Glass Fiber Textile Reinforced Microporous Insulation Board for Ladle Heat Insulation
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for Micropore Insulation Board ,Heat Insulation materials
| Type: | Other Heat Insulation Materials | Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | |
| Model Number: | M5100 | service temperature, max.: | 1150 C | Thermal conductivity, @800 C: | 0.035 W/m.K |
| typical density: | 280 kgs/m3 |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | wooden cases |
| Delivery Detail: | 10 days |
Product Description
M5100 Panel is rigid finishing from microporous technology , with opcified blend of filament reinforced fumed silica, which provides a superb thermal performance.
It is an ideal back-up insulation for various industry where the high temperature is needed, with a long time exposure of 1150 °C at highest.
M5100 Panel ---Various coverings : Naked Panels, Aluminium Foil covering, E-class Fibre Cloth Covering, Fibre Paper covering.
M5100 Panel—Four Grades available : 850 , 1000, 1100, 1200
Properties & Advantages
Extremely low thermal conductivity
High thermal stability
High compressive strength
No harmful respirable fibres
Free of organic binders
Environmentally friendly
Resistant to most chemicals
Non combustible
Easy to handle
Typical Applications
Back-up insulation in industrial furnaces
Fuel cells (SOFC)
Thermal Batteries
Aluminium industry ( launders,Smelter.etc. )
Glass & ceramics industry
Petrochemical industry (cracking furnace, reformer)
Black box & VDR (Voyage Data Recorder)
Data loggers
Working & Processing
M5100 can be shaped both manually and with stationary wood processing machinery. They can be cut, sawn, drilled and punched. The boards can be fixed in place with glue or by mechanical means such as anchors, pins and clips.
Technical Data for for Micropore Insulation Board ,Heat Insulation materials
| Description | MISSION STD Panel M5100 | ||||
| Classification Temperature | 0C | 850 | 1000 | 1100/1100S | 1200/1200S |
| Long time Exposure | 850 | 950 | 1050/1000 | 1150/1100 | |
| Nominal Density | [kg/m3] | 260-280 | 260-280 | 400-450 | 450-550 |
| Typical Density | 280 | 280 | 450 | 500 | |
| Compression Strength | [MPa] | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.72 | 0.8 |
| @10% deformation (ASTM C-165) | |||||
| Thermal Conductivity | |||||
| 200 0C | W/m.K | 0.022 | 0.022 | 0.024 0.028 | 0.027 0.029 |
| 400 0C | W/m.K | 0.025 | 0.025 | 0.028 0.032 | 0.032 0.035 |
| 600 0C | W/m.K | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.032 0.038 | 0.037 0.042 |
| 800 0C | W/m.K | 0.033 | 0.033 | 0.035 0.045 | 0.043 0.046 |
| Specific Heat Capacity | |||||
| 200 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.86 | 0.89 |
| 400 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 0.95 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.99 |
| 600 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 1.02 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 1.05 |
| 800 0C | [KJ/Kg K] | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.08 | 1.08 |
| Linear Shrinkage | |||||
| 12h full soak @ 850 0C | % | ≤2 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.1 ≤0.1 | ≤0.1 ≤0.1 |
| 24h full soak @ 950 0C | - - - | ≤2.5 | ≤0.5 ≤0.1 | ≤0.5 ≤0.5 | |
| 24h full soak @ 1050 0C | - - - | - - - | ≤2.5 - - - | ≤2.5 ≤2.5 | |
| 24h full soak @ 1150 0C | - - - | - - - | - - - - - - | ≤3.5 - - - | |

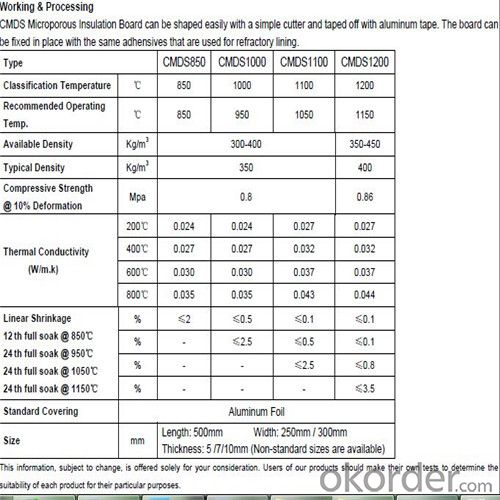
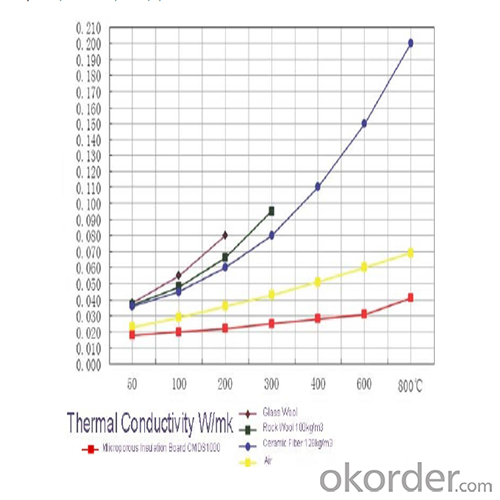
Standard Dimension:
1000(900)×600(500)×5-20mm
We can also manufacture the special dimensions as customers need.
Q1:Are you a manufacture or trader?
A:Factory+trade(mainly factories,at the same time,we operates other related products).
Q2:Can we visit your factory?
A:Sure,welcome at any time,seeing is believing.
Q3:What's the MOQ of trial order?
A:No limit,We can offer the best suggestions and solutions according to your condition.
Q4:Which payment terms can you accept?
A:T/T,L/C,Western Union,Moneygram,Paypal are available for us.
Q5:After an order is confirmed,when to deliver?
A:15-25days after deposit.
Q6:Is your company accept customization?
A:We have own factory and excellent technical team,and we accept OEM service.
Q7:How about your company's certification?
A:ISO9001 and Test Report,also we could apply other necessary certification.
Q8:How to slove the quality problems?
A:If the products are not confirmed to customer samples or have quality problems,our compay will be responsible to make compensation for it.
Q9:Can you offers samples?
A:Of coures,samples are free but freight paid by the buyers.
Q10:What is the service life of your bricks?
A:The service life of different bricks is unlike.It also depends on your using condition and method.
Thanks for your coming in,if there is any question,I will be glad to help you.
- Q: Are glass fiber textiles resistant to mildew growth?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles are resistant to mildew growth.
- Q: Can glass fiber textiles be used in optical fibers?
- Indeed, optical fibers can utilize glass fiber textiles as the core material. The core material, typically composed of glass or plastic, is responsible for carrying light signals. On the other hand, the cladding material, encompassing the core, confines the light within by utilizing total internal reflection. Glass fiber textiles, consisting of thin glass strands, possess the advantage of high transparency to light, facilitating efficient signal transmission. Moreover, their high tensile strength renders them appropriate for long-distance optical communication. Nevertheless, it is crucial to acknowledge that the process of transforming glass fiber textiles into optical fibers involves additional steps. These steps encompass coating the fibers with a protective layer and optimizing their dimensions for optimal light transmission. These additional measures guarantee the optical fibers possess the necessary optical and mechanical properties. To conclude, glass fiber textiles are undoubtedly applicable in optical fibers. Their transparency to light and high tensile strength allow for efficient and dependable optical signal transmission.
- Q: Who has a Chinese English translation about glass fiber?. About WORD3 pages will do
- Glass is a substance known for its brittleness. Interestingly, once the glass is heated after being drawn into a much thinner than a human hair fiber glass, it seems completely forget their own nature, be like synthetic fiber as soft and tough, even more than the stainless steel wire of the same thickness!So, what's the use of glass fiber?
- Q: How do glass fiber textiles resist wrinkling?
- Due to their inherent properties, glass fiber textiles have the ability to resist wrinkling. Glass fiber, being a robust and inflexible material, prevents the formation of wrinkles by resisting bending or folding. Moreover, the high elasticity of glass fiber textiles enables them to stretch and regain their original shape without wrinkling. This elasticity allows the fabric to endure tension and movement without creasing or folding. Additionally, the smooth surface of glass fiber textiles reduces the likelihood of wrinkles. The smoothness of the fabric lessens friction between fibers, thereby preventing bunching up and the subsequent formation of wrinkles. In conclusion, the combination of strength, elasticity, and smoothness in glass fiber textiles contributes to their impressive resistance to wrinkling.
- Q: Can glass fiber textiles be used in luggage and bags?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in luggage and bags. Glass fiber textiles are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio, making them an ideal material for durable and lightweight luggage and bags. The glass fibers are woven into a fabric, which can be used to create various types of bags, including suitcases, backpacks, and duffel bags. These textiles offer excellent resistance to abrasion and tearing, ensuring that the bags can withstand the rigors of travel. Additionally, glass fiber textiles provide good protection against moisture and UV radiation, making them suitable for outdoor luggage and bags as well. Overall, glass fiber textiles offer a reliable and long-lasting solution for luggage and bags.
- Q: What are the different lamination options for glass fiber textile?
- There are several lamination options available for glass fiber textiles, depending on the specific requirements and intended use of the material. One common lamination option is the use of a thermoplastic film. In this method, a thin layer of thermoplastic material is applied to the glass fiber textile and then heated to bond the two together. This provides a protective layer that enhances the strength and durability of the textile while also improving its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation. Another option is the use of a thermoset resin, such as epoxy or polyester. In this process, the resin is applied to the glass fiber textile and then cured or hardened through a chemical reaction or heating process. This creates a strong bond between the resin and the textile, resulting in a rigid and durable composite material. Thermoset laminations are often used in applications requiring high strength and stiffness, such as structural components in aerospace or automotive industries. Additionally, glass fiber textiles can be laminated with a thin layer of adhesive material. This method involves applying an adhesive layer to the textile surface and then bonding it with another material, such as a metal or plastic substrate. Adhesive laminations are commonly used in applications where the textile needs to be joined with other materials, providing a strong and reliable bond between the two. Finally, glass fiber textiles can also be laminated with a thin layer of foam material. This option is often used in applications requiring cushioning or insulation properties, such as in the construction or automotive industries. The foam layer provides additional comfort, sound absorption, and thermal insulation, enhancing the overall performance of the textile. Overall, the choice of lamination option for glass fiber textiles depends on the specific requirements of the application, including desired strength, durability, flexibility, and other functional properties.
- Q: Can glass fiber textiles be used in clothing?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in clothing. Glass fiber textiles, also known as fiberglass fabrics, are made from fine fibers of glass that are woven together to create a fabric. While glass fiber textiles are not as commonly used in clothing as natural fibers like cotton or synthetic fibers like polyester, they can still be used in certain applications. Glass fiber textiles offer several advantages that make them suitable for specific clothing purposes. Firstly, they are highly durable and have a high tensile strength, meaning they can withstand wear and tear better than many other fabrics. This makes them suitable for protective clothing, such as firefighting suits or industrial workwear, where durability and resistance to heat and flames are essential. In addition to their durability, glass fiber textiles are also resistant to chemicals and can provide insulation properties. This makes them useful for specialized clothing items like thermal wear or protective suits for hazardous environments. They can also be used in sportswear or outdoor clothing for their moisture-wicking properties, as glass fiber textiles can effectively draw moisture away from the body, keeping the wearer dry and comfortable. However, it is important to note that glass fiber textiles have some limitations when it comes to clothing. They are not as breathable as natural fibers, which can make them uncomfortable in hot and humid conditions. Their stiffness and lack of flexibility may also restrict movement and hinder comfort. Additionally, glass fiber textiles can be abrasive to the skin, so proper lining or layering is necessary to prevent irritation. Overall, while glass fiber textiles may not be commonly used in everyday clothing, they have specific applications where their unique properties are beneficial. In industries requiring protective clothing or specialized gear, glass fiber textiles can provide durability, resistance, and insulation, making them a suitable choice.
- Q: Can glass fiber textiles be used in reinforcement of wood fibers?
- Yes, glass fiber textiles can be used in the reinforcement of wood fibers. Glass fiber textiles, also known as glass fiber fabrics or glass fiber mats, are commonly used as reinforcement in composite materials due to their high strength and stiffness. When applied to wood fibers, they can enhance the mechanical properties and performance of the wood material. The glass fibers help to increase the overall strength, durability, and dimensional stability of the wood fibers, making them more resistant to cracking, warping, and other forms of damage. This combination of wood and glass fibers creates a composite material that has improved strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced structural integrity. Additionally, the glass fibers can also provide thermal insulation properties to the wood fibers. Overall, the use of glass fiber textiles in the reinforcement of wood fibers is a viable option for enhancing the properties and performance of wood-based materials.
- Q: Are glass fiber textiles flexible?
- Glass fiber textiles are indeed flexible. Their extreme thinness allows for weaving into lightweight and pliable fabrics. These fabrics possess the ability to be bent, twisted, or folded without any risk of breaking or losing their shape. Their flexibility makes them suitable for various applications, including the manufacturing of clothing, upholstery, and composite materials. Nevertheless, it should be acknowledged that the extent of flexibility can differ based on the particular construction and processing techniques employed in the production of these glass fiber textiles.
- Q: How does glass fiber textile perform in terms of gas permeability?
- Glass fiber textile has low gas permeability, meaning that it provides a barrier against the passage of gases.
Send your message to us
Glass Fiber Textile Reinforced Microporous Insulation Board for Ladle Heat Insulation
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m²
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m²/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords































