Steel Coil Manufacturer Colour Coated Steel Coils
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details
| Standard: | AISI,ASTM,BS,DIN,GB,JIS | Grade: | SGCC | Thickness: | 0.12~1.2mm |
| Place of Origin: | Shandong China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | CNBM | Model Number: | CGCC |
| Type: | Steel Coil | Technique: | Cold Rolled | Surface Treatment: | Coated |
| Application: | Boiler Plate | Special Use: | Wear Resistant Steel | Width: | 600~1250mm |
| Length: | as your requirements | Color: | all RAL colors or customers samples color | Zinc coating: | 40-275g/m2 |
| Packaging: | Standard export seaworthy packing | Paint: | PE, PVDF, SMP, HDP | Coil weight: | 3-8mt |
| Coil ID: | 508mm,610mm | Payment: | 30% deposit, 70% by T/T against B/L copy; or by L/C | Back coating thickness: | 5-7um |
| Top coating thickness: | 20-25um | Product Name: | Prepainted galvanized steel |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Detail: | Standard export packing, 4 eye bands and 4 circumferential bands in steel, galvanized metal fluted rings on inner and outer edges, galvanized metal and waterproof paper wall protection disk, galvanized metal and waterproof paper around circumference and bore protection |
| Delivery Detail: | 25 Days after 30% deposit or L/C at sight |
Specifications
PPGI/Color Coated Steel Plates
Thickness: 0.12mm-1.2mm
Width: 600mm-1250mm
Length: customized
Grade:CGCC, DX51D
Product Description
PPGI Color Coated Steel Sheet in Coil
With the sophisticated equipment, you can get the best quality with most competitiveprice PPGI as below.
Detailed Product Description of prepainted steel coil
Our prepainted steel coil production line imported from America AB Corp and British CT Corp,it can be regarded as one of the most advanced unit in China. Our prepainted steel coil have outstanding formability,superb durability,good adhesion,wide availablity.Quick and reliable delivery for both small and large orders is our promise.
Our factory specialing in the export of the prepainted steel coil PPGI,Color coated steel coil,PPGI ,prepainted steel coil,color coated steel coil,stainless steel and other building materials.And our company trading here,exporting prepainted steel coil PPGI with good qulity and low price in China
Our factory prepainted steel coil production line in Tianjin in 2008,and many factories before 2010 have not yet been established,We have a proven technology,and we ensure quality
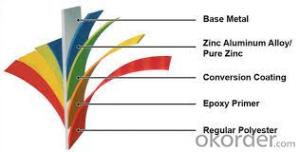
Painting
Category of Painting | Item | Code | |
Polyester | PE | ||
High-durability polyester | HDP | ||
Silicon modified polyesters | SMP | ||
Polyvinylidene fluoride | PVDF | ||
Easy-Cleaning | — | ||
Painting Thickness | Top side: 20+5microns; | ||
Bottom side: 5~7microns. | |||
Color System | Produce according to RAL Color System or as per buyer’s color sample. | ||
Painting structure | Top surface | Bottom surface | |
Primer coating | No coating | 1/0 | |
Primer coating | Primer coating | 1/1 | |
Primer coating + Finish coating | No coating | 2/0 | |
Primer coating + Finish coating | Primer coating or single back coating | 2/1 | |
Primer coating + Finish coating | Primer coating + Finish back coating | 2/2 | |
- Q: in a lab at school we did heat treatment of steelwhat are the possible phases present in the steel sample in as-received, as-quenched and as-tempered conditions? specifically when is it ferrite, austenite and pearliteis the steel originally in the ferrite phase? then when headed turns into austenite and when quenched martensite is formed and when tempered cermentite is formed...........where is pearlite involved and am i correct about the ferrite?
- hey from what i learned in uni last sem, steel is originally ferrite form at first at room conditions. it will undergo poly morphic transformation to become FCC structure austenite form at 912 degree celcius. under conditions, it can become pearlite (which is a combination of ferrite and cementite) or bainitie( a finer form of pearlite). queching conditions to room temperature will form martensite which is the strongest but brittle steel form. tempered cementite is formed when we quench it and then raise temperatures before sir cooling. hope it helps, pls vote me best answer is i deserve it. thanks
- Q: What is the average turnaround time for processing steel coils?
- The average turnaround time for processing steel coils can vary depending on various factors such as the complexity of the process, size of the coils, and the efficiency of the manufacturing facility. However, in general, the average turnaround time for processing steel coils ranges from a few days to a few weeks.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the production of agricultural trailers?
- Steel coils are used in the production of agricultural trailers to provide strength and durability. The coils are shaped into various components of the trailer's structure, such as the frame and chassis. This ensures that the trailer can withstand heavy loads and rough terrain, making it suitable for transporting agricultural equipment and produce.
- Q: I'm trying to buy a Survival,tactical knife but don't know what steel is better
- This Site Might Help You. RE: Whats better chrome vanadium steel or carbon stainless steel? I'm trying to buy a Survival,tactical knife but don't know what steel is better
- Q: Can steel coils be used in architectural applications?
- Architectural applications can indeed utilize steel coils. These coils possess versatility and can be transformed into various shapes and forms to match the distinctive design specifications of architectural ventures. They find utility in constructing structures such as buildings, bridges, and more, as well as in fabricating architectural elements like roofing, cladding, and facades. The utilization of steel coils in architectural applications presents several benefits. They exhibit exceptional durability, strength, and corrosion resistance, rendering them suitable for constructing enduring and low-maintenance structures. Steel coils can be customized in terms of thickness, width, and surface finish, granting architects the ability to achieve their desired aesthetic and functional objectives. Moreover, steel coils are renowned for their structural stability and load-bearing capacity, both of which are vital considerations in architectural designs. Their high strength-to-weight ratio makes them an ideal selection for creating spacious and open interior areas, as well as for supporting heavy loads in multi-story buildings. Additionally, steel coils are easily fabricated and installed, resulting in time and labor savings during the construction process. They can be efficiently molded, cut, and welded to create intricate shapes or architectural details. Additionally, steel coils can be pre-fabricated off-site, guaranteeing precision and quality control, and subsequently assembled on-site, reducing construction time and minimizing disruptions to the surrounding environment. All in all, steel coils present architects and designers with a wide array of possibilities in architectural applications. Whether it pertains to structural support, aesthetic appeal, or functional requirements, steel coils provide a dependable and versatile material option that can fulfill the demands of contemporary architectural projects.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the production of steel washers?
- Steel coils are used in the production of steel washers by being processed through a stamping or cutting machine. The coils are fed into the machine, which then cuts or punches out individual washer shapes. This process allows for efficient mass production of steel washers with consistent shape and size.
- Q: Hi there! I just purchased two cookie sheets labeled as non-stick 100% carbon steel. I've never heard of carbon steel before, and I'm trying to be careful about not using certain products that are harmful to health such as aluminum and Teflon. Is this a safe metal choice for baking?
- 100 carbon steel baking sheet safe
- Q: should I shoot Herters .308 steel cased ammo in my Remington 7400.and why shouldn't I?
- Won't hurt anything, but do be aware, if you're plinking with it, that FMJ (and maybe even steel core), cheap ammo offers more chance of penetration and ricochet so be sure you've got a good back-stop so you know where those rounds wind up.
- Q: Having a new kitchen and would like to know the pros and cons of stainless steel as opposed to white appliances. I can only think of finger marks on the SS, which I believe are difficult to remove. Anyone had both that they could advise please?
- A relative had a stainless steel range. It always looked a fingerprinted mess. I have never liked it. To me, it is grey with a sheen. I hate grey. I am a white appliance person all the way. White makes the room look cleaner, brighter and larger and it is easy to keep clean. Stainless is a nightmare to keep clean. Almost forgot to mention, when we bought our house a few years ago, it had a stainless steel range, horribly marked and scratched. I got rid of it, in keeping with white.
- Q: What are the guidelines for handling damaged steel coils?
- The guidelines for handling damaged steel coils typically involve inspecting the damage, assessing its severity, and determining if the coil is still safe to handle. If the damage is minor, it may be possible to repair or reinforce the coil. However, if the damage is extensive or compromises the structural integrity of the coil, it is recommended to contact a professional for further evaluation and potential disposal. Additionally, following proper safety protocols, such as wearing protective gear and using equipment suitable for handling heavy loads, is crucial when dealing with damaged steel coils.
Send your message to us
Steel Coil Manufacturer Colour Coated Steel Coils
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords