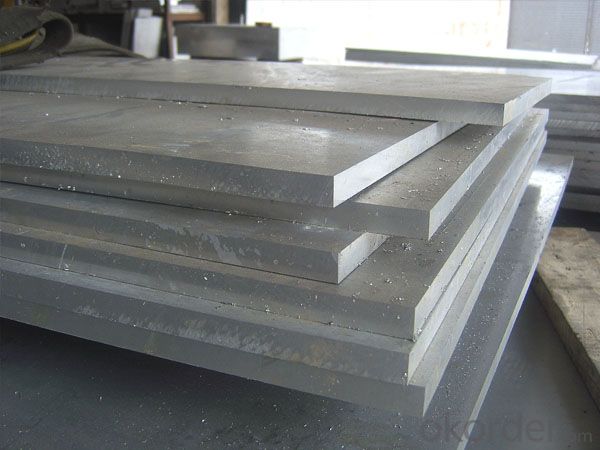
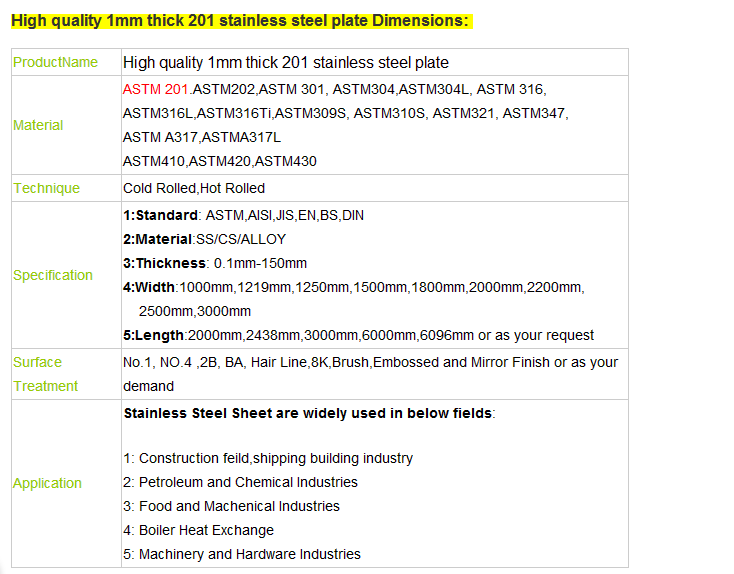
High quality 1mm thick 201 stainless steel plate
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like



- Q: How do you test the quality of stainless steel pipes?
- There are multiple methods available to test the quality of stainless steel pipes. Let's explore these methods: 1. Visual Inspection: Start by visually examining the pipes for any visible defects such as cracks, dents, or surface irregularities. Carefully observe the pipes and check for any abnormalities. 2. Dimensional Inspection: Ensure that the dimensions of the stainless steel pipes meet the specified requirements. Measure the outer diameter, inner diameter, wall thickness, and length of the pipes using calibrated measuring instruments like calipers or micrometers. 3. Chemical Composition Analysis: To guarantee corrosion resistance and durability, stainless steel pipes must have a specific chemical composition. Conduct a chemical composition analysis using techniques like spectroscopy or wet chemical analysis to determine the presence and percentage of different elements in the steel. 4. Mechanical Properties Testing: The quality of stainless steel pipes can be assessed by evaluating mechanical properties such as tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation. Employ various testing methods like tensile testing, hardness testing, impact testing, or bending testing. These tests should adhere to relevant industry standards to ensure that the pipes meet the necessary mechanical specifications. 5. Non-destructive Testing: Detect hidden defects or inconsistencies within the stainless steel pipes without causing any damage using non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic testing, X-ray inspection, or electromagnetic testing. These tests are beneficial in identifying flaws such as cracks, voids, or inclusions that may compromise the quality and performance of the pipes. 6. Corrosion Resistance Testing: Stainless steel pipes are well-known for their excellent corrosion resistance. Verify their resistance to corrosion by conducting tests such as salt spray testing or exposing them to harsh environments. These tests simulate real-life conditions and assess the pipes' ability to resist corrosion, ensuring their long-term durability. It is crucial to note that the specific testing methods and standards may vary depending on the industry or application requirements. Therefore, always refer to relevant standards and specifications when conducting quality tests on stainless steel pipes.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes spray black paint?
- Stainless steel pipes can spray black paint.The surface of stainless steel has a smooth surface
- Q: What is the difference between inside diameter and outside diameter in stainless steel pipes?
- The inside diameter refers to the measurement of the inner space or bore of a stainless steel pipe, while the outside diameter refers to the measurement of the outer circumference or width of the pipe. Essentially, the inside diameter determines the flow capacity of the pipe, while the outside diameter determines the overall size and strength of the pipe.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for chemical processing?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are highly suitable for chemical processing due to their excellent corrosion resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. They are also hygienic, durable, and have low maintenance requirements, making them a preferred choice for handling various chemicals in industries such as pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals, food processing, and more.
- Q: What are the different types of stainless steel pipe tees?
- Different applications and requirements call for various kinds of stainless steel pipe tees. 1. An equal tee is designed with three outlets of the same size, forming a 90-degree angle. It is commonly utilized to branch off or combine flow in a pipeline with equal diameters. 2. A reducing tee, as the name implies, has one outlet smaller than the other two. Its purpose is to connect pipes of different sizes, facilitating a seamless transition in fluid or gas flow. 3. In high-pressure or high-temperature applications, a barred tee provides additional support and reinforcement with a welded bar across the branch opening. This prevents stress concentration and potential failure. 4. For pipeline diversion or angled connections, a lateral tee with one outlet at a 45-degree angle is often employed. 5. A cross tee, featuring four outlets forming a cross-shaped configuration, is used when flow needs to be split or combined in multiple directions, primarily in complex piping systems. 6. Unions and socket weld tees have sockets or unions at the branch connection, allowing for easy disassembly and maintenance. They are commonly used when regular inspection, cleaning, or replacement is required. 7. Threaded tees have threaded branch connections that can be screwed onto the pipe without welding. They are frequently used in low-pressure applications or situations where frequent disassembly is necessary. Each type of stainless steel pipe tee offers specific advantages and is chosen based on the requirements of the particular piping system, including flow rates, pressure, temperature, and compatibility with the transported fluids or gases.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be threaded?
- Indeed, stainless steel pipes possess the capability to be threaded. Threading encompasses the act of generating threads either internally or externally on a substance, facilitating effortless connection and assembly with additional components. Stainless steel, being an adaptable material, can undergo threading procedures that comprise both internal and external threading. The process of threading stainless steel pipes can be accomplished through diverse means, including manual threading, machine threading, or even the utilization of specialized threading tools. By threading stainless steel pipes, a steadfast and dependable connection is achieved, rendering it suitable for numerous applications within industries like plumbing, oil and gas, construction, and beyond.
- Q: What is the average cost of stainless steel pipes?
- The average cost of stainless steel pipes can vary depending on various factors such as the size, grade, and supplier. On average, stainless steel pipes can range from $5 to $20 per foot. However, it is recommended to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to get a more accurate and current price.
- Q: What is passivation in stainless steel pipes?
- Enhancing the corrosion resistance of stainless steel pipes is achieved through the process of passivation. Despite its excellent resistance to corrosion, stainless steel can still be prone to localized corrosion in specific conditions. To prevent this, passivation is employed to eliminate any free iron or iron oxide particles from the surface of the stainless steel pipes. The passivation process involves thorough cleaning of the stainless steel pipes to eliminate any contaminants or impurities present on the surface. This can be accomplished using various techniques such as chemical or mechanical cleaning. Once the pipes are cleaned, they undergo treatment with a passivating agent, usually a solution containing nitric acid. The passivating agent functions by dissolving any iron or iron oxide particles on the surface of the stainless steel pipes. This prompts the formation of a protective oxide layer, serving as a barrier against corrosion. This oxide layer is typically thin, transparent, and capable of self-repair, providing long-lasting protection against corrosion. Passivation holds significant importance in the manufacturing of stainless steel pipes as it ensures the highest level of corrosion resistance. It is particularly crucial in industries where the pipes are exposed to harsh environments or corrosive substances, such as chemical processing plants, oil and gas refineries, or marine applications. In summary, passivation plays a critical role in maintaining the durability and performance of stainless steel pipes by improving their corrosion resistance and safeguarding them against localized corrosion.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes suitable for water treatment plants?
- Indeed, water treatment plants find stainless steel pipes to be a fitting choice. Stainless steel possesses resistance against corrosion, enabling it to endure the harsh circumstances commonly present within water treatment plants, such as exposure to chemicals, high temperatures, and high pressure. Moreover, its durability is exceptional, guaranteeing an extended lifespan and diminishing the necessity for frequent replacements. The smooth inner surface of stainless steel pipes further prevents the accumulation of deposits and enhances the efficiency of water flow. Furthermore, stainless steel upholds hygienic standards and refrains from leaching harmful substances into the water, thus ensuring the quality and safety of the treated water.
- Q: What is the external insulation used for stainless steel pipes?
- Various materials like mineral wool, fiberglass, or foam are commonly utilized for the external insulation of stainless steel pipes. These insulating materials are applied to the outer surface of the pipes, serving the purpose of thermal insulation and safeguarding against heat loss or gain. By doing so, the insulation aids in sustaining the desired temperature of the fluid or substance flowing through the pipes, thereby preventing condensation and minimizing energy loss. Moreover, the external insulation acts as a barrier against corrosion and mechanical harm, guaranteeing the durability and effectiveness of the stainless steel pipes.
Send your message to us
High quality 1mm thick 201 stainless steel plate
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






















