Hot Rolled Angle Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of Equal Angle
1. Standards: GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2. Length:6m,9m,12m
3. Material:Material: GB Q235B, Q345B or Equivalent; ASTM A36; EN 10025, S235JR, S355JR; JIS G3192, SS400;
SS540.
4. Sizes:
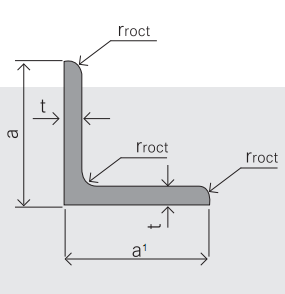
Sizes: 25mm-250mm | ||
a*t | ||
25*2.5-4.0 | 70*6.0-9.0 | 130*9.0-15 |
30*2.5-6.6 | 75*6.0-9.0 | 140*10-14 |
36*3.0-5.0 | 80*5.0-10 | 150*10-20 |
38*2.3-6.0 | 90*7.0-10 | 160*10-16 |
40*3.0-5.0 | 100*6.0-12 | 175*12-15 |
45*4.0-6.0 | 110*8.0-10 | 180*12-18 |
50*4.0-6.0 | 120*6.0-15 | 200*14-25 |
60*4.0-8.0 | 125*8.0-14 | 250*25 |
5. Chemical data: %
C | Mn | S | P | Si |
0.14-0.22 | 0.30-0.65 | ≤0.050 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.30 |
Usage & Applications of Equal Angle
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for handrails?
- Yes, steel angles can be used for handrails. Steel angles are often used as a structural component for handrails due to their strength and durability. They can provide a sturdy and stable support for handrails in various applications.
- Q: What are the common finishes available for steel angles?
- The common finishes available for steel angles include hot-dip galvanized, painted, and untreated/raw.
- Q: What are the tolerance specifications for steel angles?
- The tolerance specifications for steel angles vary depending on the specific standards and requirements set by the industry or application. These specifications typically include tolerances for dimensions such as length, width, and thickness, as well as tolerances for straightness, squareness, and surface finish. It is important to refer to the relevant standards or consult with manufacturers to determine the exact tolerance specifications for steel angles in a particular context.
- Q: What is the maximum cantilever length for a steel angle?
- The maximum cantilever length for a steel angle depends on various factors such as the material strength, the angle's dimensions, and the load it needs to support. Steel angles are commonly used as structural elements in construction and can be designed to support different loads based on their size and configuration. In general, the maximum cantilever length for a steel angle is determined by its ability to resist bending moments and deflection. Bending moments occur when a load is applied to the free end of the cantilever, causing the angle to bend. Deflection is the amount of bending or sagging that occurs under a specific load. To determine the maximum cantilever length, engineers consider the moment of inertia, which is a measure of the angle's resistance to bending, as well as the yield strength of the steel. The moment of inertia is affected by the angle's dimensions, such as the width and thickness of the flanges and the length of the legs. Additionally, the design codes and standards specific to the project or application must be followed to ensure safety and compliance. These codes provide guidelines on the maximum allowable bending stress and deflection limits for steel angles in different loading conditions. In summary, the maximum cantilever length for a steel angle depends on its material strength, dimensions, and the load it needs to support. It is determined through calculations considering the moment of inertia, yield strength, and compliance with relevant design codes and standards.
- Q: How much is a galvanized angle L50*50*5*2500
- Probably around 40 yuan
- Q: What are the different types of surface defects in steel angles?
- Some common types of surface defects in steel angles include pitting, scaling, scratches, and rust.
- Q: What is the standard length of a steel angle?
- The standard length of a steel angle is typically 20 feet or 6 meters.
- Q: Are steel angles readily available in the market?
- Indeed, the market offers a wide array of readily available steel angles. These angles, which are commonly utilized in diverse construction and manufacturing undertakings, are abundantly stocked by steel suppliers, metal fabricators, and construction material stores. To cater to different project specifications, steel angles come in an assortment of sizes, shapes, and grades. Whether you require a few for a do-it-yourself venture or a substantial quantity for a commercial construction endeavor, procuring steel angles from the market is a hassle-free endeavor.
- Q: What is a steel angle?
- A steel angle, also known as an angle iron or L-shaped bar, is a structural steel product that features two perpendicular legs joined together at a 90-degree angle. It is commonly used in construction and engineering applications as a support or reinforcement for various structures due to its strength and versatility. Steel angles are typically made from carbon steel or stainless steel and come in various dimensions, thicknesses, and lengths to suit different project requirements. They can be easily cut, welded, and bolted, making them a popular choice for framing, bracing, and supporting beams, columns, and other structural elements. Additionally, steel angles are also frequently utilized in the manufacturing of shelves, brackets, frames, and other metalwork applications.
- Q: Are steel angles suitable for vehicle ramps?
- Indeed, steel angles prove to be a fitting option for vehicle ramps. Renowned for their strength and durability, these steel angles are frequently employed in construction. Offering a robust and steadfast surface, they provide an appropriate selection for vehicle ramps. Furthermore, steel angles allow for effortless welding or bolting, enabling the creation of personalized ramp designs that cater to specific needs. In essence, steel angles present a dependable and pragmatic solution for the construction of vehicle ramps.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Angle Steel
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























