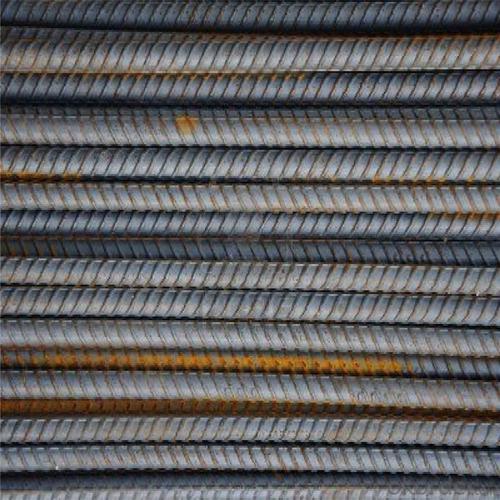
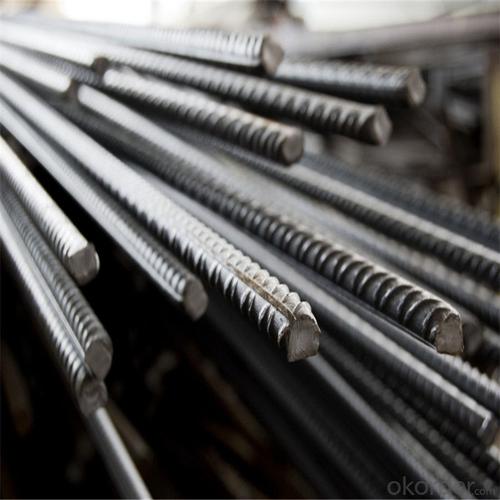
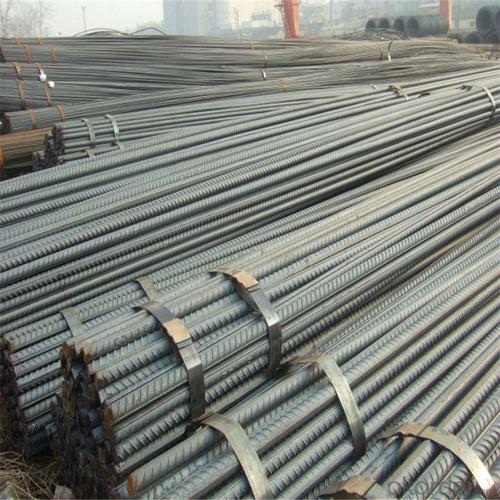
Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 120 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
Description of Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
1, Diameter: 5.5mm-10mm Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
10m- 40mm Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
2, Length: 6m, 9m, 12m or customized
3, Standard: GB, ASTM, AISI, SAE, DIN, JIS, EN
OEM technology - send detailed technical parameters for accurate quotation.
2, Produce Process: smelt iron - EAF smelt billet - ESR smelt billet -
hot rolled or forged to get the steel round bar and plate
3, Heat Treatment: annealing, normalizing, tempering, quenching
4, Surface Treatment: Black
5, Quality Assurance: We accept third party inspection for all orders.
You can ask testing organizations such as SGS, BV, etc. to test our products before shipping.
Chemical Composition of Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
Grade | Technical data of the original chemical composition(%) | |||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB335 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤1.60 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | >0.0008 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 335 | ≥490 | ≥16 | ||||
Reinforcing steel bar HRB400 | C | Mn | Si | S | P | B |
≤0.25 | ≤0.16 | ≤0.80 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | 0.04-0.12 | |
Physics Capability | ||||||
Yield Strength(N/cm2) | Tensile Strength(N/cm2) | Elongation(%) | ||||
≥ 400 | ≥ 570 | ≥ 14 | ||||
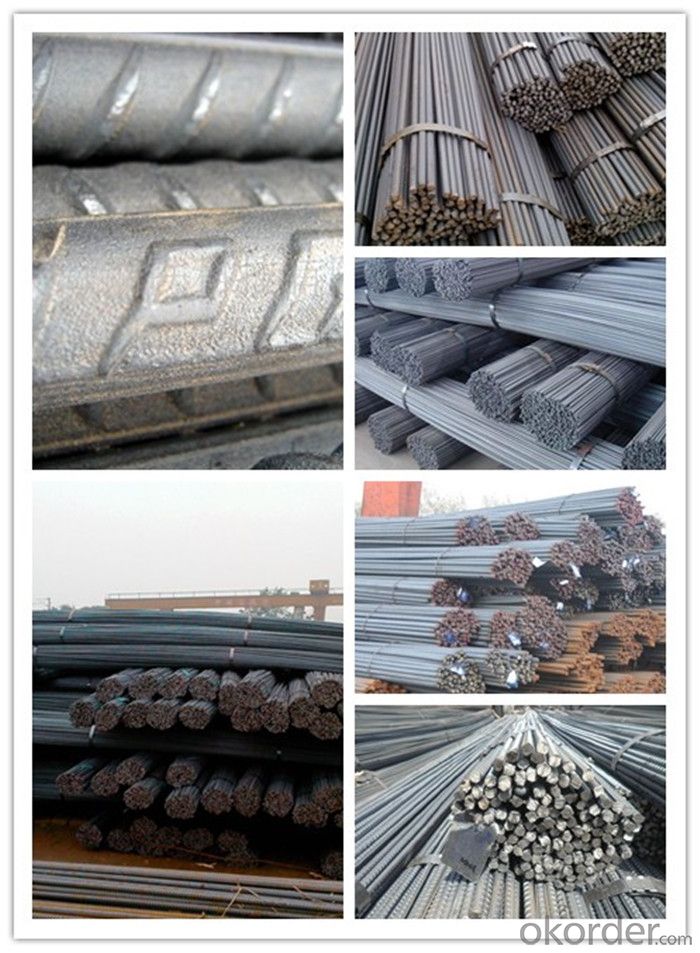
Products Show of Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
Company Information
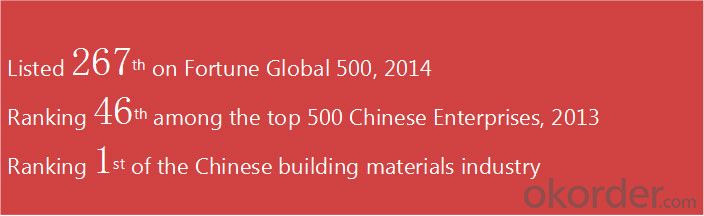
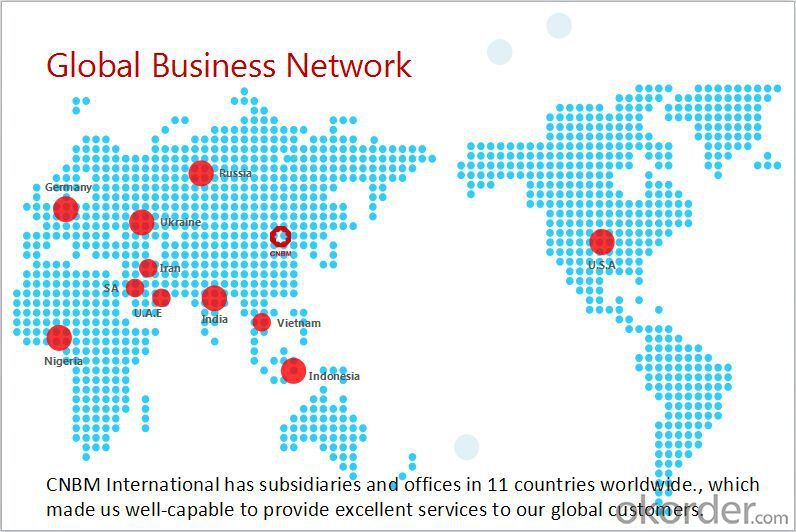
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: What are the properties of nickel-based alloys?
- Nickel-based alloys possess several desirable properties, including high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, good thermal stability, and outstanding mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. These alloys also exhibit good electrical conductivity, magnetic properties, and resistance to oxidation. Additionally, nickel-based alloys can be easily fabricated, making them suitable for various applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, chemical processing, and power generation.
- Q: How does stainless steel contribute to the production of medical implants?
- Stainless steel contributes to the production of medical implants by providing a highly durable and corrosion-resistant material that is compatible with the human body. It is used in various implants such as joint replacements, dental implants, and surgical instruments due to its strength, biocompatibility, and ability to withstand sterilization processes.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the medical device manufacturing industry?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the medical device manufacturing industry. Special steel, such as stainless steel, is often used in the production of medical devices due to its corrosion resistance, high strength, and biocompatibility. It is commonly used for surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and other medical equipment where durability and hygiene are crucial.
- Q: What are the different methods of surface thermal spraying for special steel?
- There are several different methods of surface thermal spraying for special steel, including flame spraying, arc spraying, plasma spraying, and high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF) spraying. Each method involves heating and melting a coating material, which is then propelled onto the steel surface to form a protective layer. These methods offer varying levels of coating thickness, adhesion, and durability, depending on the specific requirements of the application.
- Q: What are the advantages of using special steel in the marine sector?
- Special steel has several advantages when used in the marine sector. Firstly, special steel is highly resistant to corrosion, which is crucial in a marine environment where constant exposure to saltwater can cause regular steel to rust and deteriorate. This corrosion resistance extends the lifespan of structures and components, reducing maintenance costs and increasing safety. Secondly, special steel offers excellent strength and toughness, making it suitable for the demanding conditions of the marine sector. It can withstand high stress, impact, and vibration, ensuring the integrity of the structures even in rough seas or extreme weather conditions. Moreover, special steel can be fabricated into various shapes and sizes, allowing for customization and optimization of marine components. This versatility enables the production of lightweight yet robust structures, improving fuel efficiency, and reducing the overall weight of the vessel. Additionally, special steel can withstand low temperatures, making it suitable for marine applications in colder climates or polar regions. It retains its mechanical properties even in sub-zero temperatures, ensuring the safety and reliability of marine operations. In summary, the advantages of using special steel in the marine sector include corrosion resistance, high strength and toughness, versatility in fabrication, and low-temperature resistance. These qualities enhance the durability, safety, and efficiency of marine structures and components.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to improving product durability?
- Special steel contributes to improving product durability in several ways. Firstly, special steel has superior strength and toughness compared to regular steel, making it more resistant to wear and tear. This allows products made from special steel to withstand heavy usage and harsh conditions without losing their structural integrity. Additionally, special steel is often more corrosion-resistant, preventing rust and other forms of deterioration that can compromise a product's longevity. Lastly, special steel can be tailored to specific applications, enabling manufacturers to design products with optimal performance and durability in mind. Overall, special steel plays a crucial role in enhancing product durability and extending their lifespan.
- Q: What are the main characteristics of creep-resistant steel forgings?
- Creep-resistant steel forgings possess a range of essential qualities that render them suitable for applications involving high temperatures and prolonged stress and heat exposure. To begin with, these forgings are renowned for their exceptional resistance to creep deformation. Creep refers to the gradual deformation that occurs under constant load and elevated temperatures over an extended period. These forgings are specifically designed to withstand such deformation, retaining their shape and structural integrity. Consequently, they are ideal for use in environments with high temperatures, such as turbine blades, boiler components, and other similar settings. Another crucial characteristic of creep-resistant steel forgings is their impressive strength. These forgings are manufactured using alloying elements like chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium, which enhance their tensile strength. As a result, they exhibit excellent resistance to deformation and fracture under high-stress conditions. This strength is essential for ensuring that the forgings can endure the demands of various applications and perform reliably over time. Furthermore, creep-resistant steel forgings demonstrate good resistance to oxidation and corrosion. The presence of alloying elements creates a protective layer on the surface, safeguarding against oxidation and corrosion at elevated temperatures. This resistance is vital in preventing the degradation of the material and maintaining its mechanical properties, even in harsh environments. Moreover, creep-resistant steel forgings offer outstanding thermal stability. They can endure extreme temperature fluctuations without significant dimensional changes or loss of mechanical strength. This stability is particularly critical in applications that involve rapid heating and cooling cycles, ensuring that the forgings can sustain their performance under challenging conditions. Additionally, creep-resistant steel forgings possess excellent fatigue resistance. Fatigue refers to the weakening of a material resulting from cyclic loading, which is particularly relevant in high-temperature applications due to the combination of stress and heat. These forgings are designed to withstand cyclic loading and retain their mechanical properties, thus reducing the risk of fatigue failure and enhancing the overall reliability of the component. In conclusion, the primary characteristics of creep-resistant steel forgings encompass resistance to creep deformation, high strength, good oxidation and corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and excellent fatigue resistance. These qualities establish creep-resistant steel forgings as a reliable and durable choice for applications requiring resistance to high temperatures, stress, and prolonged exposure to challenging environments.
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the manufacturing of cutting blades?
- Special steel plays a crucial role in the manufacturing of cutting blades. Cutting blades are required to have exceptional strength, durability, and sharpness to efficiently perform their function. Special steel, also known as tool steel, possesses unique properties that make it an ideal material for manufacturing cutting blades. Firstly, special steel has excellent hardness, which enables cutting blades to maintain their sharpness for an extended period. Cutting blades made from special steel can withstand the wear and tear that occurs during cutting operations. This hardness allows the blades to retain their cutting edge, resulting in a longer lifespan and improved cutting performance. Moreover, special steel offers exceptional toughness, which is crucial for cutting blades. During cutting operations, blades are subjected to high impact and stress. Special steel's toughness helps absorb these forces and prevents the blades from breaking or chipping. This ensures that the cutting blades can withstand demanding cutting tasks without compromising their performance. Additionally, special steel provides excellent corrosion resistance. Cutting blades often come into contact with various materials, including moisture and chemicals. The corrosion resistance of special steel prevents the blades from rusting or corroding, ensuring their longevity and reducing the need for frequent replacements. Furthermore, special steel offers good machinability, making it easier to shape and form into the desired blade design. This enhances the manufacturing process by enabling the production of cutting blades with complex shapes and intricate features. The machinability of special steel allows manufacturers to create blades with precise cutting edges and optimal geometries, resulting in superior cutting performance. In conclusion, special steel contributes significantly to the manufacturing of cutting blades by providing hardness, toughness, corrosion resistance, and good machinability. These properties ensure that cutting blades made from special steel are long-lasting, durable, and capable of delivering exceptional cutting performance in various applications.
- Q: What are the different methods for case hardening special steel?
- There are several different methods for case hardening special steel, each with its own advantages and applications. 1. Carburizing: This method involves heating the steel in a carbon-rich environment at high temperatures. Carbon atoms diffuse into the surface of the steel, forming a hard and wear-resistant outer layer. Carburizing can be done through various techniques such as gas carburizing, pack carburizing, or liquid carburizing. 2. Nitriding: Nitriding is a process where the steel is heated in a nitrogen-rich environment. Nitrogen atoms diffuse into the surface of the steel, forming a hard and corrosion-resistant layer. This process is mainly used for steels with high alloy content. 3. Induction hardening: Induction hardening utilizes induction heating to selectively heat the surface of the steel. Once heated, a quenching process rapidly cools the surface, resulting in a hard layer. Induction hardening is ideal for parts that require localized hardening, such as gears or shafts. 4. Flame hardening: Flame hardening involves heating the surface of the steel with a high-temperature flame and then rapidly cooling it. This method is commonly used for large parts or components that cannot be easily treated with other methods. 5. Laser hardening: Laser hardening is a precise and localized method that uses a laser beam to heat and harden specific areas of the steel. This technique is highly controlled and allows for precise control over the hardened layer depth and hardness. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of case hardening method depends on factors such as the desired hardness, the size and shape of the part, and the specific requirements of the application.
- Q: What are the requirements for special steel used in defense equipment manufacturing?
- The requirements for special steel used in defense equipment manufacturing typically include high strength and durability, resistance to corrosion and wear, good toughness and impact resistance, as well as the ability to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh environments. Additionally, the steel must meet stringent quality control standards and industry specifications to ensure its reliability and performance in critical defense applications.
Send your message to us
Astm Gr60 Steel Reinforcing Rebar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 120 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 500000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



































