Supply H Beam Profile with Jis Material Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
1. Standard: GB700-88, Q235B2.
2. Grade: Q235, SS400 or Equivalent
3. Length: 6m,10m, 12m as following table
4. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
5.Payment: TT or L/C
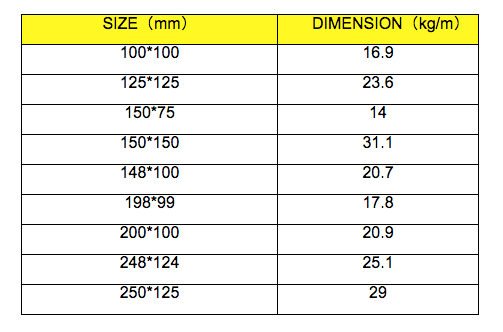
6. Sizes:
Usage & Applications of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
Commercial building structure ;Pre-engineered buildings; Machinery support structure; Prefabricated structure; Medium scale bridges; Ship-building structure. etc.
Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel
FAQ:
Q1: Why buy Materials & Equipment from OKorder.com?
A1: All products offered byOKorder.com are carefully selected from China's most reliable manufacturing enterprises. Through its ISO certifications, OKorder.com adheres to the highest standards and a commitment to supply chain safety and customer satisfaction.
Q2: Can fit in the containers of 20fts the steel beams of 6M?
A2: No proble, we can put them into the containers in the form sideling.
Q3: The products are invoicing on theoritical weight or on actual weight?
A3: We can do it in both manners, according to the customers' request.


- Q: How do steel H-beams perform in terms of buckling resistance?
- Steel H-beams are renowned for their exceptional ability to resist buckling. This is due to the H-shape, which gives the beam a higher moment of inertia, thereby reducing the likelihood of buckling when subjected to compressive loads. The flanges of the H-beam play a vital role in distributing the load evenly, minimizing the risk of localized buckling. Moreover, the vertical web of the H-beam adds extra rigidity, further increasing its resistance to buckling. Considering these factors, steel H-beams are widely regarded as one of the most durable and dependable structural components, making them exceptionally suitable for applications where buckling resistance is of utmost importance.
- Q: How do steel H-beams perform in structures with complex geometries?
- Steel H-beams perform well in structures with complex geometries due to their versatility and strength. The H-shape provides structural stability and load-bearing capacity, allowing for efficient distribution of forces in various directions. This makes them suitable for supporting complex structures, such as bridges, skyscrapers, and industrial buildings, where intricate designs and non-linear loads are involved.
- Q: Can Steel H-Beams be used in historical or heritage restoration projects?
- Yes, Steel H-Beams can be used in historical or heritage restoration projects. Steel H-Beams are versatile and strong structural elements that can provide support and stability to buildings, especially when restoring or reinforcing historic structures. They can be used to replace or reinforce deteriorated or damaged wooden beams, offering increased structural integrity while preserving the historical character of the building. Additionally, Steel H-Beams can be designed to match the original architectural aesthetics, ensuring a seamless integration into the existing structure. However, it is important to consult with preservation specialists and adhere to local heritage regulations to ensure that the use of Steel H-Beams aligns with the principles of historical preservation.
- Q: What are the requirements for steel H-beams in areas with heavy snowfall?
- In areas with heavy snowfall, the requirements for steel H-beams primarily focus on their structural integrity and load-bearing capacity to withstand the weight of accumulated snow. These requirements include: 1. Snow Load: The first consideration is the anticipated snow load in the specific area. The snow load is typically determined by local building codes or engineering standards and is expressed in pounds per square foot. The H-beams must be designed to support this snow load without excessive deflection or failure. 2. Material Strength: Steel H-beams used in heavy snowfall areas should have a high yield strength to withstand the increased load. The material used should have a minimum specified yield strength, such as ASTM A992 or equivalent, which ensures the beam's ability to resist bending and deformation under heavy snow loads. 3. Design Factors: The design of H-beams should consider additional factors such as safety margins, environmental conditions, and potential snow accumulation patterns. Structural engineers typically apply various design factors to account for uncertainties and ensure a reliable and durable structure. 4. Span Length and Section Dimensions: The span length of the H-beams, i.e., the distance between supports, should be determined considering the anticipated snow load. Longer spans may require larger section dimensions or additional support structures to prevent excessive deflection or failure. 5. Connections and Joints: The connections between H-beams and other structural elements should be appropriately designed and reinforced to withstand the snow load. Welding, bolting, or other connection methods must be chosen based on the specific requirements and engineering standards. 6. Maintenance and Inspection: Regular maintenance and inspection of steel H-beams are crucial in heavy snowfall areas. This includes removing any accumulated snow or ice, identifying any signs of corrosion or damage, and ensuring proper drainage to prevent ice dams or additional snow accumulation. It is important to consult with a qualified structural engineer or follow local building codes and regulations to determine the specific requirements for steel H-beams in areas with heavy snowfall. Additionally, local climate and snowfall patterns may vary, so a customized approach may be necessary to ensure the safety and reliability of the structure.
- Q: How do steel H-beams compare to I-beams in terms of strength?
- Steel H-beams are generally stronger than I-beams due to their wider flange and greater cross-sectional area, which allows them to withstand higher loads and provide better structural support.
- Q: What are the common surface treatments available for steel H-beams?
- There are several common surface treatments available for steel H-beams, which are used to enhance their durability, appearance, and resistance to corrosion. These treatments include: 1. Hot-dip galvanizing: This process involves immersing the steel H-beams in a bath of molten zinc, forming a protective coating on the surface. Galvanizing provides excellent corrosion resistance and is commonly used in outdoor or high-moisture environments. 2. Powder coating: Powder coating involves applying a dry powder to the surface of the steel H-beams, which is then heated and fused onto the metal. This process creates a durable and attractive finish that is resistant to chipping, scratching, and fading. 3. Epoxy coating: Epoxy coatings provide a protective layer over the steel H-beams, offering resistance to corrosion, chemicals, and abrasion. This treatment is often used in industrial settings where the beams may come into contact with harsh substances. 4. Painting: Painting is a common surface treatment for steel H-beams, providing both aesthetic appeal and protection against corrosion. The beams are typically primed and then coated with a high-quality paint that is resistant to weathering and UV rays. 5. Shot blasting: Shot blasting involves propelling small metallic or abrasive particles at high speeds onto the surface of the steel H-beams. This process removes rust, mill scale, and other impurities, leaving a clean and roughened surface that is ready for further treatment. These surface treatments can be chosen based on the specific requirements of the steel H-beams, such as the intended application, environmental conditions, and aesthetic preferences. It is essential to consider factors like cost, durability, maintenance, and the expected lifespan of the beams when selecting the most suitable surface treatment.
- Q: Are steel H-beams resistant to termites or pests?
- Yes, steel H-beams are resistant to termites and pests.
- Q: What are the differences between hot-rolled and cold-formed steel H-beams?
- Hot-rolled and cold-formed H-beams are two structural steel products commonly used in construction. Their manufacturing processes and properties differ significantly. To begin with, hot-rolled H-beams are made by heating a steel billet or slab above its recrystallization temperature, followed by shaping it using rollers. This results in a rough surface texture and a scaled outer layer. In contrast, cold-formed H-beams are created by bending and shaping steel sheets or strips at room temperature, often using rollers or press brakes. This method produces a smoother surface finish and eliminates the need for scaling. Regarding their properties, hot-rolled H-beams generally have higher strength and load-bearing capacity compared to cold-formed H-beams. This is due to the structural changes that occur during the hot-rolling process, which refine the grain structure of the steel and enhance its overall toughness. On the other hand, cold-formed H-beams exhibit greater dimensional accuracy and consistency, thanks to the precise shaping and bending process. This makes them suitable for applications that require precise measurements and tight tolerances. Another notable difference lies in their cost and availability. Hot-rolled H-beams are generally more readily available and cost-effective compared to cold-formed H-beams. The hot-rolling process is faster and more efficient, allowing for larger production volumes and lower production costs. In contrast, cold-formed H-beams may require additional processing and fabrication steps, which can increase their overall cost. In summary, hot-rolled and cold-formed H-beams differ in terms of their manufacturing processes, surface finish, properties, and cost. Hot-rolled H-beams offer higher strength and load-bearing capacity, while cold-formed H-beams provide greater dimensional accuracy and consistency. The choice between the two depends on specific project requirements, such as budget, structural needs, and aesthetic considerations.
- Q: Can Steel H-Beams be used in airport or transportation terminal construction?
- Yes, Steel H-Beams can be used in airport or transportation terminal construction. Steel H-Beams are often used in construction projects that require structural support, such as airports and transportation terminals. These beams provide excellent load-bearing capabilities and can withstand heavy loads, making them suitable for building large structures like airports and terminals. They are also known for their durability and long lifespan, which is crucial in infrastructure projects. Additionally, Steel H-Beams can be easily fabricated and installed, allowing for efficient construction processes. Overall, Steel H-Beams are a popular choice in airport and transportation terminal construction due to their strength, durability, and ease of installation.
- Q: Are steel H-beams susceptible to corrosion?
- Indeed, corrosion can affect steel H-beams. Steel, deriving mainly from iron, has a tendency to oxidize when exposed to moisture and oxygen. This oxidation results in the creation of iron oxide, commonly referred to as rust. Corrosion can manifest on both the surface and interior of the H-beams if moisture becomes trapped inside. Nevertheless, susceptibility to corrosion can be lessened through diverse preventive actions like the application of protective coatings, galvanization, or the employment of stainless steel H-beams. Consistent maintenance and inspections are also crucial in promptly detecting and addressing any indications of corrosion.
Send your message to us
Supply H Beam Profile with Jis Material Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























