7KW Solar Inverter PV35-1K Low Frequency DC to AC Solar Power Inverter 12KW
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description
What is Solar inverter?
Solar pv inverters is an electronic system that operates the photovoltaic(PV) modules in a manner that allows the modules to produce all the power they are capable of. The solar mate charge controller is a microprocessor-based system designed to implement the MPPT. It can increase charge current up to 30% or more compared to traditional charge controllers.
Features
· Power range 1KW - 12KW
· Inbuilt pure copper transformer
· Powerful charge rate up to 100Amp
· MPPT solar charge controller 45A 60A (120A Option)
· PV input:145V max
· 12V/24V/36V/48V auto work
· MPPT efficiency>99% , Peak conversion efficiency>98%
· DSP processors architecture ensure high speed and performance
· Four-stages charging mode
· Protection: PV array short circuit, PV reverse polarity, Battery reverse polarity, Over charging, Output short circuit
· High efficency design & "Power Saving Mode" to coverse energy
Specification
MODEL | PV35-1K | PV35-2K | PV35-3K | PV35-4K | |||||||||||||||
Default Battery System Voltage | 12VDC | 24VDC | 12VDC | 24VDC | 12VDC | 24VDC | 12VDC | 24VDC | |||||||||||
INVERTER OUTPUT | Rated Power | 1KW | 2KW | 3000VA/2.4KW | 4000VA/3.2KW | ||||||||||||||
Surge Rating (20ms) | 3KW | 6KW | 9KW | 12KW | |||||||||||||||
Capable Of Starting Electric Motor | 1HP | 1HP | 1.5HP | 2HP | |||||||||||||||
Waveform | Pure sine wave/ same as input (bypass mode) | ||||||||||||||||||
Nominal Output Voltage RMS | 100V/110V/120VAC 220V/230V/240VAC(+/-10% RMS) | ||||||||||||||||||
Output Frequency | 50Hz/60Hz +/-0.3 Hz | ||||||||||||||||||
Inverter Efficiency(Peak) | >88% | ||||||||||||||||||
Line Mode Efficiency | >95% | ||||||||||||||||||
Power Factor | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
Typical Transfer Time | 10ms(max) | ||||||||||||||||||
AC INPUT | Voltage | 230VAC | |||||||||||||||||
Selectable Voltage Range | 96~132VAC/155~280VAC(For Personal Computers) | ||||||||||||||||||
Frequency Range | 50Hz/60Hz (Auto sensing) 40-80Hz | ||||||||||||||||||
BATTERY | Minimum Start Voltage | 10.0VDC /10.5VDC for12VDC mode (*2 for 24VDC, *4 for 48VDC) | |||||||||||||||||
Low Battery Alarm | 10.5VDC+/-0.3V for12VDC mode (*2 for 24VDC, *4 for 48VDC) | ||||||||||||||||||
Low Battery Cutoff | 10.0VDC+/-0.3V for12VDC mode (*2 for 24VDC, *4 for 48VDC) | ||||||||||||||||||
High Voltage Alarm | 16.0VDC+/-0.3V for12VDC mode (*2 for 24VDC, *4 for 48VDC) | ||||||||||||||||||
High Battery Voltage Recover | 15.5VDC+/-0.3V for12VDC mode (*2 for 24VDC, *4 for 48VDC) | ||||||||||||||||||
Idle Consumption-Search Mode | <25W when power saver on | ||||||||||||||||||
CHARGER | Output Voltage | Depends on battery type | |||||||||||||||||
Charger AC Input Breaker Rating | 10A | 30A | 30A | 30A | |||||||||||||||
Overcharge Protection S.D. | 15.7VDC for 12VDC mode (*2 for 24VDC, *4 for 48VDC) | ||||||||||||||||||
Maximum Charge Current | 45A | 25A | 70A 35A | 90A 50A | 65A 40A | ||||||||||||||
BTS | Continuous Output Power | Yes Variances in charging voltage & S.D. voltage base on the battery temperature | |||||||||||||||||
BYPASS & PROTECTION | Input Voltage Waveform | Sine wave (grid or generator) | |||||||||||||||||
Nominal Input Frequency | 50Hz or 60Hz | ||||||||||||||||||
Overload Protection (SMPS Load) | Circuit breaker | ||||||||||||||||||
Output Short Circuit Protection | Circuit breaker | ||||||||||||||||||
Bypass Breaker Rating | 10A | 15A | 20A | 40A | |||||||||||||||
Max Bypass Current | 30Amp | ||||||||||||||||||
SOLAR CHARGER | Maximum PV Charge Current | 45A | |||||||||||||||||
DC Voltage | 12V/24V atuo work | ||||||||||||||||||
Maximum PV Array Power | 600W | 1200W | 600W | 1200W | 600W | 1200W | 600W | 3200W | |||||||||||
MPPT Range @ Operating Voltage(VDC) | 16-100VDC for 12V mode,32-100V for 24V mode | ||||||||||||||||||
Maximum PV Array Open Circuit Voltage | 100VDC | 147VDC | |||||||||||||||||
Maximum Efficiency | >98% | ||||||||||||||||||
Standby Power Consumption | <2w< span=""> | ||||||||||||||||||
MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS | Mounting | Wall mount | |||||||||||||||||
Dimensions (W*H*D) | 493*311*215mm | ||||||||||||||||||
Net Weight (Solar CHG) kg | 23.5 | 24.5 | 25.5 | 29.5 | |||||||||||||||
Shipping Dimensions(W*H*D) | 580*400*325mm | ||||||||||||||||||
Shipping Weight (Solar CHG) kg | 25.5 | 26.5 | 27.5 | 31.5 | |||||||||||||||
OTHER | Operation Temperature Range | 0°C to 40°C | |||||||||||||||||
Storage Temperature | -15°C to 60°C | ||||||||||||||||||
Audible Noise | 60dB MAX | ||||||||||||||||||
Display | LED+LCD | ||||||||||||||||||
Loading(20GP/40GP/40HQ) | 150pcs/300pcs/350pcs | ||||||||||||||||||
Images
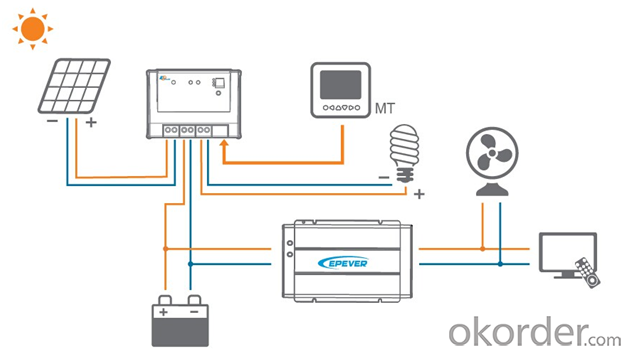
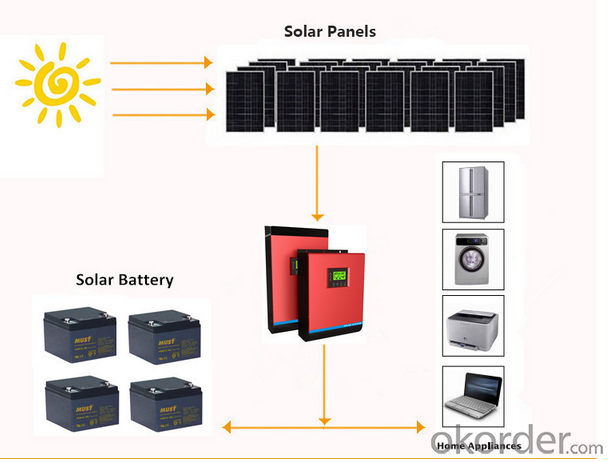
Packaging & Shipping
What is the packing?
1.Package: Carton Box for packaging, or Wooden Box advised for Samples to protect in transportations. Package designed by Clients is welcomed.
2.Shipping: DHL,FEDEX,UPS,EMS,AirWay and By Sea.
3.Payment: T/T( telegraphic transfer (T/T) and Western Union
4.Welcome to your Sample Order to test First.
FAQ
Q1: How to choose a right inverter?
A1:Tell us your demand, then our sales will recommend a suitable inverter to you.
Q2: What's the different between inverter and solar inverter?
A2: Inverter is only accept AC input, but solar inverter not only accept AC input but also can connect with solar panel to accept PV input, it more save power.
Q3: How about the delivery time?
A3: 7 days for sample; 25 days for bulk order.
- Q: What is the role of a galvanic isolation transformer in a solar inverter?
- The role of a galvanic isolation transformer in a solar inverter is to provide electrical isolation between the solar panels and the grid, ensuring the safety of the system. It prevents any direct electrical connection between the high voltage DC side and the low voltage AC side, while allowing the transfer of power between them. This isolation protects both the system components and the users from potential electrical hazards, such as short circuits or ground faults. Additionally, the galvanic isolation transformer helps reduce noise and interference in the system, enhancing the overall performance and reliability of the solar inverter.
- Q: The function of photovoltaic grid - connected inverter
- By dc / dc conversion to increase or decrease the input voltage, adjust its output to achieve maximum efficiency.
- Q: How does a solar inverter ensure safety during maintenance?
- A solar inverter ensures safety during maintenance by automatically disconnecting the system from the grid and de-energizing the circuits. This prevents any potential electrical shocks or accidents while the maintenance personnel work on the system.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in a ground-mounted solar system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in a ground-mounted solar system. A solar inverter is an essential component of a solar system that converts the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power homes or be connected to the grid. Whether the solar system is ground-mounted or rooftop-mounted, a solar inverter is required to ensure the efficient and safe operation of the system.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different types of solar tracking systems?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different types of solar tracking systems. Solar inverters are designed to convert the direct current (DC) output from solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity for use in homes or businesses. The type of solar tracking system used, such as single-axis or dual-axis tracking, does not affect the compatibility of the inverter. As long as the solar panels are generating DC electricity, the inverter can be used regardless of the tracking system in place.
- Q: What is the role of a solar inverter in reactive power compensation?
- To regulate and control the flow of reactive power in a solar power system, a solar inverter plays a crucial role in reactive power compensation. The presence of inductive or capacitive elements in the system causes reactive power to oscillate between the source and load. Although this power does not contribute to the actual work done by the system, it is necessary for the operation of specific devices. A solar inverter, specifically designed for reactive power compensation, is capable of measuring the reactive power in the system and adjusting its operation accordingly. It has the ability to generate or absorb reactive power as needed to maintain a power factor close to unity. The power factor is a measure of the efficiency of electrical energy utilization, and a high power factor indicates efficient electricity usage. By compensating for reactive power, a solar inverter ensures that the solar power system operates at optimal efficiency. It alleviates the burden on the grid by locally supplying or absorbing reactive power instead of relying on the grid for compensation. This not only improves the overall quality of power but also reduces system losses. Furthermore, it helps stabilize voltage levels and minimize voltage fluctuations, which can be advantageous for delicate electrical equipment. In conclusion, the role of a solar inverter in reactive power compensation is vital for regulating the flow of reactive power in a solar power system, maintaining a high power factor, and improving overall system efficiency. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring the optimal operation of the solar power system and diminishing the dependence on the grid for reactive power compensation.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used without solar panels?
- No, a solar inverter cannot be used without solar panels. The purpose of a solar inverter is to convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power electrical devices in a home or building. Without solar panels producing DC electricity, there would be no input for the inverter to convert.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different communication protocols?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different communication protocols. Many modern solar inverters are designed to be compatible with various communication protocols such as RS485, Modbus, Ethernet, or Wi-Fi. This allows for flexibility in integrating the inverter with different monitoring systems or smart home automation platforms.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in systems with multiple inverters?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in systems with multiple inverters. In fact, in large-scale solar installations, multiple inverters are often used to handle the increased power output. These inverters are connected in parallel or series to ensure efficient and reliable operation of the entire system.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used for both residential and commercial applications?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used for both residential and commercial applications. Solar inverters are designed to convert the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity that can be used to power homes or businesses. They can be scaled to accommodate the specific energy needs of residential or commercial properties, making them suitable for various applications.
Send your message to us
7KW Solar Inverter PV35-1K Low Frequency DC to AC Solar Power Inverter 12KW
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 watt
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 watt/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























