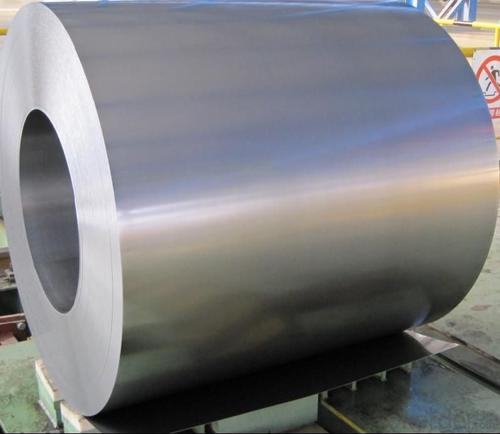
High Quality of Hot-Dip Gavalnized Steel Coil
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Hot-dip Zinc Coating Steel Building Roof Walls
1.Structure of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Description:
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications. Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
2.Main Features of the Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
• Excellent process capability
• Smooth and flat surface
• Workability, durability
• Excellent anticorrosive property
• High strength
• Good formability
• Good visual effect
3.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Images:
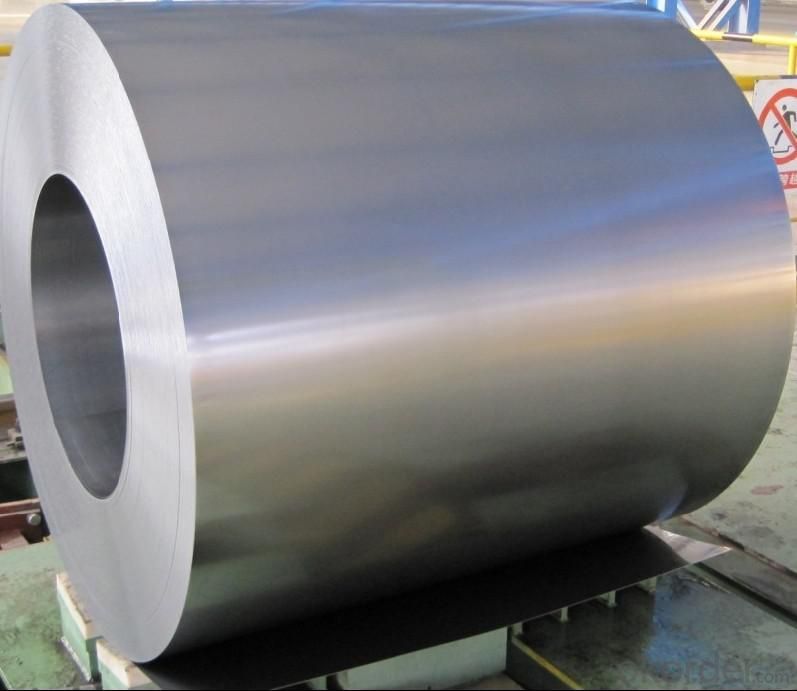


4.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Specification:
Standard: ASTM, JIS,EN
Grade: CS, DX51D+Z,SGCC, SS 230~550,S220GD+Z~S550GD+Z, SGC340~SGC570
Thickness: 0.1mm~5mm
Width: max 2000mm
Coil weight:3-12 MT
Coil ID:508/610mm
Surface structure: zero spangle, regular spangle or minimum spangle
Surface treatment: Chromate treatment, Oiled/dry, skinpassed/non-skinpassed
Packing: Standard seaworthy export package
Technology test results:
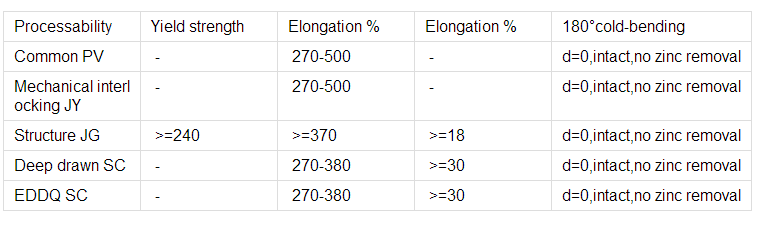
5.FAQ of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1.How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2.How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-30 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
- Q: I know that they have steel shot in smaller sized pellets....say, number 4 shot. I guess it's for waterfowl, etc.Do they make steel buckshot? If not, why not? Would the pellets be too heavy? Wouldn't they have excellent penetration ability?
- I know of no one who makes steel buckshot. Probably for several reasons. Steel is much lighter than lead. Penetration depends on energy, which is the weight of the pellet vs. the velocity of the pellet, equated into ft.lbs. Steel pellets have to travel much faster to achieve the same energy as a lead pellet. Steel, being lighter, would lose energy much faster downrange. The weight difference would be like teeing up a golf ball, and striking it with a club, and teeing up a ping pong ball and striking it with a club. The distance in flight would be obvious. Steel also, is much harder than lead, and would be hard on the barrel, and choke. It also would not deform, which would cause ricochets. Steel shot was a handicap for waterfowler's when the USFWS made non toxic shot mandatory. Waterfowl are bottom feeders, and they were eating the spent lead pellets, and dying from lead poisoning. Steel shot cut the effective range of a shotgun from 45 yards to around 35, and resulted in many cripples and lost birds. Environmetal, makes a T size shot which is .20 caliber, and is called Hevi-shot. Lead is heavier than steel, and Hevi-shot is heavier than lead. At the same velocity, you have 12 to 15% more energy than lead. and probably 20% better than steel....Hope this helps
- Q: Does anyone know the lyrics to steel driving man by Dailey and Vincent. I would really appreciate it
- watch man of steel full movie online free adf.ly/dfxYD
- Q: How are steel coils used in construction?
- Steel coils are commonly used in construction for a variety of applications, such as structural components, roof panels, and wall cladding. These coils are typically shaped and cut into specific lengths to meet the required dimensions of the construction project. They provide strength, durability, and versatility, making them an essential material for various construction purposes.
- Q: What is the average lifespan of a steel coil?
- Several factors can influence the average lifespan of a steel coil. These factors encompass the quality and type of steel utilized, the conditions in which the coil is stored or used, and the maintenance and care it receives. Typically, a steel coil that is well-maintained can endure for approximately 10 to 30 years. Nevertheless, this is merely an approximation, and the actual lifespan can be either shorter or longer depending on the aforementioned factors. For example, if the coil is exposed to severe environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or corrosive elements, its lifespan may be diminished. Regular upkeep and proper storage can significantly prolong the longevity of a steel coil. This entails ensuring that the coil is stored in a dry and safeguarded environment, frequently inspecting and addressing any indications of corrosion or damage, and conducting routine cleaning and lubrication as necessary. Ultimately, the average lifespan of a steel coil is contingent upon various factors, and it is advisable to consult the manufacturer or industry experts for a more precise estimation based on specific circumstances and conditions.
- Q: Is 440 steel relatively strong or weak?
- medium-strong....you probably mean Steel 44... right?
- Q: melting point, as compare to stainless steel
- Mild steel melting point is 1350-1530°C (2462-2786°F). Stainless steel is 1510°C (2750°F)
- Q: What are the safety precautions to be followed while handling steel coils?
- When handling steel coils, it is important to follow certain safety precautions to prevent accidents and injuries. Here are some safety precautions to be followed: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE, such as safety glasses, gloves, steel-toed boots, and hard hats. These items will protect you from potential hazards like falling objects, sharp edges, and chemicals. 2. Proper Lifting Techniques: Use proper lifting techniques to prevent strains and back injuries. Lift with your legs, not your back, and avoid twisting or jerking motions while handling the coils. If the coils are too heavy or awkward to lift manually, use mechanical lifting equipment like forklifts or cranes. 3. Secure Storage: Store steel coils in a secure and stable manner to prevent them from falling or rolling over. Use proper racks, shelves, or storage containers designed specifically for steel coils. Ensure that the storage area is clean, organized, and free from obstructions. 4. Handling Tools: Use appropriate handling tools like coil hooks, lifting clamps, or coil tongs to securely grip the steel coils. Avoid using makeshift or improper tools, as they can cause the coils to slip, resulting in accidents. 5. Secure Transportation: When transporting steel coils, ensure they are properly secured on the truck or flatbed. Use appropriate tie-downs, straps, or chains to prevent the coils from shifting or falling during transit. Follow all transportation regulations and guidelines to ensure safe transportation. 6. Awareness of Surroundings: Be aware of your surroundings and the presence of other workers or equipment in the area. Maintain a safe distance from moving machinery, forklifts, or other vehicles to avoid collisions or accidents. 7. Hazard Communication: Ensure that all employees handling steel coils are trained on proper safety procedures and understand the potential hazards involved. Display safety signs or labels to indicate the presence of heavy loads or hazardous materials. 8. Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain equipment, such as lifting devices or storage racks, to ensure they are in good working condition. Report any defects or malfunctions to the appropriate personnel for prompt repairs. By following these safety precautions, you can minimize the risk of accidents, injuries, and damage when handling steel coils. It is important to prioritize safety in order to protect yourself and your coworkers in the workplace.
- Q: How are steel coils inspected for coil set using deflection measurement?
- Steel coils are commonly inspected for coil set, a condition where the coil exhibits a curvature along its length, by utilizing deflection measurement techniques. Deflection measurement involves applying a force on the coil and measuring the resulting deviation from its original shape. To inspect for coil set, the steel coil is placed on a testing apparatus that can apply controlled pressure to the coil. This apparatus typically consists of a set of rollers or hydraulic cylinders that can exert force on the coil's surface. The first step in the inspection process is to secure the coil in place, ensuring it is properly aligned and centered on the testing apparatus. Once the coil is in position, the apparatus applies a known force along the length of the coil. This force is typically applied in a consistent and controlled manner to ensure accurate measurements. As the force is applied, the deflection of the coil is measured using sensors or gauges positioned at specific points along the length of the coil. These sensors can detect even small deviations from the original shape of the coil. The deflection measurements are recorded and analyzed to determine the severity of coil set. Typically, a set of predetermined acceptance criteria is used to assess the coil's condition. If the recorded deflection measurements exceed these criteria, it indicates the presence of coil set. The severity of the coil set can be determined by comparing the actual deflection measurements with the acceptable range specified by the criteria. Deflection measurement is an effective method for inspecting steel coils for coil set as it provides quantitative data on the deviation from the original shape. This information allows manufacturers to identify and address any coil set issues, ensuring the quality of the steel coils before further processing or shipment to customers.
- Q: I have a job where I'm required to wear ANSI certified steel toed boots or shoes(so long as its ANSI). Thing is, I'm a vegan. I do NOT want to buy leather, and I will go to great lengths to buy a non leather shoe/boot I can wear on the job! I AM currently borrowing my dad's leather ANSI boots, but would very much love to be able to rock a pair of cruelty free boots/shoes on the job!It does not have to be certified vegan just all man-made materials and no leather/sued and other such stuff where animals have to die. It would make me no better than the massive slaughterhouse industries and such. Valueing money of ver live/morals. I don't want one of the first things I need to do in my manufacturing job is compromising my morals. :3So if you know of an ANSI vegan friendly boot brand PLEASE TELL ME! *gets on knees begging*Money isn't really an option for me, I'll just continue borrowing my dad's boots till I save up enough!Thanks in advance! :D
- This Site Might Help You. RE: Vegan ANSI Steel Toes? I have a job where I'm required to wear ANSI certified steel toed boots or shoes(so long as its ANSI). Thing is, I'm a vegan. I do NOT want to buy leather, and I will go to great lengths to buy a non leather shoe/boot I can wear on the job! I AM currently borrowing my dad's leather ANSI...
- Q: What is the average flatness tolerance for steel coils?
- The average flatness tolerance for steel coils typically ranges between 0.25% and 0.5% of the coil's width.
Send your message to us
High Quality of Hot-Dip Gavalnized Steel Coil
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























