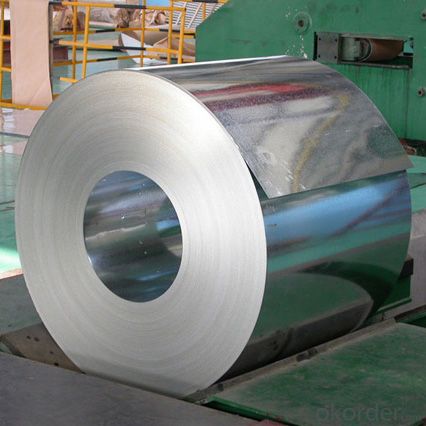
Al-Zinc Coated steel rolled coil for Roofing
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Structure of Al-Zinc coated steel coil
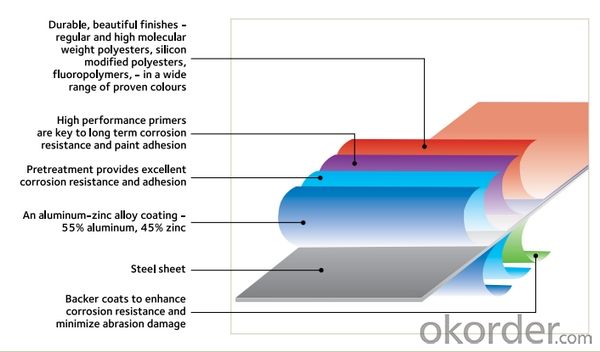
Description of Aluminum Zinc Rolled Coil
The detailed information for the Al-Zinc coated steel coil is as following and it is mainly using for roofing producing, making ceiling grid and all kinds of roll forming structure.
Thickness: 0.20mm to 1.20mm
Width: 914mm, 1000mm, 1200mm, 1219mm and 1250mm, or slit narrow strip according to customer request, can be slit from 20mm to 610mm.
Coil ID: 508mm
Coil weight: 3 tons to 6 tons
Thickness tolerance: +/- 0.02mm or according to customer request.
Main Feature of Al-Zinc coated steel coil
1.Corrosion resistance: It mainly depends on the aluminum protection. When the zinc being worn, the aluminum will form a dense layer of aluminum oxide, resist corrosion material to prevent further corrosion inside.
2. Heat resistance: Aluminum zinc alloy steel sheet has excellent heat resistance, can withstand high temperatures over 300 centigrade, and is similar with aluminized steel high temperature oxidation resistance. It often used in chimney pipes, ovens, fluorescent lighting device and the device cover.
3. Heat reflective: Galvanized steel plate heat-reflective high rate is twice as galvanized steel, often used to make insulation materials.
4. Economy: Because density of 55% AL-Zn is smaller than the density of Zn, so in the same weight and thickness of Galvanized zinc layer, aluminum-zinc steel plate is larger area more than 3% of galvanized steel sheet.
Applications of Al-Zinc coated steel coil
1. Construction and building: roofing; ventilating duct; handrail; partition panel;etc.
2. Electric appliance: refrigerator; washing machine; refrigerator; DVD;etc.
3.Transportation: oil tank; road sign; etc.
4.Agriculture:barn; etc.
5.Others:vending machine; game machine; etc.

Specifications of Al-Zinc coated steel coil
Prepainted galvanized steel coil ( PPGI ) | Prepainted galvalume steel coil ( PPGL ) | |
Standard | JIS G3312 CGCC | J IS G3322 CGLCC |
Valid thickness | 0. 16 ~1. 2 0mm | 0. 16 ~1. 2 0mm |
Coil width | 600~1250mm | 600~1250mm |
Coil ID | 508mm & 610mm | 508mm & 610mm |
Coil weight | 3~5 tons | 3~5 tons |
Coating | 4 0~275 g/m2 | AZ30 to AZ150 |
Paint t hickness , top side | 15~25 microns | 15~25 microns |
P aint t hickness , reverse | 5~7 microns or 15~25 microns | 5~7 microns or 15~25 microns |
Color | any RAL code | any RAL code |
Package | vertical, eye to sky & horizontal | vertical, eye to sky & horizontal |
MOQ | 25 tons | 25 tons |
FAQ of Al-Zinc coated steel coil
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1. What is the minimum order quantity ?
Our MOQ is 50mt for each size. And we will consider to give more discount if you make big order like 1000 tons and more. Further more, the more appropriate payment term your offer the better price we can provide.
2. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-25 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
3. How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
- Q: I was just thinking, is their a way to make steel qualities inherent in concrete, therefore eliminating the need for re bar?
- There is an iron powder reinforced concrete flooring that improves abrasion resistance. However, you cannot get the tensile strength enhancement that is possible with rebar.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the manufacturing of industrial boilers?
- Steel coils are used in the manufacturing of industrial boilers as they are shaped and welded to form the boiler shell. The coils provide the necessary strength and durability to withstand high pressure and temperature conditions in the boiler. Additionally, the coils are often used to create the tubes and pipes that circulate the hot gases and water within the boiler, facilitating efficient heat transfer and steam generation.
- Q: i found a similar question asking what metals were in stainless steel but i don't know if they are the same.... they probably aren't.
- steel is iron with a little bit of carbon mixed in. how much carbon determines the hardness of the steel. stainless steel is the same mostly, it has nickle and chromium added in to make it corrosion resistant.
- Q: On a free standing carport with an 8 inch, 22 foot long aluminum i-beam, would a steel 8-inch i-beam be just as strong? I am looking into it since they are cheaper.
- Yes-- just make sure that your connection to the beam is secure. Since you call it an I beam -- I assume that it is steel. Don't do any drilling -- use two heavy duty c-clamps to hang your bar from.
- Q: is stainless steel a good steel for sensitive skin? or does it have to be surgical or sterling silver?
- When I worked at Spencer's the jewelry would usually said what grade/type of metal it was. As long as it says 316L surgical steel you should be ok. But like another person said, go to a professional piercer and buy jewelry there because you know that you're getting good quality. You get what you pay for!
- Q: How are steel coils protected during storage and transportation?
- Steel coils are protected during storage and transportation through various measures. Firstly, they are typically wrapped with a layer of protective material such as plastic or paper to shield them from moisture, dust, and other contaminants. Additionally, steel coils are often stored in a controlled environment, such as a warehouse, to prevent exposure to extreme temperatures and weather conditions. During transportation, they are secured using specialized equipment such as steel coil racks, which prevent movement and minimize the risk of damage. These protective measures ensure the integrity and quality of steel coils throughout their storage and transportation processes.
- Q: .Yea, so I just saw the old Conan movie with Arnold. Good movie, but I still don't get it. What IS the riddle of steel???I get that like from the begining Conan's dad is like telling him a story about Crom and giants, and people got steel once Crom killef the giants. Then, later on in the movie Conan's talking to his lil' asian homie, and Conan tells him that when he dies... he'll go before Crom, and Crom will ask him what the riddle of steel is, and if he doesn't know it he'll get kicked out of barbarian heaven!But, what is the riddle of steel???C'mon guys... I want to in to barbarian heaven! LolBut, seriously though... what us it???.
- Riddle Of Steel
- Q: What are the different surface treatments available for steel coils?
- There are several different surface treatments available for steel coils, including galvanizing, painting, and powder coating. Galvanizing involves applying a layer of zinc to the surface of the steel to provide corrosion resistance. Painting involves applying a layer of paint to the surface to enhance its appearance and protect it from rusting. Powder coating is a process where dry powder is electrostatically applied to the steel surface and then cured under heat to form a protective and decorative coating.
- Q: bullets are normally made out of lead...are there bullets that are completely steel?? (not plated)
- I personally know of no steel bullets. In order to be soft enough to engage the rifling in the barrel, it would have to have a jacket at least the thickness of the groove depth. Separate loading(those which a projectile is loaded followed with various sized powder charges) howitzer projectiles are cast steel with copper driving bands set in grooves to engage the rifling.
- Q: What are the safety considerations when handling steel coils?
- When handling steel coils, there are several safety considerations that should be taken into account. Firstly, it is essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots. This protective gear helps to minimize the risk of injuries from sharp edges, flying debris, or accidental contact with the coils. Secondly, it is important to have a clear understanding of the weight and dimensions of the steel coils being handled. Steel coils can be extremely heavy, and improper lifting techniques can result in back strains, muscle pulls, or even more severe injuries. Therefore, it is crucial to use proper lifting techniques, such as bending the knees and keeping the back straight, or utilizing lifting equipment like cranes or forklifts when necessary. Additionally, steel coils can be unstable and prone to rolling or shifting during handling. To prevent accidents, it is crucial to secure the coils properly before moving or stacking them. This can be done by using appropriate lifting attachments, banding the coils together, or utilizing racks or other storage systems specifically designed for steel coils. Furthermore, it is important to be aware of the potential hazards associated with the steel coils, such as sharp edges, oil or grease coatings, or even damage to the coils themselves. It is essential to inspect the coils for any abnormalities or defects before handling them, as well as ensuring that they are stored in a safe and stable manner to prevent accidents. Lastly, proper communication and training are essential when handling steel coils. It is crucial to establish clear communication channels between workers to ensure that everyone is aware of their roles and responsibilities. Additionally, providing training on safe handling techniques, potential hazards, and emergency procedures can help minimize the risk of accidents and injuries. In conclusion, when handling steel coils, it is important to wear appropriate PPE, use proper lifting techniques, secure the coils properly, be aware of potential hazards, and ensure proper communication and training. By following these safety considerations, the risk of accidents and injuries can be significantly reduced.
Send your message to us
Al-Zinc Coated steel rolled coil for Roofing
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 30000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























