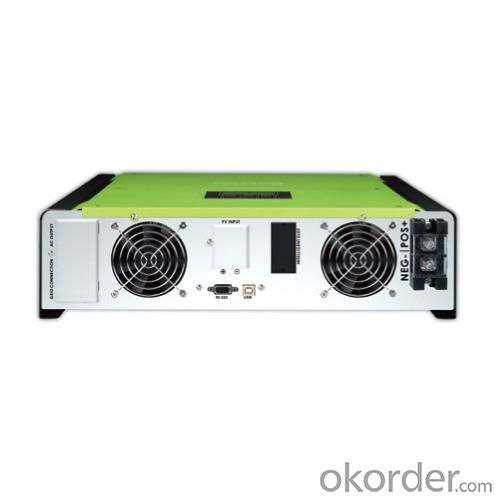
Solar Inverter Fan - On-grid Inverter with Energy Storage 2000W
- Loading Port:
- Shenzhen
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 Unit pc
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 Units/month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description of On-Grid Inverter With Energy Storage 2000W
1.Pure sine wave output
2.Microprocessor controlled to guarantee stable charging system
3.Multiple operations: Grid tie, Off grid, and grid tie with backup
4.Built-in MPPT solar charger
5.LCD display panel for comprehensive information
6.Multiple communication
7.Green substitution for generators
8.User adjustable charging current up to 25A
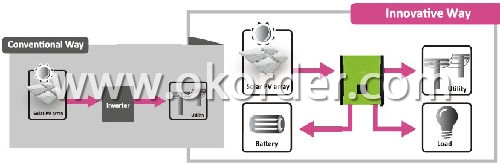
Feed-in is not only choice
In comparison with conventional grid-tie inverter, CNBM hybrid inverter is able to not only feed-in power to grid but also store solar power to battery for future usage and directly power to the loads.
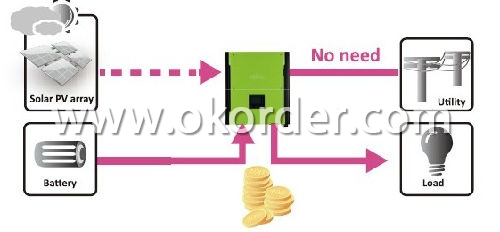
Save money by discharging battery for self-consumption first
CNBM hybrid inverter can save money by using battery energy first when PV energy is low. Until battery energy is low, CNBM will extract AC power from the grid.
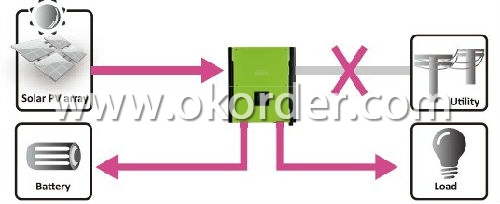
Power backup when AC failed
CNBM hybrid inverter can operate as an off-grid inverter to provide continuous power even without the grid.
It's perfect power solution for remote regions or temporary AC power source such as camping or flea market.
Datasheet of On-Grid Inverter With Energy Storage 2000W
MODEL | CNBM-H 2KW | CNBM-H 3KW |
RATED POWER | 2000W | 3000W |
GRID-TIE OPERATION | ||
PV INPUT (DC) | ||
Maximum DC power | 2250W | 3200W |
Nominal DC voltage / Maximum DC voltage | 300 VDC / 350VDC | 360 VDC / 500VDC |
Start voltage / Initial Feeding Voltage | 80 VDC / 120VDC | 116 VDC / 150 VDC |
MPP voltage range | 150 VDC ~ 320 VDC | 250 VDC ~ 450 VDC |
Number of MPP Trackers / Max. input current | 1 / 1×15A | 1 / 1×13A |
GRID OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Output Voltage Range | 88 - 127 VAC | 184 – 264.5 VAC |
Nominal Output Current | 18 A | 13.1 A |
Power Factor | > 0.99 | |
EFFICIENCY | ||
Maximum Conversion Efficiency (DC/AC) | 95% | 96% |
European Efficiency@ Vnominal | 94% | 95% |
OFF-GRID OPERATION | ||
AC INPUT | ||
AC Startup Voltage / Auto Restart Voltage | 60 - 70 VAC / 85VAC | 120 - 140 VAC / 180VAC |
Acceptable Input Voltage Range | 85 - 130 VAC | 170 - 280 VAC |
Maximum AC Input Current | 30A | 25A |
PV INPUT (DC) | ||
Maximum DC voltage | 350 VAC | 500 VAC |
MPP Voltage Range | 150 VAC ~ 320 VDC | 250 VAC ~ 450 VDC |
Maximum Input Current | 1 / 1×15A | 1 / 1×13A |
BATTERY MODE OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Output Frequency | 50 Hz / 60 Hz (auto sensing) | |
Output Waveform | Pure sine wave | |
Efficiency (DC to AC) | 90% | 93% |
HYBRID OPERATION | ||
PV INPUT (DC) | ||
Nominal DC voltage / Maximum DC voltage | 300 VDC / 350VDC | 360 VDC / 500VDC |
Start voltage / Initial Feeding Voltage | 80 VDC / 120VDC | 116 VDC / 150 VDC |
MPP voltage range | 150 VDC ~ 320 VDC | 250 VDC ~ 450 VDC |
Maximum Input Current | 1 / 1×15A | 1 / 1×13A |
GRID OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Output Voltage Range | 88 - 127 VAC | 184 – 264.5 VAC |
Nominal Output Current | 18 A | 13.1 A |
AC INPUT | ||
AC Startup Voltage / Auto Restart Voltage | 60 - 70 VAC / 85VAC | 120 - 140 VAC / 180VAC |
Acceptable Input Voltage Range | 85 - 130 VAC | 170 - 280 VAC |
Maximum AC Input Current | 30A | 25A |
BATTERY MODE OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Efficiency (DC to AC) | 90% | 93% |
BATTERY & CHARGER | ||
Nominal DC Voltage | 48 VDC | |
Maximum Charging Current | 25A | |
GENERAL | ||
PHYSICAL | ||
Dimension, D X W X H (mm) | 420 x 415 x 170 | |
Net Weight (kgs) | 15.5 | |
INTERFACE | ||
Communication Port | RS-232 / USB | |
Intelligent Slot | Optional SNMP, Modbus, and AS400 cards available | |
ENVIRONMENT | ||
Humidity | 0 ~ 90% RH (No condensing) | |
Operating Temperature | 0 to 40°C | |
Altitude | 0 ~ 1000 m | |
COMPLIANCE | ||
Standard | CE, VDE 0126-1-1,VDE-AR-N 4105 | |
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with solar-powered recreational vehicles (RVs)?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with solar-powered recreational vehicles (RVs). Solar inverters convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various appliances and devices in the RV. This allows RV owners to utilize solar energy for their electrical needs while on the road.
- Q: How do you choose the right size of solar inverter for a solar power system?
- To choose the right size of solar inverter for a solar power system, you need to consider the total capacity of your solar panels and the maximum power output they can generate. The solar inverter's capacity should be equal to or slightly higher than the maximum power output of your solar panels to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Additionally, you should also consider any future expansion plans for your solar power system to account for potential increases in capacity. It is recommended to consult with a professional solar installer or engineer to accurately determine the appropriate size of the solar inverter for your specific requirements.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in systems with multiple solar arrays?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in systems with multiple solar arrays. A solar inverter is designed to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into usable alternating current (AC) for powering electrical devices or feeding back into the grid. It can be connected to multiple solar arrays in parallel or series to increase the overall power output of the system. However, it is important to ensure that the inverter is properly sized and matched to the combined capacity of all the solar arrays to ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
- Q: What is the maximum current output of a solar inverter?
- The maximum current output of a solar inverter depends on various factors such as the size and capacity of the inverter, the number and capacity of the solar panels connected to it, and the specific technology and design of the inverter. Generally, solar inverters have a maximum current output ranging from a few amps to several hundred amps, with larger commercial-scale inverters having higher current outputs compared to residential or smaller scale inverters. It is crucial to select an inverter that can handle the current requirements of the solar panel system to ensure optimal performance and safety.
- Q: What is the role of a solar inverter in power factor correction?
- The role of a solar inverter in power factor correction is to adjust the power factor of the solar power system to ensure efficient energy conversion. It helps in balancing the reactive power and real power, leading to improved overall power quality and reduced system losses.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with different types of grid support functions?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with different types of grid support functions. Solar inverters are designed to convert the direct current (DC) power generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) power that can be used in homes or fed back into the grid. They can also have additional functionalities to support the grid, such as reactive power control, voltage regulation, frequency control, and anti-islanding protection. These grid support functions allow solar inverters to effectively integrate renewable energy into the existing power grid infrastructure.
- Q: How does a solar inverter handle voltage sag and swell?
- A solar inverter handles voltage sag and swell by continuously monitoring the voltage levels of the solar panels and grid connection. When a sag or swell is detected, the inverter adjusts its output voltage accordingly to maintain a stable and consistent supply of power to the connected devices. This helps to protect the electrical equipment from potential damage and ensures efficient operation of the solar power system.
- Q: What maintenance is required for a solar inverter?
- Regular maintenance for a solar inverter typically includes visual inspections, cleaning, and ensuring proper ventilation. It is also important to monitor and clean the solar panels to prevent any shading or debris that could affect the overall performance of the inverter. Additionally, checking and tightening all electrical connections, as well as updating the firmware and software, may be necessary to ensure optimal functionality.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with solar-powered telecommunications systems?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with solar-powered telecommunications systems. A solar inverter is an essential component in converting the direct current (DC) power generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) power, which is compatible with telecommunications equipment. This enables solar-powered telecommunications systems to operate efficiently and effectively.
- Q: What are the main components of a solar inverter system?
- Solar inverter systems consist of several key components, namely solar panels, the inverter itself, and various electrical elements. The primary component of a solar inverter system is the solar panel. These panels are composed of photovoltaic cells that transform sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. To maximize exposure to sunlight, they are typically installed on rooftops or in open areas. Another crucial component is the inverter, which plays a vital role in converting the DC electricity produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, the type commonly used in homes and businesses. Inverters also regulate the electricity flow, ensuring it aligns with the voltage and frequency of the utility grid. In addition to the solar panels and inverter, other electrical components are present in a solar inverter system. These include wiring, switches, fuses, and circuit breakers, which facilitate the connection of the solar panels, inverter, and other equipment to the electrical grid. Monitoring systems and data loggers are often included as well, providing valuable information on energy production and system performance. Lastly, a solar inverter system may incorporate a battery storage system. This allows surplus electricity generated by the solar panels to be stored for later use, such as during periods of low sunlight or power outages. Battery storage systems are gaining popularity as they offer greater energy independence and the ability to utilize solar energy even when sunlight is scarce. In summary, the main constituents of a solar inverter system encompass solar panels, the inverter, electrical elements, and potentially a battery storage system. Each component has a crucial role in harnessing solar energy and converting it into usable electricity for residential and commercial purposes.
Send your message to us
Solar Inverter Fan - On-grid Inverter with Energy Storage 2000W
- Loading Port:
- Shenzhen
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 Unit pc
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 Units/month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























