Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Roofing Steel
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Basic description Info.
Surface Treatment:Coated
Technique:Cold Rolled
Standard:JIS
Color:All Ral Color Are Available
Zinc Coating:30-120G/M2
Width:914-1250mm
Thickness:0.18-0.6mm
Export Markets:Global
Additional Info.
Trademark:VST
Packing:Standard Export Package
Origin:China
Production Capacity:10000t/Month
Main Feature:
1, Pre-painted Steel Coil Can be used in building material field, galvanized wire steel tape and mainly other fields.
2, All color can be customized
3, Good quality with competitive price
Secifications
Performance testing of color coated steel coil | ||
Item | Method | Consequence |
Tensile Test | Tic-Tac-9mm 5mm cross cupping | No damage |
Bending Test | T≤ 3 | No damage |
Boiling Test | 100° Cboiling 1 hour | No damage |
Water Resistance | 1000hours immersion in 40° C(edge) | No damage |
Moisture Resistance | 50° C90%100hours(edge) | No damage |
Fire Resistance | Samples were placed in incubators, remove greenhouse cooling, and then test the adhesion | Long-term Environment in 100° C |
Fire Extinction | Liquefied petroleum gas or natural gas burner | Immediately turn off |
Drug Resistance | 10%hydrochloric acid, saturated calcium, 10%H2SO4, 10%NAOH, gasoline, ethanol | No color and trace change |
Salt spray test | 5%Nacl, 35± 2° C, 500hours | No damage |
Coating performance test standard | ||
Test item | Positive standard | Back standard |
Dry film thickness(um) | 14-16 | 7-9 |
Glass(60degree) | High 70± 5, medium40± 5, low30± 5 | 30± 5degree |
T bending | 3 | 3 |
Impact strength | 6.3 | 5.8 |
Pencil hardness(H) | H | H |
MEK(Per) | > 100 | > 100 |
Cross cut | 0 class | 0 class |
Acid resistance | 50%H2SO4 immersion in300hrs, no color, wrinkling, fading, change | |
Alkali resistance | 50%H2SO4 immersion in300hrs, no color, wrinkling, fading, change | |
Aging-resistance | 1 st class loss of color and glass | |
Salt spray | 500 | |
Images
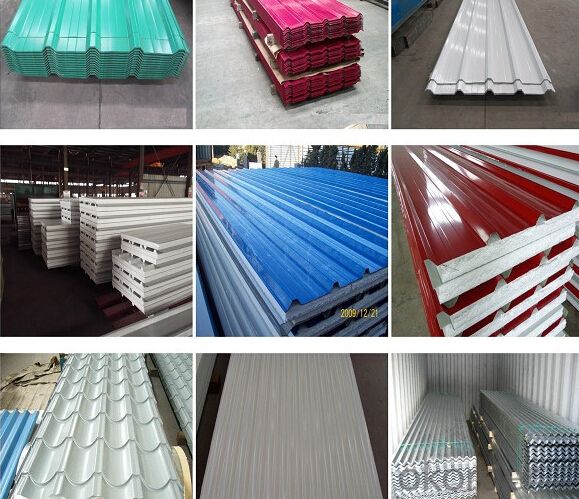
FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
25MT, it is for one container.
2.Do you have QC teams?
Yeah, sure, our QC team is very important, they will keep the quality control for our products.
3. What's your normal delivery time?
Our delivery time about 10-20days for standard sizes, if you have other requirements like hardness and width ,it is about 20-40days. But don't worry ,we also try our best for the delivery time ,because time longer and our cost is higher.
4.Are the products tested before shipping?
Yes, all of our PPGI and GI was qualified before shipping. We test every batch every day.
- Q: What are the different types of edge treatments for steel coils?
- There are several different types of edge treatments for steel coils, including slit edge, mill edge, and deburred edge. Slit edge is the standard edge treatment, where the coil is slit to the desired width and the edges are left with a rough, jagged finish. Mill edge is a smoother edge treatment that is achieved by cutting the coil using a circular saw, resulting in a cleaner edge. Deburred edge is a further refinement of the mill edge, where the sharp edges are removed through a deburring process, creating a smooth, rounded edge.
- Q: What are the different methods of transporting steel coils?
- There are several methods of transporting steel coils, including using flatbed trucks, railcars, and ocean vessels. Flatbed trucks are commonly used for short distances and local deliveries, while railcars are utilized for longer distances and intermodal transportation. For international shipments, steel coils are typically transported on ocean vessels, either in containers or as breakbulk cargo. The choice of method depends on factors such as distance, destination, and cost-effectiveness.
- Q: were iron age weapons made of steel?
- Even in very early iron, a small amount of steel was produced by carburization, where the iron picks up carbon by laying in hot coals before quenching. This produces a thin layer of steel on the surface of the iron. By about 300 BC Damascus steel was being produced by the crucible method on the Indian subcontinent, and the Romans used steel from Noricum. In the first century BC the Chinese were melting cast iron and wrought iron together to make steel.
- Q: Nickel is ferro magnetic in nature. But when it is added with stainless steel, it makes stainless steel non-magnetic. What is the structural changes happened with the presence of nickel?
- Steel is magnetic because of the alignment of the spin in the electrons of the atoms in the crystaline matrix of the steel. Nickel atoms are not the same size as Iron atoms and Chromium atoms. by having several different sizes of atoms in the alloy, it prevents a uniform crystaline matrix from being formed. If you imagine a box of marbles that are all the same size, they will all settle into a regular pattern in the box. But a bunch of mismatched marbles will be jumbled together in irregular patterns. This prevents the magnetic properties of either element from asserting itself.
- Q: Should I stick with the all steel kit over the acrylic tapers and steel plugs? or would the acrylic be ok? I keep hearing that steel is the best and acrylic can cause problems. I just want to do it correctly and take my time with it, no rushing.thanks
- It depends on your body and what you prefer. If you body is allergic to one of them you would have to chose for another one. If it's not allergic to any, than you can use whatever you like the most, just try both.
- Q: What is the maximum width of steel coils?
- The maximum width of steel coils is subject to variation, influenced by factors like steel type, manufacturing capabilities, and intended usage. Nevertheless, in most cases, steel coils tend to have a maximum width of approximately 2,200 millimeters or 86.6 inches. This width is widely employed in the steel industry for coils of standard sizes. It is worth mentioning that wider widths may be achievable through specialized steel coils or custom manufacturing methods, albeit less frequently and possibly necessitating particular equipment or processes.
- Q: How are steel coils inspected for quality assurance?
- Steel coils are inspected for quality assurance through a rigorous process that involves various tests and checks. Firstly, visual inspection is conducted to look for any surface defects such as scratches, dents, or rust. This ensures that the coils are in good condition and free from any obvious flaws. Next, dimensional inspection is performed to verify the dimensions and tolerances of the coils. This involves measuring the width, thickness, and length of the coils to ensure they meet the specified requirements. Any deviations from the standard dimensions are noted and addressed. Additionally, mechanical testing is carried out to assess the strength and durability of the steel coils. This includes conducting tensile tests to measure the strength and elasticity of the steel, as well as impact tests to evaluate its ability to withstand sudden loads or shocks. Furthermore, chemical analysis is conducted to determine the composition and purity of the steel. This involves taking samples from the coils and analyzing them in a laboratory to check for the presence of any impurities or elements that may affect the quality of the steel. To ensure the coils meet specific industry standards, non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection may be employed. These techniques allow for the detection of internal defects or irregularities that may not be visible to the naked eye. In addition to these tests, the coils may undergo surface treatment inspections, such as galvanization or coating checks, to ensure the protective layers are applied correctly and meet the required specifications. Overall, steel coil inspection for quality assurance involves a combination of visual, dimensional, mechanical, chemical, and non-destructive testing methods. These comprehensive inspections help to ensure that the steel coils meet the necessary quality standards and are suitable for their intended applications.
- Q: can steel boil and turn into a gaseous state?? if so how hot does it have to be for it to boil
- hahah umm ya u could boil steel but prob not at your house hahah and the boiling point of a medium carbon steel to be around 3000K
- Q: How much should someone sell a 6 ft stainless steel counter? How about one with a sink?
- Sheet stainless steel is about $2.00 to $2.75 per lb. in the US right now for a 2B stainless steel without any special finish. The cost of a sink or counter is going to vary widely. The labor to fabricate it is going to be a lot higher than the material cost so the price per pound is not going to tell you much. In California a custom 6' counter would be somewhere between $1,200 and $3,000. A standard size single compartment sink would be about half of that.
- Q: How do steel coils contribute to the manufacturing of oil and gas equipment?
- Steel coils are essential in the manufacturing of oil and gas equipment because they provide the necessary raw material for various components. Coils are used to fabricate pipes, valves, tanks, and other critical parts, ensuring their strength, durability, and resistance to high pressure and extreme temperatures. Additionally, steel coils can be easily shaped and formed into different sizes and specifications, enabling manufacturers to meet the specific requirements of oil and gas equipment.
Send your message to us
Prepainted Rolled Steel Coil for Roofing Steel
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 30 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























