High Quality Hot Rolled IPEAA Beams for Constrcution
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
OKorder is offering high quality Hot Rolled Steel I-Beams at great prices with worldwide shipping. Our supplier is a world-class manufacturer of steel, with our products utilized the world over. OKorder annually supplies products to European, North American and Asian markets. We provide quotations within 24 hours of receiving an inquiry and guarantee competitive prices.
Product Applications:
Hot Rolled Steel I-Beams are ideal for structural applications and are widely used in the construction of buildings and bridges, and the manufacturing, petrochemical, and transportation industries.
1. Supporting members, most commonly in the house raising industry to strengthen timber bears under houses. Transmission line towers, etc
2. Prefabricated structure
3. Medium scale bridges
4. It is widely used in various building structures and engineering structures such as roof beams, bridges, transmission towers, hoisting machinery and transport machinery, ships, industrial furnaces, reaction tower, container frame and warehouse etc.
Product Advantages:
OKorder's Steel I-Beams are durable, strong, and resist corrosion.
Main Product Features:
· Premium quality
· Prompt delivery & seaworthy packing (30 days after receiving deposit)
· Corrosion resistance
· Can be recycled and reused
· Mill test certification
· Professional Service
· Competitive pricing
Product Specifications:
1. Product name: IPE/IPEAA Beam Steel
2. Standard: EN10025, GB Standard, ASTM, JIS etc.
3. Grade: Q235B, A36, S235JR, Q345, SS400 or other equivalent.
4. Length: 5.8M, 6M, 9M, 10M, 12M or as your requirements
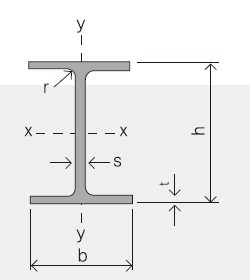
Section | Standard Sectional Dimensions(mm) | ||||
h | b | s | t | Mass Kg/m | |
IPE80 | 80 | 46 | 3.80 | 5.20 | 6.00 |
IPE100 | 100 | 55 | 4.10 | 5.70 | 8.10 |
IPE120 | 120 | 64 | 4.80 | 6.30 | 10.40 |
IPE140 | 140 | 73 | 4.70 | 6.90 | 12.90 |
IPE160 | 160 | 82 | 5.00 | 7.40 | 15.80 |
IPE180 | 180 | 91 | 5.30 | 8.00 | 18.80 |
IPE200 | 200 | 100 | 5.60 | 8.50 | 22.40 |
IPE220 | 220 | 110 | 5.90 | 9.20 | 26.20 |
IPE240 | 240 | 120 | 6.20 | 9.80 | 30.70 |
IPE270 | 270 | 135 | 6.60 | 10.20 | 36.10 |
IPEAA80 | 80 | 46 | 3.20 | 4.20 | 4.95 |
IPEAA100 | 100 | 55 | 3.60 | 4.50 | 6.72 |
IPEAA120 | 120 | 64 | 3.80 | 4.80 | 8.36 |
IPEAA140 | 140 | 73 | 3.80 | 5.20 | 10.05 |
IPEAA160 | 160 | 82 | 4.00 | 5.60 | 12.31 |
IPEAA180 | 180 | 91 | 4.30 | 6.50 | 15.40 |
IPEAA200 | 200 | 100 | 4.50 | 6.70 | 17.95 |
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
FAQ:
A1: All products offered byOKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: How do we guarantee the quality of our products?
A2: We have established an advanced quality management system which conducts strict quality tests at every step, from raw materials to the final product. At the same time, we provide extensive follow-up service assurances as required.
Q3: How soon can we receive the product after purchase?
A3: Within three days of placing an order, we will begin production. The specific shipping date is dependent upon international and government factors, but is typically 7 to 10 workdays.
Q4: What makes stainless steel stainless?
A4: Stainless steel must contain at least 10.5 % chromium. It is this element that reacts with the oxygen in the air to form a complex chrome-oxide surface layer that is invisible but strong enough to prevent further oxygen from "staining" (rusting) the surface. Higher levels of chromium and the addition of other alloying elements such as nickel and molybdenum enhance this surface layer and improve the corrosion resistance of the stainless material.
Q5: Can stainless steel rust?
A5: Stainless does not "rust" as you think of regular steel rusting with a red oxide on the surface that flakes off. If you see red rust it is probably due to some iron particles that have contaminated the surface of the stainless steel and it is these iron particles that are rusting. Look at the source of the rusting and see if you can remove it from the surface.
Images:


- Q: Can steel I-beams be used for industrial shelving?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used for industrial shelving. Steel I-beams are commonly used in construction and can provide excellent strength and durability for industrial shelving applications. They offer high load-bearing capacity, making them suitable for storing heavy items or equipment. Additionally, the versatility of steel allows for the customization of shelving units to meet specific industry requirements.
- Q: How heavy is the steel rope for lifting I-beam?
- The main varieties of wire rope are phosphating coating, steel wire rope, galvanized steel wire rope and stainless steel wire rope.
- Q: What's the difference between I-beam ipeaaa and IPE?
- I-beam is divided into ordinary I-beam and light I-beam, H steel three. It is a section steel whose shape is trough.
- Q: Can steel I-beams be used in modular construction?
- Yes, steel I-beams can be used in modular construction. They provide a strong structural support system and can be easily integrated into modular building designs.
- Q: How do you calculate the cost of steel I-beams?
- In order to determine the cost of steel I-beams, one must take into account several factors. The weight of the beam is of utmost importance and is influenced by various dimensions, including the flanges and webs' height, width, and thickness. This data can be acquired from a steel manufacturer or supplier. Moreover, it is necessary to establish the price per pound or kilogram of steel. Steel prices fluctuate due to factors such as market demand, availability, and location. It is advisable to reach out to multiple suppliers or consult online platforms to obtain the most precise and competitive prices. Once the weight of the I-beam and the cost per unit weight have been determined, the total cost of the steel I-beam can be calculated by multiplying the weight by the cost per unit weight. For instance, if the I-beam weighs 500 pounds and the cost per pound of steel is $1.50, the total cost would amount to 500 pounds x $1.50/pound = $750. It is crucial to take into consideration additional expenses, such as transportation, taxes, and any specialized cutting or fabrication services when calculating the overall cost of steel I-beams. Therefore, it is recommended to consult suppliers or professionals for a comprehensive estimate of the total cost of steel I-beams.
- Q: How do steel I-beams perform in terms of thermal expansion and contraction?
- Steel I-beams exhibit favorable thermal expansion and contraction characteristics. The nature of steel results in a low coefficient of thermal expansion, indicating that it undergoes minimal expansion or contraction when subjected to temperature variations. This quality enhances the stability and dependability of steel I-beams across a range of applications, particularly in the realms of construction and structural engineering. When subjected to heat, steel I-beams undergo a gradual expansion. However, this expansion is negligible in comparison to other materials. Consequently, these beams are capable of preserving their structural integrity even under extreme fluctuations in temperature. Similarly, when the temperature decreases, steel I-beams contract slightly, yet this effect is inconsequential. The limited thermal expansion and contraction of steel I-beams contribute to their durability and capacity to withstand diverse environmental conditions. The thermal stability they possess ensures that the beams maintain their shape and strength, thereby reducing the risk of structural failure or deformity. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that steel is not entirely impervious to thermal expansion and contraction. In instances of extreme temperature changes, such as during fire incidents or rapid cooling, steel may experience more substantial expansion or contraction. Hence, it is imperative to incorporate appropriate design considerations and implement fire protection measures to mitigate these potential thermal effects. In conclusion, steel I-beams exhibit exceptional performance in terms of thermal expansion and contraction, making them the preferred choice for structural applications where stability and reliability are paramount.
- Q: Are steel I-beams resistant to earthquakes?
- Indeed, earthquakes pose no threat to steel I-beams. Steel, being an incredibly resilient and pliable substance, can endure the tremendous pressures exerted in the midst of seismic tremors. I-beams, in particular, possess a remarkable strength-to-weight ratio, rendering them sufficiently robust to withstand the lateral forces and vibrations generated by seismic disturbances. Moreover, steel I-beams can be further fortified through the addition of braces or other seismic-resistant techniques, thereby bolstering their resilience against earthquakes. All in all, due to their capacity to deliver structural stability and guarantee the protection of buildings and infrastructure amidst seismic occurrences, steel I-beams are extensively employed in areas prone to earthquakes.
- Q: What are the considerations for steel I-beam design in high-traffic areas?
- When designing steel I-beams for high-traffic areas, several considerations need to be taken into account to ensure the structural integrity and safety of the construction. 1. Load-bearing capacity: High-traffic areas are subjected to heavy loads, such as vehicles or heavy machinery. The I-beam design should be able to withstand these loads without excessive deflection or failure. Engineers need to calculate the maximum load that the I-beam will experience and design it accordingly, considering both static and dynamic loads. 2. Material selection: The choice of steel grade is crucial in high-traffic areas. High-strength steels, such as ASTM A992 or A572, are commonly used due to their excellent strength-to-weight ratio. These steels offer higher yield and tensile strength, ensuring the beam can support heavy loads and resist fatigue. 3. Span length and support considerations: The distance between supports, or span length, is an important factor to consider. Longer spans may require larger and heavier I-beams to prevent excessive deflection. The type and arrangement of supports, such as columns or beams, should be carefully designed to distribute the load evenly and avoid concentrated stress points. 4. Vibration control: High-traffic areas often experience vibrations due to moving vehicles or machinery. Vibrations can affect the structural integrity of the I-beam, leading to fatigue failure over time. Engineers may need to incorporate vibration dampening techniques, such as adding dampers or isolators, to mitigate the impact of vibrations on the steel I-beam. 5. Fire resistance: In high-traffic areas, fire safety is crucial. Steel I-beams can be designed to have fire resistance by applying fireproof coatings or encasing them in fireproof materials. The design should also consider the fire protection measures in place, such as fire sprinkler systems, to ensure the I-beams can withstand the elevated temperatures during a fire. 6. Corrosion protection: High-traffic areas are often exposed to harsh environmental conditions, including moisture or chemicals. Corrosion protection measures, such as galvanization or epoxy coatings, should be implemented to prevent rust and corrosion, which can weaken the steel I-beam over time. 7. Accessibility and maintenance: Considerations should be made for accessibility and maintenance of the steel I-beam. High-traffic areas may require regular inspections and maintenance. Access points, such as walkways or platforms, should be incorporated into the design to facilitate inspections and repairs without disrupting the traffic flow. By carefully considering these factors, engineers can design steel I-beams that can safely withstand the demands of high-traffic areas, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the structure.
- Q: How do steel I-beams resist bending and deflection?
- The resistance of steel I-beams to bending and deflection is due to their unique structural design and material properties. Firstly, the I-beam's shape is crucial in preventing bending. The wider and stiffer top and bottom flanges, connected by a vertical web, create a larger moment of inertia. This measure of resistance to bending allows the load to be spread over a larger area, reducing stress on individual sections. Additionally, the material properties of steel play a significant role in its bending resistance. Steel is an incredibly strong and rigid material that can withstand high loads without significant deformation. When combined with the shape of the I-beam, it efficiently transfers and distributes the applied load, minimizing deflection. Furthermore, the manufacturing process of steel I-beams, specifically hot rolling, enhances their strength and rigidity. The steel is heated to a high temperature and then shaped into the desired I-beam profile using rollers. This aligns the grain structure of the steel, resulting in a stronger and more uniform material with improved resistance to bending and deflection. To sum up, steel I-beams resist bending and deflection due to their structural design, which includes wider and stiffer flanges, and their material properties, such as high tensile strength and rigidity. The hot rolling manufacturing process further enhances their resistance to bending and deflection.
- Q: Are steel I-beams prone to rust or corrosion?
- Indeed, rust and corrosion are common issues that steel I-beams are susceptible to. Since steel is primarily composed of iron, it is highly prone to rusting when it comes into contact with moisture and oxygen. Consequently, if steel I-beams are not adequately protected, they can gradually develop rust and corrosion, ultimately compromising their structural integrity. To combat this problem, various protective coatings and treatments, such as galvanization or painting, are applied to the steel beams. These coatings serve as a barrier, effectively preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the underlying steel and minimizing the risk of rust and corrosion. Additionally, regular maintenance and inspection play a crucial role in promptly detecting and addressing any signs of rust or corrosion, ensuring the long-term strength and stability of the I-beams.
Send your message to us
High Quality Hot Rolled IPEAA Beams for Constrcution
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























