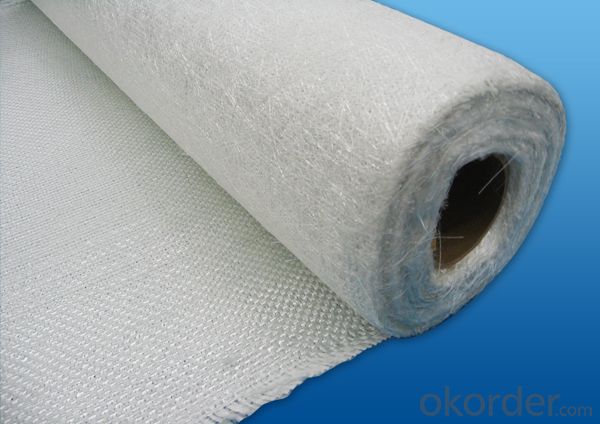
Fiberglass Fabric Lowes Stitched Combo Mat
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 12000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 200000Kg Per Month kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1.Brief Introduction
(0°/90°) series mat:
Two layers of roving(550g/㎡-1250g/㎡) are aligned at 0°/90° with or without a layer of chopped strands(0g/㎡-500g/㎡)。The product has a maximum width of 100 inches.This product can be used for manufacturing boats,cases and shell of car.
2.Product Structure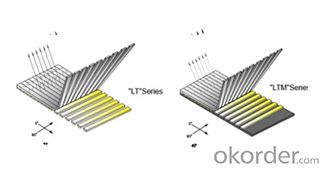
3.Product Specifications
Product No. | Overall Density | .0° Roving Density | .90° Roving Density | Chop Density | Polyester Yarn Density |
(g/m2) | (g/m2) | (g/m2) | (g/m2) | (g/m2) | |
E-LTMC1603 | 671.74 | 303.8 | 247.96 | 101.62 | 18.36 |
E-LTMC1608 | 844.76 | 303.8 | 247.96 | 274.64 | 18.36 |
E-LTMC1808 | 903.8 | 303.8 | 307 | 274.64 | 18.36 |
E-LTMC1810 | 934.31 | 303.8 | 307 | 305.15 | 18.36 |
E-LTMC1815 | 1086.89 | 303.8 | 307 | 457.73 | 18.36 |
E-LTMC2408 | 1101.04 | 405.66 | 401.46 | 274.64 | 19.28 |
E-LTMC2415 | 1284.13 | 405.66 | 401.46 | 457.73 | 19.28 |
E-LTMC3205 | 1272.69 | 607.6 | 491.86 | 152.58 | 20.65 |
E-LTMC3205-HS | 1388.43 | 607.6 | 607.6 | 152.58 | 20.65 |
E-LTMC3208 | 1394.75 | 607.6 | 491.86 | 274.64 | 20.65 |
E-LTMC3610 | 1541 | 607.6 | 607.6 | 305.15 | 20.65 |
E-LTMC3615 | 1693.58 | 607.6 | 607.6 | 457.73 | 20.65 |
E-LTC1800 | 629.16 | 303.8 | 307 | - | 18.36 |
E-LTC2400 | 826.4 | 405.66 | 401.46 | - | 19.28 |
E-LTC3600 | 1235.85 | 607.6 | 607.6 | - | 20.65 |
E-UDL450 | 479.14 | 405.66 | 55.12 | - | 18.36 |
E-UDL500 | 490.85 | 405.66 | 66.83 | - | 18.36 |
E-UDL600 | 608.9 | 566.92 | 23.62 | - | 18.36 |
E-UDL1200 | 1207.34 | 1133.86 | 55.12 | - | 18.36 |
E-UDLM1250 | 1258.98 | 1133.86 | 55.12 | 50.00 | 20 |
E-UDLM1300 | 1338.68 | 1215.2 | 55.12 | 50.00 | 18.36 |
Special specification can be produce according to customer requirements.
4.FAQ
Packaging:
Each roll is wound onto a paper tube which has an inside diameter of 76mm and the roll has a diameter of 275mm. The roll is wrapped up with plastic film,and then packed in a cardboard box or wrapped up with kraft paper. The rolls can be horizontally placed. For transportation, the rolls can be loaded into a cantainer directly or on pallets.
Storage:
Unless otherwise specified, It should be stored in a dry, cool and rain-proof area. It is recommended that the room temperature and humidity should be always maintained at 15℃~35℃ and 35%~65% respectively.

- Q: Can fiberglass fabric be used for heat-resistant curtains?
- Yes, fiberglass fabric can be used for heat-resistant curtains. Fiberglass is known for its excellent heat resistance properties, making it suitable for applications where high temperatures are present. Using fiberglass fabric as a material for heat-resistant curtains can provide insulation and protection against heat, making it a suitable choice for such applications.
- Q: How does fiberglass fabric perform in shear strength?
- Fiberglass fabric has excellent shear strength performance. Due to its composition of intertwined glass fibers, it possesses strong resistance to forces applied parallel to its surface. The interlocking fibers create a strong and rigid structure that allows it to withstand shear stresses and prevent deformation or failure. This makes fiberglass fabric highly suitable for applications where shear strength is important, such as in the construction of lightweight, high-strength composites, reinforcement of concrete, and the manufacturing of various industrial products. Additionally, fiberglass fabric's shear strength is not significantly affected by exposure to moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures, making it a durable and reliable material for a wide range of applications.
- Q: How is fiberglass fabric cut and shaped?
- Fiberglass fabric is typically cut and shaped using a few different methods. One common method is to use scissors or a utility knife to cut the fabric to the desired size and shape. This method is commonly used for smaller or more intricate cuts. For larger cuts or more precise shaping, a technique called "hot knife cutting" is often employed. This involves using a heated blade or wire to cleanly cut through the fiberglass fabric. The heat helps to seal the edges of the fabric, preventing fraying and ensuring a smooth finish. Another method used for shaping fiberglass fabric is molding. In this process, the fabric is laid over a mold or form and then a resin or adhesive is applied to secure it in place. The fabric is then allowed to cure or harden, taking on the shape of the mold. This method is commonly used in the production of fiberglass products such as boat hulls or automotive parts. Overall, the cutting and shaping of fiberglass fabric requires precision and attention to detail. Whether using scissors, a hot knife, or molding techniques, it is important to ensure clean cuts and proper shaping in order to achieve the desired result.
- Q: Can fiberglass fabric be used for insulation sleeves?
- Indeed, insulation sleeves can be created using fiberglass fabric. Fiberglass, a material commonly utilized for insulation purposes, possesses exceptional fire resistance properties and boasts high thermal resistance. Its ability to withstand elevated temperatures, combined with its capability of being woven into fabric form, renders it suitable for the production of insulation sleeves. These sleeves serve the purpose of safeguarding and insulating various components such as pipes, wires, and cables, shielding them from both heat and cold. By acting as a barrier, the fiberglass fabric effectively hampers heat transfer and provides insulation to the enclosed area. Additionally, fiberglass fabric boasts the advantages of being lightweight, flexible, and durable, thereby ensuring ease of use and long-lasting performance in insulation applications.
- Q: What are the temperature resistance capabilities of fiberglass fabric?
- Fiberglass fabric is widely chosen for a range of industrial and commercial uses due to its exceptional temperature resistance. It has the ability to endure temperatures as high as 1000°C (1832°F) without experiencing any significant deterioration in its mechanical or physical properties. The reason behind this temperature resistance lies in the inherent characteristics of fiberglass, which is a composite material crafted by embedding delicate glass fibers in a resin or polymer matrix. These fibers possess a high melting point and are capable of withstanding thermal degradation, thereby enabling the fabric to retain its structural integrity even in the face of extreme heat. Moreover, fiberglass fabric also possesses commendable thermal insulation properties, thereby further bolstering its resistance to temperature. As a result, fiberglass fabric is well-matched for applications that involve exposure to high temperatures, including insulation, fire protection, aerospace, automotive, and other industries.
- Q: How is fiberglass fabric used in insulation?
- Fiberglass fabric is commonly used in insulation due to its excellent thermal properties. It is primarily used in two main forms: batts and loose-fill insulation. In the case of fiberglass batts, the fabric is woven into sheets, which are then cut to fit between the studs, joists, and beams of buildings. These batts are typically installed in walls, ceilings, and floors to provide a barrier against heat transfer. The fiberglass fabric helps to trap air within its fibers, creating pockets of still air that significantly reduce the conduction of heat. This process, known as thermal insulation, helps to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature and reduce energy consumption by minimizing the need for heating and cooling. Another application of fiberglass fabric in insulation is loose-fill insulation. In this form, the fabric is processed into tiny fibers and blown or poured into walls, attics, and other enclosed spaces. The fabric fibers intertwine, creating a dense layer that acts as a thermal barrier. Loose-fill insulation is particularly effective in filling irregularly shaped or hard-to-reach spaces, ensuring that there are no gaps or voids where heat can escape or enter the building. Fiberglass fabric is also used in combination with other materials to enhance insulation performance. For example, it is often combined with foam or foil to create rigid panels or reflective insulation. These composite materials provide additional benefits such as moisture resistance, soundproofing, and enhanced thermal resistance. In summary, fiberglass fabric is used in insulation to minimize heat transfer, improve energy efficiency, and create a comfortable indoor environment. Whether in the form of batts or loose-fill, fiberglass fabric acts as a thermal barrier, reducing the conduction of heat and enhancing the insulation properties of buildings.
- Q: Can fiberglass fabric be used for insulation in storage tanks?
- Yes, fiberglass fabric can be used for insulation in storage tanks. It is commonly used due to its excellent thermal insulation properties, as it helps to maintain the temperature of the stored contents and prevent heat loss or gain. Additionally, fiberglass fabric is resistant to moisture, chemicals, and corrosion, making it a suitable choice for insulation in storage tanks.
- Q: What are the different types of fiberglass fabrics?
- There are several different types of fiberglass fabrics available, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. Some common types include: 1. E-Glass Fabric: This is the most commonly used type of fiberglass fabric. It is known for its excellent electrical insulation properties and high tensile strength. E-glass fabric is used in a wide range of applications, including boat building, automotive parts, and aerospace components. 2. S-Glass Fabric: S-glass fabric is a higher-performance alternative to E-glass. It has a higher tensile strength and better resistance to impact, making it suitable for applications that require superior strength, such as military equipment and high-performance sports equipment. 3. C-Glass Fabric: C-glass fabric is resistant to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for use in applications where exposure to chemicals is a concern. It is commonly used in chemical plants, wastewater treatment facilities, and other industrial settings. 4. A-Glass Fabric: A-glass fabric is an alkali-resistant type of fiberglass fabric. It is commonly used in the construction industry for reinforcing cement and concrete structures, such as bridges and buildings. 5. Roving Fabric: Roving fabric consists of untwisted strands of fiberglass. It is typically used in applications that require high strength and dimensional stability, such as wind turbine blades, pipes, and pressure vessels. 6. Chopped Strand Mat (CSM): CSM is a type of fiberglass fabric made from randomly oriented chopped strands held together with a binder. It is commonly used in applications that require a smooth and uniform surface finish, such as boat hulls and automotive parts. 7. Woven Roving: Woven roving is a heavy-duty type of fiberglass fabric that consists of closely woven strands. It is known for its high strength and stiffness, making it suitable for applications that require structural reinforcement, such as boat hulls, wind turbine blades, and automotive body panels. Overall, the choice of fiberglass fabric depends on the specific requirements of the application, including strength, electrical insulation properties, chemical resistance, and surface finish.
- Q: Is fiberglass fabric resistant to chemicals in laboratories?
- Yes, fiberglass fabric is generally resistant to a wide range of chemicals commonly used in laboratories. Its inherent chemical resistance makes it a preferred material for protective clothing, lab aprons, and other applications where exposure to chemicals is expected.
- Q: How is fiberglass fabric used in the production of wind turbine blades?
- Fiberglass fabric is extensively used in the production of wind turbine blades due to its exceptional properties and advantages. The fabric is typically made from woven fiberglass filaments, which are lightweight, strong, and highly durable. One of the most significant uses of fiberglass fabric in wind turbine blades is as the main structural material. The fabric is typically layered and impregnated with a resin, such as epoxy, to form a composite material known as fiberglass-reinforced polymer (FRP). This FRP composite provides the required strength and stiffness to withstand the forces and stresses experienced by the blades while operating in the wind. The process of incorporating fiberglass fabric into wind turbine blades involves several steps. First, a mold is created in the shape of the blade using a positive model. Layers of fiberglass fabric are then carefully placed onto the mold, with each layer oriented in a specific direction to optimize the blade's mechanical properties. The fabric layers are impregnated with resin, ensuring that the entire structure is bonded together. This process is often repeated multiple times to increase the thickness and strength of the blade. The advantages of using fiberglass fabric in wind turbine blades are numerous. Firstly, the fabric's lightweight nature allows for the construction of longer and larger blades, enabling more efficient energy capture from the wind. Additionally, fiberglass fabric is highly resistant to corrosion, making it an ideal choice for outdoor applications, where the blades are constantly exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Furthermore, the inherent flexibility of fiberglass fabric allows the blades to bend and twist with the changing wind conditions, effectively reducing unnecessary stress and enhancing overall performance. The fabric is also resistant to fatigue, meaning that it can withstand repeated loading cycles without compromising its structural integrity. Overall, fiberglass fabric plays a crucial role in the production of wind turbine blades by providing the necessary strength, durability, and flexibility required for efficient and reliable energy generation. Its lightweight nature, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance make it an ideal material choice for constructing blades that can withstand the demanding operating conditions of wind turbines.
Send your message to us
Fiberglass Fabric Lowes Stitched Combo Mat
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 12000 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 200000Kg Per Month kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords