A110*110*9 Equal steel Angle for construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of JIS SS400 Angle Steel
1.Standards:GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2.Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
3.Material: JIS G3192,SS400;SS540.
4. Payment terms:
1).100% irrevocable L/C at sight.
2).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against the copy of B/L.
3).30% T/T prepaid and the balance against L/C
5.Sizes:
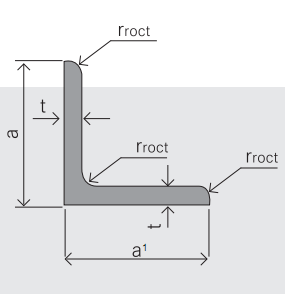
EQUAL ANGLES SIZES |
| ||
a(mm) | a1(mm) | thickness(mm) | length |
25 | 25 | 2.5---3.0 | 6M/12M |
30 | 30 | 2.5---4.0 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 2.5 | 6M/12M |
38 | 38 | 3.0---5.0 | 6M/12M |
40 | 40 | 3.0---6.0 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3 | 6M/12M |
50 | 50 | 3.7---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
60 | 60 | 5.0---6.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
63 | 63 | 6.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
65 | 65 | 5.0---8.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
70 | 70 | 6.0---7.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
75 | 75 | 5.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
80 | 80 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
90 | 90 | 6.0---10.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
100 | 100 | 6.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
120 | 120 | 8.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
125 | 125 | 8.0---12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
130 | 130 | 9.0-12.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
140 | 140 | 10.0-16.0 | 6M/9M/12M |
150 | 150 | 10---15 | 6M/9M/12M |
160 | 160 | 10---16 | 6M/9M/12M |
180 | 180 | 12---18 | 6M/9M/12M |
200 | 200 | 14---20 | 6M/9M/12M |
5. Material Specifications:
Grade | Yield Strength,N/mm² | Extension Strength N/mm² | |||
Thickness of Steel,mm | |||||
≦16 | >16-≦40 | >40-≦100 | >100 | ||
SS330 | ≧205 | ≧195 | ≧175 | ≧165 | 330-430 |
SS400 | ≧245 | ≧235 | ≧215 | ≧205 | 400-510 |
SS490 | ≧285 | ≧275 | ≧255 | ≧245 | 490-610 |
SS540 | ≧400 | ≧390 | - | - | ≧540 |
Usage & Applications Angle Steel
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
Packaging & Delivery of Angle Steel
1. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
2. With bundles and load in 20 feet/40 feet container, or by bulk cargo, also we could do as customer's request.
3. Marks:
Color mark: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: There will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
Production flow of Angle Steel
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation



- Q: How do you determine the required angle size for a specific application?
- Several factors must be taken into consideration in order to determine the necessary angle size for a specific application. First and foremost, it is crucial to understand the purpose or function of the application. Different applications may require different angle sizes depending on the desired outcome. For instance, if the application involves cutting or shaping materials, the angle size must be determined based on the desired level of precision or detail. Secondly, the materials used in the application must be carefully considered. Some materials may be more brittle or prone to damage, while others may be more flexible. The chosen angle size should take into account the properties of the materials and minimize the risk of damage or failure. Thirdly, the specific conditions or environment in which the application will be used should be taken into account. Factors such as temperature, pressure, or moisture levels can impact the performance of the application and influence the required angle size. It is essential to select an angle size that can withstand the expected conditions and provide optimal functionality. Furthermore, consulting industry standards or guidelines that may exist for the specific application can be beneficial. These standards often provide recommended angle sizes based on best practices and past experiences. They serve as a useful reference point in determining the required angle size. Lastly, it may be necessary to conduct testing or simulations to verify the selected angle size. By creating prototypes or using computer-aided design (CAD) software, one can evaluate the performance and effectiveness of different angle sizes before making a final decision. In conclusion, determining the necessary angle size for a specific application involves considering the purpose, materials, environmental conditions, industry standards, and potentially conducting testing or simulations. By analyzing these factors, one can make an informed decision and select the most suitable angle size for the application.
- Q: What is the difference between mill finish and hot-dip galvanized steel angles?
- Mill finish and hot-dip galvanized steel angles are two different types of steel finishes that have distinct characteristics and applications. Mill finish refers to the surface finish of steel angles straight from the mill, without any additional coatings or treatments. It has a dull, matte appearance and may have slight imperfections such as small scratches or marks. Mill finish steel angles are typically used in structural applications where aesthetics are not a priority, such as in construction projects or industrial settings. They are also commonly used as structural support in buildings, bridges, and machinery. On the other hand, hot-dip galvanized steel angles undergo a process called hot-dip galvanizing. This involves immersing the steel angles in a bath of molten zinc, which creates a protective coating on the surface. The zinc coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, making hot-dip galvanized steel angles suitable for outdoor applications or environments where the angles may be exposed to moisture, chemicals, or harsh weather conditions. The galvanized coating also gives the steel angles a shiny, metallic appearance. In summary, the main difference between mill finish and hot-dip galvanized steel angles lies in their surface finishes and corrosion resistance properties. Mill finish steel angles have a dull appearance and are used primarily for structural purposes, while hot-dip galvanized steel angles have a shiny appearance and offer superior corrosion protection, making them ideal for outdoor applications.
- Q: Are steel angles available in different finishes?
- Indeed, there are a variety of finishes available for steel angles. To enhance their appearance or provide extra protection against corrosion, steel angles can undergo different coatings or treatments. Some popular finishes for steel angles include galvanized, painted, or powder-coated options. Galvanized steel angles are coated with a layer of zinc to prevent rusting, while painted or powder-coated finishes offer a wide range of color choices for aesthetic purposes. Moreover, steel angles can also be left unfinished, creating a raw and industrial look. The diverse range of finishes for steel angles provides greater flexibility in their applications, allowing them to be customized to meet specific functional and aesthetic requirements.
- Q: 100 x 100 x 10 equal angle steel, per meter weight?
- The angle iron can be made up of different force components according to the different structure, and can also be used as the connecting piece between the components. Widely used in a variety of architectural and engineering structures, such as beams, bridges, towers, hoisting and conveying machinery, ships, industrial furnace, reaction tower, container frame and warehouse shelves steel base.
- Q: What are the weight per meter calculations for steel angles?
- The weight per meter calculations for steel angles depend on the dimensions of the angle and the density of the steel being used. To calculate the weight per meter of a steel angle, you need to know the dimensions of the angle, specifically the thickness, width, and length. The formula to calculate the weight per meter is: Weight per meter = (Thickness x Width x Length) x Density The density of steel varies depending on the type of steel being used. The most common type of steel used for angles is mild steel, which has a density of approximately 7.85 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or 7850 kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). For example, let's say we have a steel angle with a thickness of 10 millimeters (mm), a width of 100 mm, and a length of 1 meter (1000 mm). Using the formula and assuming a density of 7850 kg/m³, the weight per meter would be: Weight per meter = (10 mm x 100 mm x 1000 mm) x 7850 kg/m³ Weight per meter = 10,000,000 mm³ x 7850 kg/m³ Weight per meter = 78,500,000,000 mm³/kg To convert the weight to a more common unit, we can divide by 1,000,000 to get the weight per meter in kilograms: Weight per meter = 78,500,000,000 mm³/kg / 1,000,000 Weight per meter = 78,500 kg/m Therefore, the weight per meter of this steel angle would be 78,500 kilograms.
- Q: What is the thickness of the national standard 8# angle steel? Thank you
- Test method: to test the chemical composition, test methods commonly used standards GB223, JISG1211-1215, BS1837, BS, C, f 19 manual is 22536.
- Q: How do steel angles resist bending or deflection?
- Steel angles resist bending or deflection due to their shape and material properties. The L-shape of steel angles provides structural rigidity, preventing excessive bending or deflection under load. Additionally, the high tensile strength and stiffness of steel as a material enable angles to withstand external forces and distribute them evenly, ensuring minimal bending or deflection.
- Q: What is the typical size range for steel angles?
- The typical size range for steel angles can vary depending on the specific application and industry. However, in general, steel angles are available in a range of sizes that typically fall within the dimensions of 20-200 millimeters (mm) in width and 3-20 mm in thickness. The length of steel angles can vary as well, typically ranging from 3 to 12 meters. These dimensions allow for a versatile range of applications, including structural support in construction, manufacturing of machinery and equipment, and various architectural uses. It's important to note that these size ranges are common, but there may be variations and custom sizes available depending on the specific requirements of a project.
- Q: How do steel angles perform in chemical industry applications?
- Steel angles are widely used in chemical industry applications due to their excellent performance in corrosive environments. These angles, made of high-strength steel, exhibit exceptional resistance to chemicals, acids, and other corrosive substances commonly found in the chemical industry. The chemical industry often involves the handling and processing of various chemicals, which can lead to corrosion and degradation of structural materials. Steel angles, with their high corrosion resistance, provide a reliable and durable solution in such environments. Moreover, steel angles offer excellent load-bearing capacity and structural stability, making them ideal for supporting heavy equipment, tanks, and platforms in chemical plants. Their versatility allows for the construction of various structures and equipment, ensuring the safe and efficient operation of chemical processes. Steel angles can be fabricated into different sizes and shapes, allowing for easy customization to meet specific requirements. This versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications such as piping systems, storage tanks, chemical reactors, and support structures. In addition to their corrosion resistance and structural strength, steel angles are also cost-effective. They have a long lifespan, require minimal maintenance, and can withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and chemical exposures. This durability and low maintenance requirement contribute to reducing downtime and overall operating costs in the chemical industry. Overall, steel angles perform exceptionally well in chemical industry applications by providing a combination of corrosion resistance, structural strength, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Their ability to withstand harsh chemical environments makes them an essential component in the safe and efficient operation of chemical processes.
- Q: What are the different types of steel angles used in storage racks?
- There are primarily two types of steel angles used in storage racks: perforated angles and slotted angles. Perforated angles have evenly spaced holes along the length, allowing for flexibility in adjusting shelf heights. Slotted angles, on the other hand, have elongated slots that provide the option for adjustable shelving as well as easier assembly and disassembly of the storage racks.
Send your message to us
A110*110*9 Equal steel Angle for construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords





























