Prepainted Galvanized Steel Sheets in Coil
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Hot-dip Zinc Coating Steel Building Roof Walls
1.Structure of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Description:
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications. Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
2.Main Features of the Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
• Excellent process capability
• Smooth and flat surface
• Workability, durability
• Excellent anticorrosive property
• High strength
• Good formability
• Good visual effect
3.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Images:


4.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Specification:
Standard: ASTM, JIS,EN
Grade: CS, DX51D+Z,SGCC, SS 230~550,S220GD+Z~S550GD+Z, SGC340~SGC570
Thickness: 0.1mm~5mm
Width: max 2000mm
Coil weight:3-12 MT
Coil ID:508/610mm
Surface structure: zero spangle, regular spangle or minimum spangle
Surface treatment: Chromate treatment, Oiled/dry, skinpassed/non-skinpassed
Packing: Standard seaworthy export package
Technology test results:
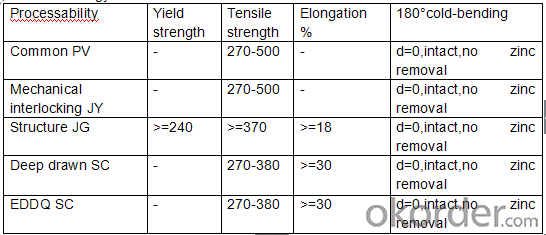
5.FAQ of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1.How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2.How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-30 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in seismic zones?
- Steel sheets perform well in seismic zones due to their high tensile strength and ductility. They have the ability to absorb and redistribute energy during seismic events, reducing the risk of structural failure. Additionally, steel structures can be designed to be flexible and resistant to lateral forces, making them a preferred choice for buildings in areas prone to earthquakes.
- Q: Are the steel sheets suitable for outdoor signage?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for outdoor signage. Steel is known for its strength, durability, and resistance to weather conditions. It can withstand harsh outdoor environments, including extreme temperatures, rain, wind, and sunlight, without warping or deteriorating. The thickness of steel sheets can be adjusted based on the size and design of the signage to ensure stability and longevity. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily customized and painted to match the desired aesthetic, making them a popular choice for outdoor signage projects.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used in earthquake-resistant construction?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used in earthquake-resistant construction. Steel has excellent strength and ductility properties that allow it to withstand the forces generated during an earthquake. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily fabricated, assembled, and incorporated into various structural systems, making them a popular choice for earthquake-resistant construction.
- Q: What is the difference between a smooth and patterned steel sheet?
- A plain and uniform surface characterizes a smooth steel sheet, devoid of any visible patterns or textures. It boasts a consistent and sleek appearance, rendering it ideal for situations that call for a clean and contemporary look. In contrast, a patterned steel sheet showcases a myriad of designs or textures that are either embossed or etched onto its surface. These patterns can range from simple geometric shapes to intricate motifs. People often opt for patterned steel sheets due to their decorative appeal, as they have the ability to enhance the visual interest of a space. They are commonly employed in architectural elements, such as wall panels or ceiling tiles, to create a distinct and artistic effect. When it comes to functionality, smooth steel sheets might offer slightly superior corrosion resistance due to their smoother surface. This makes them well-suited for applications that require protection against rust, such as in outdoor or marine environments. On the other hand, patterned steel sheets may exhibit reduced corrosion resistance due to the variation in surface texture, potentially providing less safeguarding against rust. In conclusion, the decision between a smooth and patterned steel sheet hinges on the desired aesthetic, functional requirements, and the intended application.
- Q: What are the common finishes available for steel sheets?
- Some common finishes available for steel sheets include hot rolled, cold rolled, galvanized, and stainless steel.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for agricultural fencing or enclosures?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for agricultural fencing or enclosures. They are durable, strong, and provide excellent security. Steel sheets can be welded or fastened together to create a sturdy barrier that can withstand the elements and keep livestock contained. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily customized to suit specific fencing or enclosure requirements.
- Q: Are the steel sheets resistant to chemical spills?
- Yes, steel sheets are generally resistant to chemical spills. Steel is known for its durability and ability to withstand various environmental conditions, including exposure to chemicals. The non-reactive nature of steel makes it highly resistant to corrosion, which means it can effectively protect against chemical spills. However, the specific resistance of steel sheets to chemical spills may depend on the type and concentration of the chemicals involved. It is always recommended to consult with experts or refer to specific steel grades and their compatibility with different chemicals to ensure optimal resistance.
- Q: How do steel sheets compare to aluminum sheets in terms of weight?
- Steel sheets are generally heavier than aluminum sheets when comparing materials of the same size and thickness.
- Q: Are the steel sheets easy to install?
- Yes, steel sheets are generally easy to install. They are lightweight, making them easier to handle and maneuver during the installation process. Additionally, steel sheets often come with pre-drilled holes or interlocking systems, simplifying the installation further. With the appropriate tools and basic construction knowledge, individuals can easily install steel sheets on various surfaces such as roofs, walls, or fences. However, it's important to follow the manufacturer's instructions and safety guidelines to ensure a proper and secure installation.
- Q: How do you cut steel sheets?
- Steel sheets can be cut using various methods such as shearing, laser cutting, plasma cutting, or using a water jet cutter. The chosen method depends on factors like the thickness of the steel sheet, desired precision, and the available equipment.
Send your message to us
Prepainted Galvanized Steel Sheets in Coil
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























