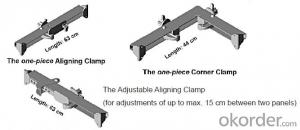
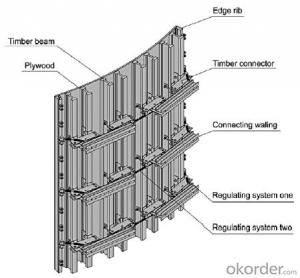
Timber Beam H-20 for formwork and scaffolding systems
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Characteristics:
◆ Standardized production lines.
Supply capability: 3000m/day, Lmax = 6600mm.
◆ Finger jointing of the flange and web, the strength of timber beam is highly improved.
Max. shearing force failure load:40KN
◆ Well treated to prevent from water penetration or erosion, so the service life maximally extended.
Normally, CNBM timber beam H20 can be used for 4 to 5 years, the exact using time would depend on maintenance & storage.
◆ Robust caps at the end of the girders protect against damages.




- Q: How is steel formwork supported during concrete pouring?
- During the pouring of concrete, steel formwork relies on a support system consisting of props, beams, and scaffolding. Props, which are vertical supports, are strategically positioned beneath the steel formwork to maintain stability and prevent any sagging or collapsing under the weight of the wet concrete. These props can be adjusted to achieve precise positioning and leveling of the formwork. In addition to props, horizontal beams are employed to provide additional support for the steel formwork. These beams are typically placed at regular intervals and connected to the props, creating a robust framework capable of withstanding the pressure exerted by the concrete. The beams also aid in distributing the load evenly across the formwork, ensuring its balance and security. Scaffolding is another essential component in supporting the steel formwork during concrete pouring. It is erected around the formwork to provide a secure working platform for workers to access and maneuver the formwork. Scaffolding also facilitates the installation and removal of the formwork, streamlining the construction process. In summary, the combination of props, beams, and scaffolding plays a crucial role in supporting steel formwork during concrete pouring. This support system ensures the stability of the formwork, allowing for accurate pouring and curing of the concrete, resulting in a structurally sound and long-lasting building.
- Q: What is the cost of steel formwork compared to other types of formwork?
- The cost of steel formwork is generally higher compared to other types of formwork due to its durability, reusability, and strength. While it may have a higher upfront cost, it provides long-term cost benefits over time as it can be used multiple times and requires minimal maintenance.
- Q: What are the common design considerations for steel formwork in hot climates?
- When designing steel formwork for use in hot climates, there are several common considerations that need to be taken into account. 1. Thermal Expansion: Steel has a high coefficient of thermal expansion, meaning it expands and contracts with temperature changes. In hot climates, where temperatures can reach extreme levels, it is important to account for this expansion in the design of the formwork. Adequate expansion joints and allowances should be provided to accommodate the thermal movement of the steel. 2. Heat Resistance: Steel formwork should be designed to withstand high temperatures without significant deformation or loss of strength. This may involve selecting steel grades with higher heat resistance or employing additional cooling measures to prevent overheating. 3. Corrosion Protection: Hot and humid climates can accelerate the corrosion process, so it is important to incorporate effective corrosion protection measures into the design. This can be achieved through the use of corrosion-resistant coatings, such as galvanization or epoxy coatings, or by incorporating sacrificial anodes to protect the steel from corrosion. 4. Ventilation: Hot climates often require adequate ventilation to prevent the buildup of heat and moisture within the formwork. Properly designed openings and vents should be included to facilitate air circulation and prevent the formation of condensation, which can lead to corrosion and reduce the lifespan of the formwork. 5. Insulation: In extremely hot climates, insulation can help to reduce the transfer of heat to the formwork, minimizing the effect of thermal expansion and reducing the risk of deformation. Insulation materials, such as foam or reflective coatings, can be used to provide a barrier between the steel formwork and the external environment. 6. Durability: The design of steel formwork should take into consideration the long-term durability requirements of the project. This includes selecting materials and construction methods that are resistant to degradation from UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and other environmental factors commonly found in hot climates. Overall, designing steel formwork for use in hot climates requires careful consideration of thermal expansion, heat resistance, corrosion protection, ventilation, insulation, and durability. By addressing these factors, the formwork can withstand the challenges posed by hot climates and ensure the successful completion of construction projects.
- Q: I was engaged in the patent agency, the two days of receipt of a patent application on the bridge, it is a drawing section map, the other nothing, no label no text, I am on mechanical, civil engineering drawings and utterly ignorant of ah, so simple, later on the Internet for a long time and recall ratio of patent it is unclear whether the drawings, sections of the box girder template, now the goal is clear, but a box girder template knowledge I don't know much about the Internet, did not find out what things, patent is only a few patents, I want to know more about the box girder and box girder template for example, the box girder template with cast-in-place prefabricated, full steel structure, steel wood structure, the hydraulic support system, but also ordinary (the ordinary I don't know what), etc. So, anyway, more detailed information as possible, thank you ~ ~ no more, I don't mind ah, not much, have a point with the province oh
- I am specialized in Civil Engineering (design and construction), you see the drawings are box girder template for the design of template
- Q: What is the maximum load that steel formwork can bear?
- The maximum load capacity of steel formwork relies on several factors including the steel type and thickness, formwork design and construction, and the support system in place. Steel formwork is renowned for its robustness and endurance, enabling it to withstand heavy loads. Nevertheless, it is essential to refer to the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines to determine the precise maximum load capacity of a specific steel formwork system. These specifications are typically established through comprehensive testing and engineering calculations, guaranteeing the formwork's safety and structural integrity. Moreover, it is vital to account for other considerations such as load distribution, formwork arrangement, and overall structural stability. The involvement of professional engineers and contractors in the design and installation process is crucial to ensure that the maximum load capacity is not exceeded and that the formwork remains securely supported during construction.
- Q: How does steel formwork affect the overall construction site safety measures?
- The overall construction site safety measures can be significantly impacted by steel formwork in various ways. To start with, the high strength and durability of steel formwork ensure stability and structural integrity during construction, thus reducing the risk of accidents like collapses or structural failures. This, in turn, enhances the safety of workers and the entire site. Moreover, steel formwork offers superior fire resistance compared to other formwork materials. This characteristic helps prevent or slow down the spread of fire, allowing workers enough time to evacuate the site safely and enabling emergency services to respond effectively. It also decreases the chances of fire-related accidents, safeguarding both human lives and the surrounding environment. Another safety advantage of steel formwork lies in its ability to withstand extreme weather conditions such as strong winds or heavy rain. This resilience lowers the likelihood of formwork damage or failure, ensuring worker safety and preventing potential accidents caused by adverse weather. Furthermore, steel formwork is often designed with integrated safety features like handrails and platforms to provide secure working surfaces for construction workers. These features enable workers to perform their tasks safely at heights, reducing the risk of falls and injuries. Lastly, steel formwork is reusable and requires minimal maintenance, contributing to overall site safety. The use of reusable formwork minimizes waste and clutter, resulting in a cleaner and more organized working environment. This, in turn, reduces the risk of accidents caused by tripping or falling over debris. In conclusion, steel formwork positively impacts construction site safety measures by providing stability, fire resistance, weather resistance, built-in safety features, and a cleaner working environment. These benefits reduce the risk of accidents, ensure worker safety, and contribute to the successful completion of construction projects.
- Q: What are the different types of steel used in formwork construction?
- There are several types of steel commonly used in formwork construction, including mild steel, high-strength low-alloy steel (HSLA), and high-strength steel. Additionally, stainless steel may be utilized in specific applications where corrosion resistance is required. The choice of steel type depends on factors such as the desired strength, durability, and cost-effectiveness of the formwork system.
- Q: How does steel formwork affect the overall thermal insulation of a building?
- Steel formwork has minimal impact on the overall thermal insulation of a building. Since steel is a good conductor of heat, it does not provide sufficient insulation on its own. However, when combined with appropriate insulation materials, such as foam or mineral wool, steel formwork can contribute to a well-insulated building by providing structural support while the insulation material retains heat or cold temperatures.
- Q: How does steel formwork contribute to the overall strength of a structure?
- Using steel panels and frames, steel formwork is a construction technique employed to create temporary molds for pouring concrete. This method offers several advantages over traditional wooden formwork, particularly in terms of strengthening a structure. Firstly, steel formwork boasts exceptional durability and resistance to wear and tear. Steel is a sturdy material capable of withstanding heavy loads and extreme weather conditions. Unlike wooden formwork, it does not warp, crack, or deteriorate over time, ensuring the structure's strength and integrity are maintained for an extended period. Furthermore, steel formwork provides superior dimensional stability compared to other materials. The precision fabrication of steel panels and frames guarantees accurate measurements and consistent shapes. This precision allows for a more even distribution of concrete, resulting in a stronger structure with reduced cracks or weaknesses. Moreover, steel formwork allows for greater flexibility in design and construction. The strength of steel permits the creation of intricate and complex structures that may not be achievable with alternative formwork materials. The versatility of steel formwork enables engineers to design structures with unique shapes and configurations, ultimately enhancing their overall strength and load-bearing capacity. Additionally, steel formwork contributes to the overall strength of a structure by offering excellent support and reinforcement during the concrete pouring process. Acting as a framework, the steel panels and frames hold the concrete in place until it solidifies and gains strength. This ensures proper and optimal curing of the concrete, resulting in a structurally sound and resilient structure. In conclusion, steel formwork plays a vital role in enhancing the overall strength of a structure. Its durability, dimensional stability, flexibility in design, and support during the concrete pouring process all contribute to creating a robust and long-lasting structure. By choosing steel formwork, construction projects can achieve higher levels of strength, durability, and structural integrity.
- Q: How does steel formwork affect the overall durability of a structure?
- The durability of a structure can be greatly influenced by steel formwork. Steel formwork is known for its strength and durability, which provides excellent support and stability during the construction process. This ensures accurate construction according to required specifications, which is vital for long-term durability. Using steel formwork offers several advantages. It has the ability to withstand high pressures and loads, which is especially important in large-scale construction projects involving heavy concrete pours. The steel formwork effectively distributes the weight and pressure exerted by the concrete, preventing any deformation or collapse. This helps maintain the structure's integrity and durability over time. In addition, steel formwork is highly resistant to environmental factors such as moisture, humidity, and temperature changes. This resistance protects the structure from potential damage such as corrosion, rot, or warping, enhancing its overall durability. This reduces the need for expensive repairs or maintenance. Furthermore, steel formwork provides a smooth and even surface for the concrete to adhere to during the curing process. This results in a uniform and consistent finish, reducing the risk of cracks or weak points in the structure. This absence of defects improves the structure's durability, as it is less prone to structural weaknesses that can compromise its integrity over time. Moreover, steel formwork is reusable and can be easily dismantled and reassembled for multiple construction projects. This not only reduces construction costs but also minimizes waste and environmental impact. The ability to reuse steel formwork ensures consistent use of high-quality materials, contributing to the structure's long-term durability. In conclusion, steel formwork plays a significant role in determining the overall durability of a structure. Its strength, resistance to environmental factors, ability to distribute loads, and provision of a uniform finish all contribute to the long-term durability and structural integrity of the building. By utilizing steel formwork, builders can ensure that the structure is built to last, minimizing the need for future repairs or replacements.
Send your message to us
Timber Beam H-20 for formwork and scaffolding systems
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords