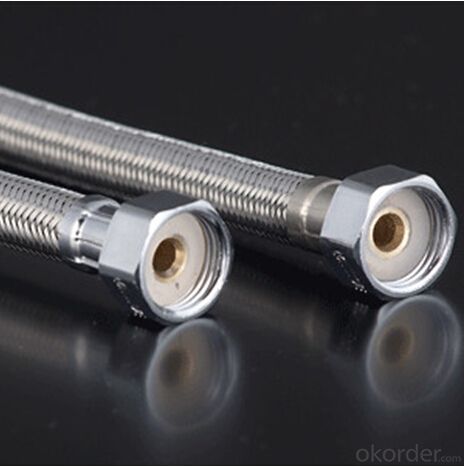
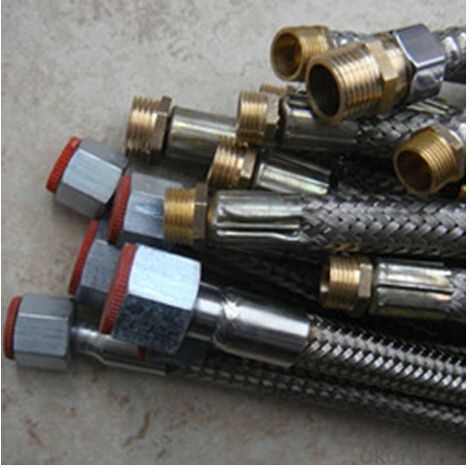
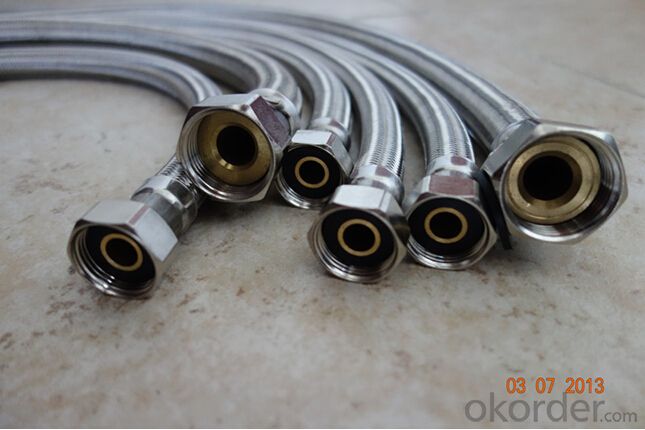
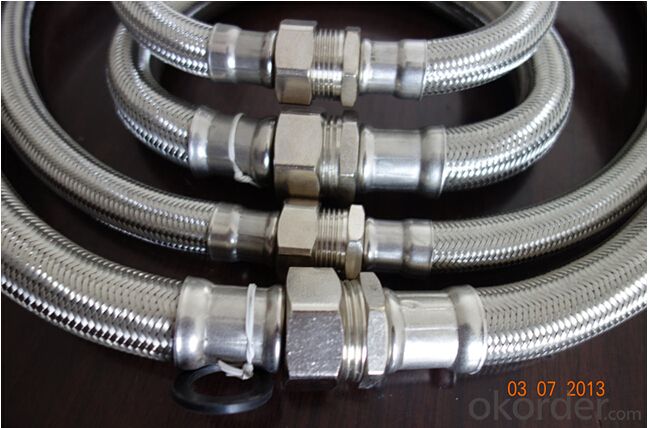
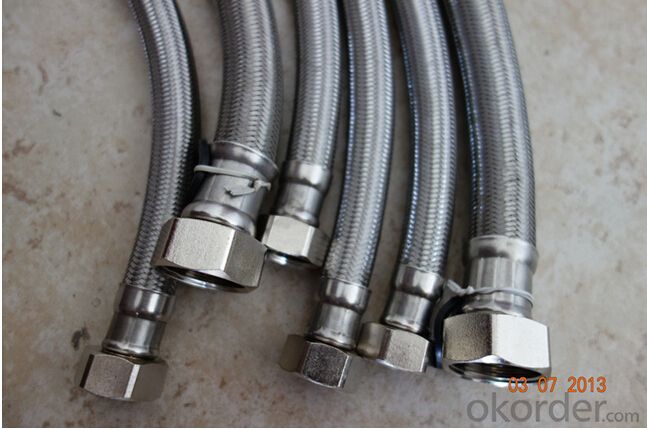
Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated
Applications of Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated:
--Refueling system
--Chemical and pharmaceutical industry
--Industrial hydraulic systems
--Air conditioners in industrial and construction –site vehicles
--Food and beverage industry
--Special and standard industrial applications
--Water and cleaning management
Features of Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated:
1. )O. D.: 13-18MM 0.2-3M long
2. )Nut.: Nickel/Chrome Plated Brass (Zinc / Iron / Aluminum is available)
3. )Size Of Nut.: Female&Male 1/2''; 3/4''; 3/8''; 7/8''; 5/16'', and M10...
4. )Insert.: Brass (Zinc / Aluminum / Plastic is available)
5. )Inner tube.: Rubber/ EPDM/PVC
6. )Covered Material: Stainless Steel 201, 301, 304 /Aluminium Wire
7. )Working Pressure: 5Kg-15Kg
8. )Temperature: 0-92° C
9. )Quality Assurance: 3 years
RemarkAPPLICATION: HOUSEEHOLD WARE, BATHROOM WARE, SHOWER HOSE
PAYMENT: T/T, L/C
DELIVERY TIME: 20DAYS OR 30DAYS AFTER RECEIVED 30% DEPOSITS
MOQ: 5000PCS
ODM&OEM IS ACCEPTABLE
PackageInner: PP bag /Blister packing Outer: Carton box
Specifications of Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated:
NO | I.D | Refer to O.D | Working pressure | Burst pressure | approximate Weight | |||||
(inch) | (mm) | (inch) | (mm) | MPa | Psi | MPa | Psi | kg/m | lbs/ft | |
1 | 1/8 | 3.2±0.2 | 0.35 | 9±0.3 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.078 | 0.12 |
2 | 5/32 | 4±0.2 | 0.4 | 10±0.3 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.092 | 0.14 |
3 | 3/16 | 4.8±0.2 | 0.43 | 11±0.3 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.108 | 0.16 |
4 | 1/4 | 6.3±0.3 | 0.5 | 12.7±0.3 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.134 | 0.2 |
5 | 5/16 | 8.0±0.3 | 0.56 | 14±0.3 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.147 | 0.22 |
6 | 3/8 | 9.5±0.3 | 0.63 | 16±0.4 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.182 | 0.27 |
7 | 15/32 | 12±0.3 | 0.75 | 19±0.5 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.238 | 0.35 |
8 | 1/2 | 12.7±0.4 | 0.78 | 20±0.5 | 2.06 | 300 | 8.27 | 1200 | 0.262 | 0.39 |
9 | 5/8 | 16±0.4 | 0.94 | 24±0.5 | 1.03 | 150 | 4.12 | 600 | 0.351 | 0.52 |
10 | 3/4 | 19±0.4 | 1.13 | 28.8±0.5 | 1.03 | 150 | 4.12 | 600 | 0.515 | 0.77 |
11 | 1 | 25.4±0.5 | 1.38 | 35±0.6 | 1.03 | 150 | 4.12 | 600 | 0.637 | 0.95 |
Images of Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated:
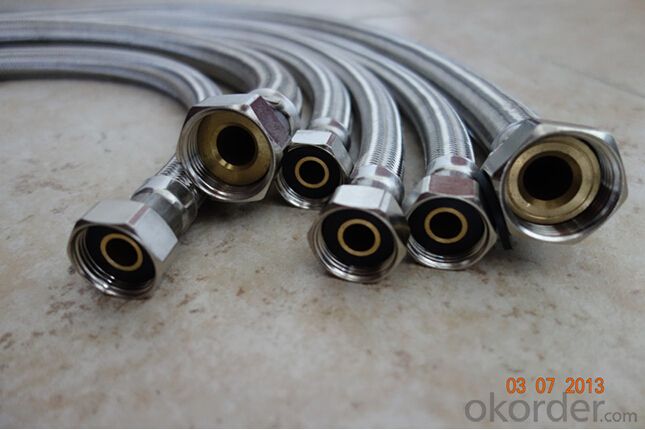
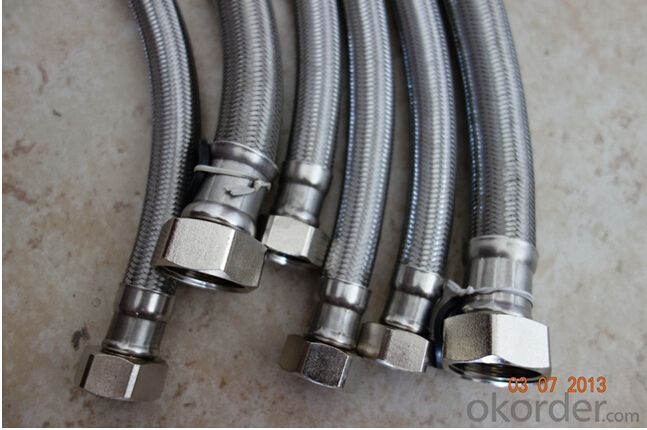
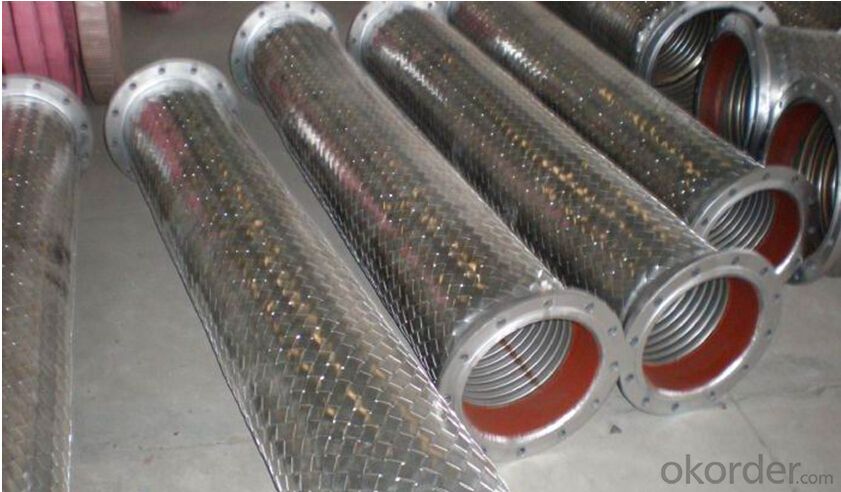
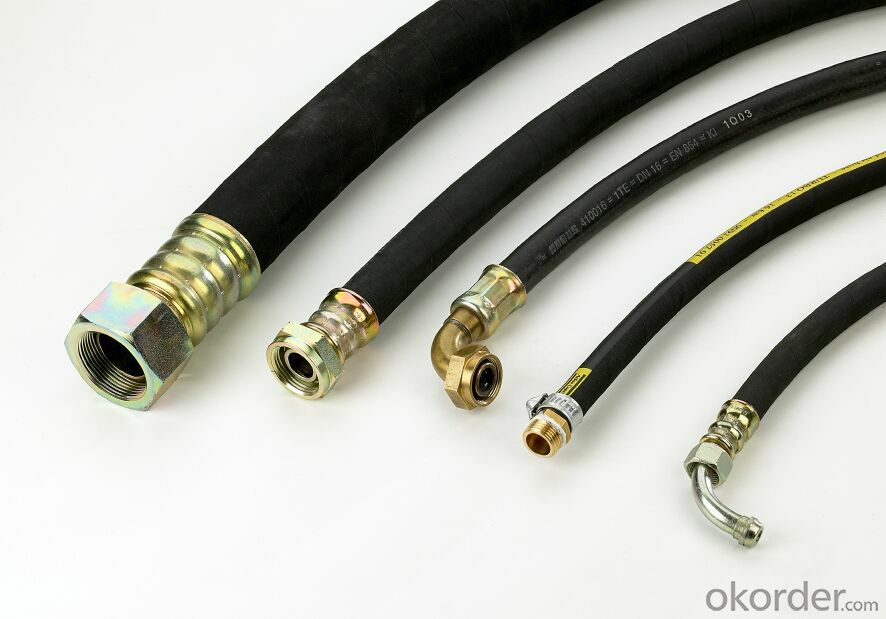




Package of Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated:
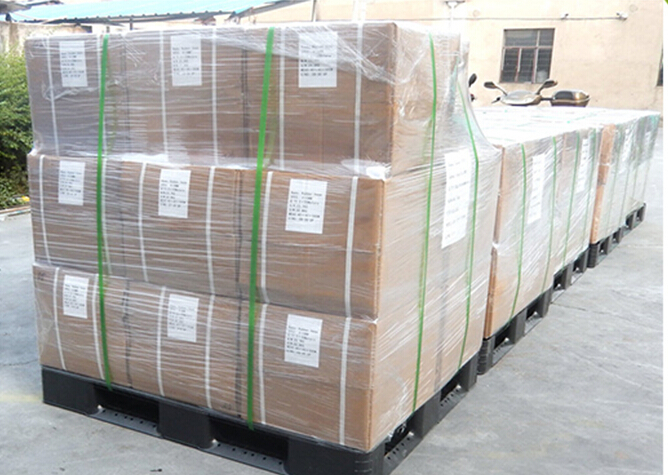


FAQ of Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated:
Who we are:
Answer: We CNBM is a Chinese state-owned enterprise ranked 267th among the Global Fortune 500, as the largest building materials company,we have over 300 affiliated companies,and so many production lines and branch office distribute in China.
2. About our quality:
Answer: Every product needs to be quality proved before shipping.
3. About our service:
Answer: We could gurantte that we can reply you in 2 working hours.
- Q: How do you prevent clogging in stainless steel pipes?
- There are several steps that can be taken to prevent clogging in stainless steel pipes: 1. Regular maintenance is crucial. It is important to regularly inspect and clean the pipes to remove any build-up or debris that could cause blockages. 2. Proper waste disposal is essential. Only dispose of appropriate materials in the pipes and avoid flushing items like paper towels, sanitary products, or grease down the drain. These can accumulate and lead to clogs. 3. Install drain filters or strainers. These can catch large particles or debris that may cause clogs. Clean or replace them as needed. 4. Avoid corrosive materials. Certain chemicals or substances can corrode stainless steel pipes, leading to damage and potential clogs. Follow manufacturer guidelines and avoid using corrosive materials near the pipes. 5. Ensure proper water flow. Run water regularly, especially in pipes that are not frequently used, to maintain adequate water flow and prevent clogs. 6. Consider using water softeners. If your water supply is hard and contains minerals that can build up, installing a water softener can reduce mineral deposits and prevent clogs. 7. Seek professional assistance if needed. If you experience persistent clogging or are unsure about prevention methods, consult with a professional plumber. They can assess the situation, provide guidance, and effectively address any existing clogs. By following these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of clogs in stainless steel pipes and maintain the efficient operation of your plumbing system.
- Q: What is the difference between hot rolled and cold drawn stainless steel pipes?
- The production of hot rolled stainless steel pipes involves heating a solid steel billet or ingot to a high temperature and then rolling it into the desired shape and size. This process yields a rougher surface finish and a larger grain structure, increasing the pipe's susceptibility to corrosion. Nevertheless, hot rolled pipes are generally more cost-effective and convenient for large-scale production. In contrast, cold drawn stainless steel pipes are crafted by pulling a solid steel billet or bar through a die at room temperature. This method results in a smoother surface finish and a smaller grain structure, enhancing the pipe's ability to resist corrosion. Cold drawn pipes are typically pricier and require more time and effort to manufacture, but they offer superior quality and performance for various applications. To summarize, the primary distinction between hot rolled and cold drawn stainless steel pipes lies in the manufacturing process and the resulting surface finish and grain structure. Hot rolled pipes are less expensive and easier to produce but may be more vulnerable to corrosion, whereas cold drawn pipes are more costly and time-consuming to manufacture but provide better corrosion resistance and overall quality.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for wastewater treatment ponds?
- Indeed, wastewater treatment ponds can employ stainless steel pipes. Renowned for their resistance to corrosion, durability, and capacity to endure severe conditions, stainless steel pipes prove well-suited for such usage. These attributes render them appropriate for wastewater treatment ponds, which frequently encounter chemicals, moisture, and other corrosive elements. Moreover, stainless steel pipes facilitate easy cleaning and maintenance, essential factors for preserving the efficiency and efficacy of the wastewater treatment procedure.
- Q: Do stainless steel pipes require any special coatings?
- No, stainless steel pipes do not require any special coatings as they are already highly resistant to corrosion and do not need additional protection.
- Q: Why can't stainless steel be put together with carbon steel tube?
- Potential difference: the stainless steel pipe with a more positive potential and the carbon steel pipe with negative potential are even connected. The stainless steel tube is cathode, and the carbon steel tube is anode. The greater the potential difference between the two, the greater the galvanic corrosion tendency.
- Q: How do you calculate the wall thickness for stainless steel pipes under external pressure?
- When calculating the wall thickness for stainless steel pipes under external pressure, various factors such as material properties, design codes, and applied external pressure must be taken into account. Here is a general method for calculating the wall thickness: 1. Identify the design pressure: Begin by determining the external pressure that the stainless steel pipe will experience. This pressure may be caused by factors like fluid flow, environmental conditions, or operational requirements. 2. Determine the properties of the material: Stainless steel pipes come in different grades, each with its own mechanical properties. Consult the material specifications to find the values for the yield strength (Sy) and ultimate tensile strength (Su) of the specific stainless steel grade being used. 3. Establish the allowable stress: The allowable stress (Sa) is the maximum stress that the material can handle under the given conditions. This information is usually provided by design codes or standards like ASME B31.3 for process piping or ASME Section VIII for pressure vessels. 4. Calculate the thickness for design pressure: Use the following formula to calculate the thickness required for design pressure (t): t = (P * D) / (2 * Sa) P represents the design pressure and D is the outside diameter of the stainless steel pipe. 5. Determine the corrosion allowance: Since stainless steel is prone to corrosion, it is important to consider a corrosion allowance to ensure the pipe's longevity. The design codes or industry standards typically specify the corrosion allowance. 6. Calculate the final wall thickness: Add the corrosion allowance to the thickness calculated for design pressure in step 4 to obtain the final wall thickness. It is important to note that this is a general method, and specific design codes or standards may have additional requirements or factors to consider. Therefore, it is recommended to consult the relevant design codes, standards, or a qualified engineer to ensure accurate and safe calculations for your specific application.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for irrigation sprinkler systems?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for irrigation sprinkler systems. Stainless steel is highly resistant to corrosion and rust, making it a durable choice for outdoor applications like irrigation systems. Additionally, stainless steel pipes have excellent strength and can withstand high-pressure conditions, making them suitable for sprinkler systems.
- Q: What is the difference between 17-4 and 316 stainless steel pipes?
- The main difference between 17-4 and 316 stainless steel pipes lies in their composition and properties. 17-4 stainless steel is a precipitation-hardening stainless steel that contains 17% chromium, 4% nickel, and 4% copper. It is known for its high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and good toughness. This type of stainless steel is commonly used in applications that require high strength and resistance to wear and corrosion, such as aerospace components, industrial equipment, and oil and gas applications. On the other hand, 316 stainless steel is an austenitic stainless steel that contains 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum. It is highly corrosion-resistant and has good heat resistance. 316 stainless steel pipes are widely used in industries that require resistance to chemicals, saltwater, and various corrosive environments, such as marine applications, chemical processing, and pharmaceutical equipment. In summary, while both 17-4 and 316 stainless steel pipes offer corrosion resistance, 17-4 is known for its high strength and toughness, making it suitable for demanding applications, whereas 316 stainless steel is preferred for its exceptional corrosion resistance, particularly in harsh environments.
- Q: How are stainless steel pipes measured?
- Stainless steel pipes are typically measured using two main dimensions: the outer diameter (OD) and the wall thickness (WT). The OD represents the overall size of the pipe, while the WT indicates the thickness of the pipe's walls. These measurements are crucial in determining the suitability of a stainless steel pipe for specific applications and ensuring compatibility with fittings and connections.
- Q: What is the maximum temperature that stainless steel pipes can handle?
- The maximum temperature that stainless steel pipes can handle depends on the specific grade of stainless steel being used. Generally, most stainless steel pipes can withstand temperatures up to 1500°F (815°C) without significant deformation or damage. However, there are specialized grades of stainless steel that can withstand even higher temperatures, reaching up to 2200°F (1204°C). It is important to consult the manufacturer or engineer for the specific stainless steel grade and intended application to determine the precise maximum temperature limit.
Send your message to us
Rubber Metal Hose with High Pressure Corrugated
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords