D2 Round Steel Bar,Alloy Steel Round Bars 1.2379,Forged SKD11 Round Steel Bar
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
D2 Round Steel Bar,Alloy Steel Round Bars 1.2379,Forged SKD11 Round Steel Bar
Product information:
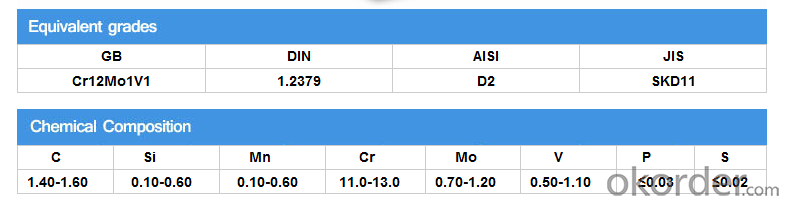
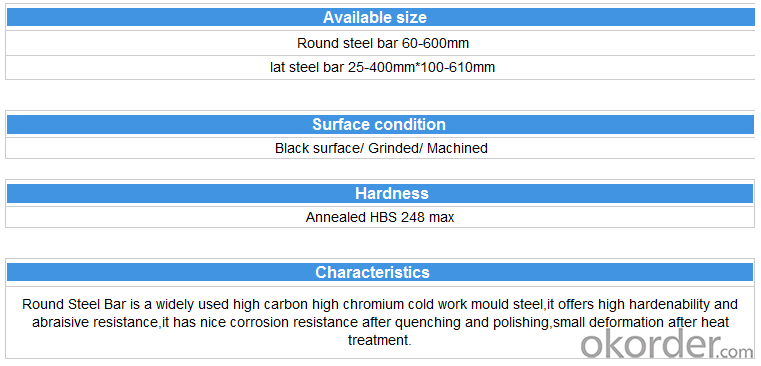
Product show

Workshop show

Our service:
-High manufacturing accuracy
-High strength
-Small inertia resistance
-Strong heat dissipation ability
-Good visual effect
-Reasonable price
Chose happens because of quality, then price, We can give you both.Additionally, we can also offer professional products inquiry, products knowledge train(for agents), smooth goods delivery, exellent customer solution proposals.Our service formula: good quality+good price+good service=customer's trust
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem.
If you need the sample, please feel free to let me know. Any question, we will contact you ASAP!
- Q: How does special steel contribute to the manufacturing of medical implants?
- The unique properties and characteristics of special steel make it vital in the production of medical implants. These implants need materials that are durable, corrosion-resistant, and biocompatible. Stainless steel, titanium alloys, and cobalt-chromium alloys are special steels that possess these desired qualities, making them ideal for medical implant manufacturing. Stainless steel, for instance, is widely used in the production of medical implants due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and high strength. It finds applications in surgical instruments, orthopedic implants, and dental devices. Stainless steel implants can endure the harsh physiological conditions within the body, ensuring long-term performance and reducing the risk of complications. Titanium alloys, on the other hand, are extensively utilized in medical implant manufacturing. These alloys offer a high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance. Orthopedic surgeries, including joint replacements, as well as dental implants, commonly employ titanium implants. The biocompatible nature of titanium allows for better integration with the surrounding bone, facilitating faster healing and reducing the risk of rejection. Cobalt-chromium alloys are also utilized in the production of medical implants. These alloys possess outstanding mechanical strength, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. Orthopedic surgeries and cardiovascular interventions, such as stents, often make use of cobalt-chromium implants. Their high strength ensures stability and durability, while their biocompatibility minimizes adverse reactions and aids in patient recovery. Overall, special steel provides the necessary qualities for manufacturing medical implants. Whether it is stainless steel, titanium alloys, or cobalt-chromium alloys, these materials contribute to the creation of biocompatible, corrosion-resistant, and durable implants that enhance patients' quality of life and ensure successful medical procedures.
- Q: Can special steel be used for making springs?
- Yes, special steel can be used for making springs. Special steel, also known as alloy steel, offers enhanced mechanical properties such as high tensile strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance. These characteristics make it an ideal material for manufacturing springs that require durability and reliability in various applications. The specific type of special steel used for springs depends on the requirements of the application, such as the desired level of flexibility or resistance to fatigue. Overall, special steel provides excellent performance and longevity in spring manufacturing.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the production of artistic sculptures?
- Certainly, artistic sculptures can indeed be produced using special steel. Special steel, which pertains to steel alloys specifically designed and manufactured for specific applications, presents a plethora of benefits that render it suitable for the creation of sculptures. Primarily, special steel alloys boast exceptional strength and durability, enabling sculptors to fashion large and intricate structures that can withstand external forces and environmental conditions. This robustness and resilience prove crucial, especially for sculptures placed outdoors and exposed to weather elements such as rain, wind, and extreme temperatures. Moreover, special steel alloys offer pliability and malleability, allowing for easy shaping and forming. Artists can effortlessly mold and manipulate the steel into various shapes and sizes, bringing their creative visions to life. By employing techniques like welding, cutting, and bending, sculptors can shape the steel into their desired forms, resulting in one-of-a-kind and captivating sculptures. Furthermore, special steel alloys can be finished in diverse ways, such as polishing, painting, or coating, to enhance their aesthetic appeal. This grants artists the ability to incorporate different textures, colors, and surface finishes into their sculptures, further augmenting their artistic value. Additionally, special steel alloys provide resistance to corrosion, which is especially significant for sculptures situated in outdoor or humid environments. This corrosion resistance ensures that the sculptures retain their visual allure and structural integrity over time, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repairs. In conclusion, special steel presents a wide array of advantages that make it an exceptional choice for the production of artistic sculptures. Its strength, pliability, aesthetic appeal, and resistance to corrosion equip artists with the necessary tools to create visually striking and enduring sculptures that can be cherished for years to come.
- Q: How is special steel recycled?
- Special steel is typically recycled through a process called electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking. In this process, scrap steel is collected and melted down in an electric arc furnace, where high temperatures are used to separate impurities. Once the impurities are removed, the molten steel is then refined and cast into new forms to create various specialized steel products, ensuring that the steel is effectively recycled and reused.
- Q: Can special steel be used in power generation applications?
- Yes, special steel can certainly be used in power generation applications. Special steel refers to various types of steel that are specifically designed to have enhanced properties such as high strength, durability, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. These properties make special steel ideal for use in power generation applications where the materials need to withstand high temperatures, pressures, and mechanical stresses. In power generation, special steel can be used in various components and equipment, such as turbine blades, boiler tubes, heat exchangers, steam pipes, and high-pressure valves. For example, in thermal power plants, where fossil fuels are burned to generate electricity, special steel is commonly used in boiler tubes and heat exchangers to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the steam generation process. Additionally, in nuclear power plants, special steel is used in critical components like reactor vessels, steam generators, and fuel cladding due to its excellent strength, resistance to radiation damage, and corrosion resistance. Furthermore, special steel is also used in renewable energy power generation applications. For instance, in wind turbines, special steel is used in the construction of turbine towers, rotor blades, and gearboxes, as it needs to withstand high wind speeds, vibrations, and fatigue. Overall, special steel plays a crucial role in power generation applications due to its exceptional properties, ensuring the reliability, efficiency, and longevity of the equipment and components used in various power generation systems.
- Q: What are the different non-destructive evaluation techniques used for special steel?
- Some different non-destructive evaluation techniques used for special steel include ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle inspection, dye penetrant inspection, eddy current testing, and radiographic testing. These methods allow for the detection of internal and surface defects in the steel without causing any damage to the material.
- Q: Is special steel recyclable?
- Yes, special steel is recyclable.
- Q: How does special steel perform in high-vibration applications?
- Special steel is known for its excellent performance in high-vibration applications. Its unique composition and properties make it highly resistant to the effects of vibration, ensuring optimal performance and durability in such environments. One of the key features of special steel is its high tensile strength. This strength allows it to withstand the forces and stresses generated by vibration without undergoing deformation or failure. This property is vital in high-vibration applications, where constant movement and oscillation can subject materials to significant stress. Moreover, special steel exhibits exceptional fatigue strength, meaning it can endure repeated cycles of stress and vibration without compromising its structural integrity. This makes it ideal for applications that involve continuous or cyclic vibration, such as machinery, equipment, and structures subjected to dynamic loads. Additionally, special steel possesses excellent damping properties. Damping refers to the ability of a material to absorb and dissipate energy generated by vibrations. Special steel's superior damping characteristics help reduce the magnitude and duration of vibrations, minimizing the impact on the surrounding components and structures. This contributes to overall system stability and reduces the risk of fatigue or premature failure. Furthermore, special steel is often engineered to have high resistance to corrosion and wear. This resistance ensures that the material remains robust and reliable even in harsh environments where vibration-induced corrosion or erosion may occur. By maintaining its protective coating and integrity, special steel can effectively withstand the challenges posed by high-vibration applications. In summary, special steel performs exceptionally well in high-vibration applications due to its high tensile strength, fatigue resistance, damping properties, and corrosion/wear resistance. Its combination of these properties ensures optimal performance, longevity, and safety in environments characterized by significant vibration and dynamic loads.
- Q: Can special steel be used in the manufacturing of sports equipment?
- Yes, special steel can be used in the manufacturing of sports equipment. Special steel, such as carbon steel or stainless steel, provides durability, strength, and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for various sports equipment like golf clubs, tennis racquets, or bicycle frames.
- Q: What are the different methods for tempering special steel?
- There are several methods for tempering special steel, each with its own advantages and considerations. Some of the common methods used for tempering special steel include: 1. Air Tempering: This method involves heating the steel to a specific temperature and then allowing it to cool in still air. Air tempering is often used for low alloy steels and results in a uniform hardness throughout the steel. 2. Oil Tempering: In this method, the steel is heated to a specific temperature and then quenched in oil to cool it rapidly. Oil tempering is commonly used for tool steels as it provides a good balance between hardness and toughness. 3. Water Tempering: Similar to oil tempering, water tempering involves quenching the steel in water after heating it to a specific temperature. This method provides a higher rate of cooling and results in a harder steel, but it may also lead to increased brittleness. 4. Salt Bath Tempering: In this method, the steel is immersed in a molten salt bath at a specific temperature. The salt bath provides a more controlled and uniform heat transfer, resulting in a consistent hardness throughout the steel. 5. Cryogenic Tempering: Cryogenic tempering involves cooling the steel to extremely low temperatures, often below -100°C (-148°F), using liquid nitrogen or helium. This method helps to further reduce residual stresses and increase the wear resistance of the steel. It is important to note that the specific method chosen for tempering special steel depends on various factors, including the type of steel, desired hardness, intended application, and the desired balance between hardness and toughness. It is crucial to follow proper heat treatment guidelines and consult with experts to ensure the best results for a specific steel alloy.
Send your message to us
D2 Round Steel Bar,Alloy Steel Round Bars 1.2379,Forged SKD11 Round Steel Bar
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 25 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























