provide an extra layer of protection against abrasive substances. Regular maintenance and inspection to identify any signs of wear and promptly address them can also help prolong the lifespan of steel angles.
- Q: How are steel angles measured and specified?
- Steel angles are measured and specified based on their dimensions, which include the length of the legs and the thickness of the angle. This is typically provided in millimeters or inches. The dimensions are presented in a specific order, such as leg length × leg length × thickness. Additionally, the angle's weight per unit length or its cross-sectional area may also be specified to provide further information about its size and strength.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in industrial or heavy-duty applications?
- Absolutely, steel angles are a perfect fit for industrial or heavy-duty uses. Renowned for their robustness, endurance, and flexibility, steel angles are highly versatile and find application across a wide range of industries. They play a vital role in providing structural reinforcement, support, and stability to heavy-duty machinery, equipment, and infrastructure projects. Construction, manufacturing, engineering, transportation, and various other industries commonly employ steel angles. Their usage spans frames, supports, bracings, platforms, beams, and trusses, where strength and load-bearing capacity are paramount. Moreover, steel angles can withstand extreme temperatures, harsh weather conditions, and heavy loads, making them ideal for demanding industrial environments. In summary, steel angles are a dependable and efficient choice for industrial or heavy-duty applications, thanks to their strength, durability, and adaptability.
- Q: Can steel angles be drilled or machined?
- Yes, steel angles can be drilled or machined. Steel angles are commonly used in construction and manufacturing industries due to their strength and durability. They can be easily drilled or machined to create holes or cut into specific shapes or sizes. However, it is important to use appropriate tools and techniques when working with steel angles as they are made of a hard material that requires high-speed drilling or machining equipment. Additionally, using lubricants or coolant during the drilling or machining process can help to reduce friction and heat buildup, ensuring a smooth and efficient operation.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Steel Angle Euqal Angle Bar Uneuqal Angle Bar Made In China
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























