A90*90*8 Equal steel Angle for construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
Specifications of Equal Steel Angle
1. Standards: GB,ASTM,BS,AISI,DIN,JIS
2. Length:6m,9m,12m
3. Material:Material: GB Q235B, Q345B or Equivalent; ASTM A36; EN 10025, S235JR, S355JR; JIS G3192,
SS400; SS540.
4. Sizes:
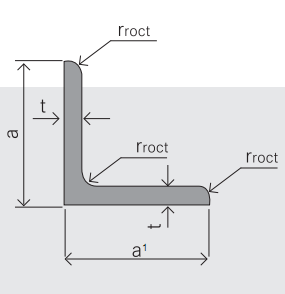
Sizes: 25mm-250mm | ||
a*t | ||
25*2.5-4.0 | 70*6.0-9.0 | 130*9.0-15 |
30*2.5-6.6 | 75*6.0-9.0 | 140*10-14 |
36*3.0-5.0 | 80*5.0-10 | 150*10-20 |
38*2.3-6.0 | 90*7.0-10 | 160*10-16 |
40*3.0-5.0 | 100*6.0-12 | 175*12-15 |
45*4.0-6.0 | 110*8.0-10 | 180*12-18 |
50*4.0-6.0 | 120*6.0-15 | 200*14-25 |
60*4.0-8.0 | 125*8.0-14 | 250*25 |
5. Material details:
Alloy No | Grade | Element (%) | |||||
C | Mn | S | P | Si | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 0.12—0.20 | 0.3—0.7 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.3 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Alloy No | Grade | Yielding strength point( Mpa) | |||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | ||||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
Q235 | B | 235 | 225 | 215 | 205 | ||
Alloy No | Grade | Tensile strength (Mpa) | Elongation after fracture (%) | ||||
Thickness (mm) | |||||||
| ≤16 | >16--40 | >40--60 | >60--100 | |||
≥ | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Q235 | B | 375--500 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | |
Usage & Applications of Equal Steel Angle
Trusses;
Transmission towers;
Telecommunication towers;
Bracing for general structures;
Stiffeners in structural use.
Packaging & Delivery of Equal Steel Angle



- Q: How do you straighten a bent steel angle?
- To straighten a bent steel angle, you will need a few tools and equipment. Here's a step-by-step process to help you straighten the bent steel angle effectively: 1. Safety first: Ensure you are wearing appropriate protective gear, including gloves and safety goggles, to protect yourself from any potential hazards. 2. Assess the damage: Examine the bent steel angle to determine the severity of the bend. This will help you decide the best approach to straightening it. 3. Secure the angle: Place the bent steel angle securely in a bench vise or clamp, ensuring that it is firmly held in place. This will prevent any movement during the straightening process. 4. Apply heat (optional): If the bend is severe or the steel angle is hardened, you may need to apply heat to make it more malleable. Use a blowtorch or heat gun to heat the bent area until it becomes red-hot. 5. Use a hammer: With the bent steel angle secured, use a hammer to gently tap the bent area in the opposite direction of the bend. Start from the outer edges and work your way towards the center. Apply gradual force and avoid striking the steel angle with excessive force, as it may cause further damage. 6. Check progress: Periodically release the angle from the vise or clamp to inspect the progress. If necessary, reposition the steel angle to a different area in the vise to continue straightening. 7. Repeat if needed: Depending on the severity of the bend, you may need to repeat steps 4-6 multiple times to achieve the desired straightness. Be patient and take your time to ensure you do not overcorrect or cause any additional damage. 8. Test the angle: Once you believe the steel angle is straightened, carefully remove it from the vise or clamp and test its straightness. Place it on a flat surface and check if it lies completely flat without any visible bends or wobbling. Remember, this process requires precision and caution. If you're unsure or uncomfortable handling this task, it's best to consult a professional or experienced metalworker who can assist you in straightening the bent steel angle safely and effectively.
- Q: What are the standard dimensions for equal leg steel angles?
- The standard dimensions for equal leg steel angles vary depending on the industry and country. However, in general, the standard dimensions for equal leg steel angles are typically measured in terms of the length of each leg and the thickness of the angle. Common dimensions include leg lengths ranging from 20mm to 200mm, with thicknesses ranging from 3mm to 20mm. These dimensions are often specified in millimeters and can be further customized to meet specific project requirements. It is important to consult industry standards and specifications to determine the exact dimensions for equal leg steel angles in a particular context.
- Q: What are the different types of connections used for steel angles in industrial applications?
- In industrial applications, steel angles are commonly used for various structural purposes, and therefore, different types of connections are employed to ensure their stability and strength. Some of the different types of connections used for steel angles in industrial applications include: 1. Welded Connections: Welding is a widely used method to connect steel angles in industrial applications. It involves melting the edges of two steel angles together and allowing them to solidify, creating a permanent and strong connection. Welded connections provide excellent strength and durability, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications. 2. Bolted Connections: Bolted connections involve using bolts and nuts to secure steel angles together. Holes are typically drilled into the angles, and bolts are inserted through these holes and tightened using nuts. Bolted connections offer the advantage of being easily dismantled and modified, making them suitable for applications where frequent adjustments or repairs are necessary. 3. Riveted Connections: Riveting is a traditional method of connecting steel angles, although it is less commonly used in modern industrial applications. Riveted connections involve inserting a rivet through holes in the steel angles and then deforming the rivet to secure the angles together. Although riveted connections provide good strength, they are time-consuming and require specialized equipment. 4. Clip Connections: Clip connections involve using metal clips or brackets to connect steel angles. These clips are typically bolted or welded to the steel angles, providing a secure connection. Clip connections are often used in applications where quick and easy assembly and disassembly are required, such as temporary structures. 5. Gusset Plate Connections: Gusset plates are thin steel plates that are used to connect steel angles in industrial applications. These plates are typically bolted or welded to the steel angles, providing additional strength and stability. Gusset plate connections are commonly used in applications where higher loads or forces are expected. It is worth noting that the type of connection used for steel angles in industrial applications depends on various factors, including the load requirements, structural design, ease of assembly and disassembly, and the expected lifespan of the structure.
- Q: How do you protect steel angles from weathering?
- One way to protect steel angles from weathering is by applying a protective coating, such as paint or galvanization. These coatings create a barrier between the steel and the elements, preventing moisture and oxygen from reaching the surface and causing corrosion. Regular inspections and maintenance are also important to identify and address any signs of deterioration or damage early on.
- Q: How do you determine the plastic section modulus of a steel angle?
- The plastic section modulus of a steel angle can be determined by calculating the moment of inertia of the angle about its centroid and dividing it by the distance from the centroid to the farthest fiber. This value represents the resistance of the angle to plastic bending and is crucial in analyzing its structural behavior.
- Q: Can steel angles be used in agricultural buildings?
- Agricultural buildings can indeed make use of steel angles. Steel angles, also referred to as angle iron, are widely employed in construction as they possess both strength and versatility. Within agricultural buildings, steel angles serve diverse purposes such as framing, bracing, and supporting the structure. They can be utilized to fashion robust frames for walls, roof trusses, and other structural components. Moreover, steel angles exhibit exceptional load-bearing capacity, rendering them appropriate for supporting heavy equipment or machinery commonly found in agricultural buildings. Additionally, steel angles display resistance to corrosion, which is crucial in agricultural environments where exposure to moisture and various chemicals is prevalent. In conclusion, steel angles prove to be a pragmatic and dependable choice for agricultural buildings owing to their strength, durability, and ability to withstand environmental factors.
- Q: Can steel angles be used to create decorative elements in architecture?
- Yes, steel angles can definitely be used to create decorative elements in architecture. These versatile structural components can be bent or shaped into various angles and forms, allowing architects and designers to incorporate them into the overall aesthetic of a building. From ornamental railings and window frames to decorative beams and columns, steel angles offer both strength and design possibilities, making them an ideal choice for decorative elements in architecture.
- Q: What are the common shapes and dimensions of steel angles?
- There is a wide range of options for steel angles in terms of shape and dimensions to accommodate various uses. The most common shapes are L-shaped or right angles, with legs that can be equal or unequal. These angles are typically created by bending a piece of steel into the desired shape. In terms of size, steel angles can vary depending on their intended purpose. The length of the legs, which are the two sides of the angle, can range from a few inches to several feet. The thickness or gauge of the steel used to make angles can also vary, with thinner gauges being lighter and thicker gauges providing more strength. The most commonly used dimensions for steel angles are as follows: - Equal Leg Angles: These angles have legs of equal length, forming a 90-degree angle. Common sizes for equal leg angles range from 1/2 inch to 6 inches in leg length, with thicknesses ranging from 1/8 inch to 1/2 inch. - Unequal Leg Angles: These angles have legs of different lengths, forming a 90-degree angle. The longer leg is usually referred to as the "vertical leg" and the shorter leg as the "horizontal leg." Common sizes for unequal leg angles range from 1 inch to 6 inches in vertical leg length, with thicknesses ranging from 1/8 inch to 1/2 inch. It's important to note that these dimensions serve as general guidelines, and custom-made steel angles can be produced to meet specific requirements. Additionally, steel angles can be hot-rolled or cold-formed, which affects their structural properties and manufacturing processes. Therefore, it's crucial to consult the specific standards and regulations applicable to your project or industry when selecting steel angles.
- Q: Can steel angles be used for support beams in warehouse construction?
- Steel angles have the capability to function as support beams in warehouse construction. They are widely employed as structural elements in diverse construction endeavors, including the construction of warehouses. They possess remarkable strength and endurance, rendering them suitable for carrying substantial loads and ensuring structural stability. Steel angles can be effortlessly fabricated and tailored to fulfill particular design necessities, making them an adaptable preference for constructing support beams in warehouse construction. Moreover, steel angles exhibit resistance to corrosion, a fundamental trait in warehouse settings where exposure to moisture and chemicals is prevalent. All things considered, steel angles present themselves as a dependable and cost-efficient alternative for support beams in warehouse construction.
- Q: What are the different types of steel angles used in HVAC systems?
- There are several types of steel angles commonly used in HVAC systems, including L-shaped angles, V-shaped angles, and Z-shaped angles. These angles are used to provide structural support, reinforcement, and stability in ductwork and other HVAC components.
Send your message to us
A90*90*8 Equal steel Angle for construction
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches





























