Hot Rolled Deformed Steel Rebars for Constrution
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specifications of Hot Rolled Deformed Steel Rebars for Constrution:
Standard | GB UK USA | HRB335 HRB400 HRB500 G460B, B500A, B500B,B500C GR40, GR60 | |
Diameter | 6mm,8mm,10mm,12mm,14mm,16mm,18mm,20mm, 22mm,25mm,28mm,32mm,36mm,40mm,50mm | ||
Length | 6M, 9M,12M or as required | ||
Price | Keep lower operating costs so as to offer competitive price for our clients | ||
Delivery Detail | within 45 days after received advanced payment or LC. | ||
Application | mainly used in construction industry to reinforce concrete structures and so on | ||
Invoicing | Actual or Theoretical Weight Basis as buyer’s request. | ||
Type | Hot rolled steel rebar | ||
Brand name | DRAGON | ||
Theoretical weight and section area of each diameter as below for your information:
Diameter(mm) | Section area (mm²) | Mass(kg/m) | Weight of 12m (kg) | Pcs/ton |
6 | 28.27 | 0.222 | 2.664 | 375.38 |
8 | 50.27 | 0.395 | 4.74 | 210.97 |
10 | 78.54 | 0.617 | 7.404 | 135.06 |
12 | 113.1 | 0.888 | 10.656 | 93.84 |
14 | 153.9 | 1.21 | 14.52 | 68.87 |
16 | 201.1 | 1.58 | 18.96 | 52.74 |
18 | 254.5 | 2.00 | 24 | 41.67 |
20 | 314.2 | 2.47 | 29.64 | 33.74 |
22 | 380.1 | 2.98 | 35.76 | 27.96 |
25 | 490.9 | 3.85 | 46.2 | 21.65 |
28 | 615.8 | 4.83 | 57.96 | 17.25 |
32 | 804.2 | 6.31 | 75.72 | 13.21 |
36 | 1018 | 7.99 | 98.88 | 10.43 |
40 | 1257 | 9.87 | 118.44 | 8.44 |
50 | 1964 | 15.42 | 185.04 | 5.40 |
The production process of Steel Rebar
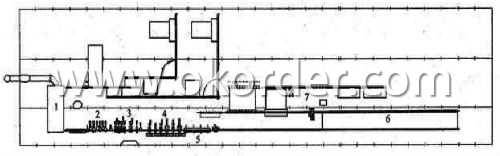
1-Waling beam furnace 2-Roughing rolling group 3-Intermediate rolling train
4-Finishing rolling group 5-Water-cooling device 6-Walking beam cooler
7-Finishing equipment(including the cold scale shear,short feet collection system,
automatic counting device,bundling machine, collect bench)
Usage and Applications of Hot Rolled Deformed Steel Rebars for Constrution:
Deformed bar is widely used in buildings, bridges, roads and other engineering construction. Big to highways, railways, bridges, culverts, tunnels, public facilities such as flood control, dam, small to housing construction, beam, column, wall and the foundation of the plate, deformed bar is an integral structure material. With the development of world economy and the vigorous development of infrastructure construction, real estate, the demand for deformed bar will be larger and larger..
Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Deformed Steel Rebars for Constrution:
Packaging Detail: products are packed in bundle and then shipped by container or bulk vessel, deformed bar is usually naked strapping delivery, when storing, please pay attention to moisture proof. The performance of rust will produce adverse effect.
Each bundle weight: 2-3MT, or as required
Payment terms: TT payment in advance or Irrevocable LC at sight.
Trade terms :FOB, CFR, CIF
Label:to be specified by customer, generally, each bundle has 1-2 labels
Steel Rebar in stock

Note:
1. Our products are produced according to national standard (GB), if not, supply according to national standards (GB) or agreement as customer required.
2. Other Grade and Standard Deformed Steel Bar we can supply:
Grade: GR40/GR60, G460B/B500A/B500B/B500C,BST500S
Standard: ASTM, BS, DIN
The Minimum Order Quantity of these products is high, and need to be confirmed.
3. We can not only supply Deformed Steel Bar; if you need anything about building materials, please contact us for further information.
4. Please send us your detail specifications when inquire. We will reply to you as soon as possible. We sincerely hope we can establish a long stable business relationship.
- Q: What are the design considerations for using steel rebars in construction?
- Some important design considerations for using steel rebars in construction include the required strength and load-bearing capacity, corrosion resistance, compatibility with other construction materials, durability, and ease of installation. Steel rebars should be chosen based on their appropriate diameter, grade, and spacing to ensure structural integrity and safety. Additionally, proper detailing and placement of rebars are essential to ensure that they are effectively embedded within concrete and can withstand the anticipated stresses and forces during construction and throughout the lifespan of the structure.
- Q: How are steel rebars specified in construction drawings?
- Steel rebars are typically specified in construction drawings by indicating their size, shape, and spacing, along with any specific requirements such as grade or coating. This information is usually provided through symbols, labels, or callouts on the drawings.
- Q: Can steel rebars be used in structures with high thermal insulation requirements?
- In structures requiring high thermal insulation, the use of steel rebars is possible, but precautions must be taken to minimize thermal bridging. Steel, being an efficient conductor of heat, can compromise the insulation of the structure if the rebars are not adequately insulated. However, there are various strategies available to tackle this issue. One possible approach involves utilizing rebars with lower thermal conductivity, like stainless steel rebars, which offer superior insulation properties compared to regular steel rebars. Another option is to thermally separate the rebars by applying insulation materials or coatings around them to prevent heat transfer. Additionally, meticulous detailing and design play a crucial role in reducing thermal bridging. Ensuring proper embedding of rebars within the insulation layer and avoiding direct contact between the rebars and the structure's exterior or interior surfaces can effectively minimize heat transfer. In conclusion, although steel rebars can be used in structures with high thermal insulation requirements, it is essential to implement appropriate measures to address thermal bridging and maintain the desired insulation level.
- Q: Can steel rebars be used in historical bridge restoration?
- Yes, steel rebars can be used in historical bridge restoration. In many cases, historical bridges may have deteriorated or suffered damage over time, and steel rebars can provide strength and stability during the restoration process. Steel rebars are commonly used in reinforced concrete structures and can help reinforce the bridge's structural integrity. However, it is important to consider the aesthetics of the historical bridge and ensure that the use of steel rebars does not compromise its historical value or appearance. Preservation guidelines and consultations with historical experts can help determine the appropriate use of steel rebars in historical bridge restoration projects.
- Q: What are the different types of steel rebars used in underground structures?
- There are several types of steel rebars commonly used in underground structures, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. The choice of rebar type depends on various factors such as the specific requirements of the project, the load-bearing capacity needed, and the environmental conditions of the underground structure. 1. Mild Steel Rebars: Also known as carbon steel rebars, these are the most commonly used type due to their affordability and availability. Mild steel rebars have a low carbon content and provide good tensile strength, making them suitable for general construction purposes in underground structures. 2. High Strength Deformed (HSD) Rebars: HSD rebars are made from carbon steel and undergo additional heat treatment processes, which result in higher yield strength and improved resistance to corrosion. These rebars are commonly used in areas with high seismic activity or where increased load-bearing capacity is required. 3. Epoxy-Coated Rebars: Underground structures can be exposed to aggressive environments, including moisture and chemicals, which can lead to corrosion. Epoxy-coated rebars are designed to provide enhanced corrosion resistance by applying an epoxy coating to the surface of the rebar. This coating acts as a protective barrier, reducing the risk of corrosion and extending the lifespan of the rebar. 4. Stainless Steel Rebars: Stainless steel rebars are highly resistant to corrosion and are therefore suitable for use in harsh underground environments. They are particularly beneficial in structures where chloride or other corrosive agents are present, such as underground water treatment facilities or sewer systems. 5. Galvanized Rebars: Galvanized rebars are coated with a layer of zinc to provide corrosion protection. This type of rebar is commonly used in underground structures where moisture or exposure to corrosive elements is a concern. The zinc coating acts as a sacrificial layer, corroding in place of the rebar and extending its service life. In conclusion, the different types of steel rebars used in underground structures include mild steel rebars, high strength deformed rebars, epoxy-coated rebars, stainless steel rebars, and galvanized rebars. The selection of the appropriate rebar type depends on the specific requirements and environmental conditions of the underground structure.
- Q: How do steel rebars affect the overall cost of a construction project?
- Steel rebars can significantly affect the overall cost of a construction project. While they add to the material and labor costs, rebars also provide structural strength and reinforcement to concrete, reducing the risk of structural failures and increasing the project's durability. Therefore, although rebars may increase the upfront expenses, their use can help prevent expensive repairs and maintenance in the long run, making them a cost-effective investment in the overall construction project.
- Q: What is the process of installing steel rebars in slabs and beams?
- The process of installing steel rebars in slabs and beams involves several steps to ensure proper reinforcement of the concrete structure. 1. Design and engineering: Before starting the installation process, the structural engineer designs the reinforcement layout based on the specific requirements of the project. This design considers factors such as load-bearing capacity, span length, and structural integrity. 2. Marking and layout: Once the design is finalized, the layout is marked on the slab or beam using chalk lines or other appropriate methods. This helps guide the installation process and maintain accuracy. 3. Cutting and bending rebars: Steel rebars are usually delivered in long lengths and need to be cut and bent according to the specific dimensions and angles required by the design. This process is done using specialized tools like rebar cutters and benders. 4. Placement and support: After the rebars are cut and bent, they are placed in the marked positions on the slab or beam. The rebars are supported using rebar chairs, spacers, or other suitable devices to ensure they remain in the correct position during the pouring of concrete. 5. Tying and securing: Once the rebars are correctly positioned, they are tied together using wire or other appropriate binding material. This ensures the rebars remain in their designated spots and maintain proper spacing and alignment. 6. Inspection and approval: After the rebars are installed, an inspection is carried out to verify that they meet the design specifications and are properly positioned. This inspection is usually performed by a qualified engineer or inspector who checks for compliance with building codes and standards. 7. Concrete pouring: After the rebars are inspected and approved, the concrete is poured over the reinforced area. The rebars act as reinforcement, providing added strength and stability to the structure. 8. Curing and finishing: Once the concrete is poured, it needs to cure and harden over a specific period. During this time, it is essential to protect the newly installed rebars and concrete from excessive moisture and temperature fluctuations. After curing, finishing processes such as leveling, smoothing, and surface treatments may be carried out to achieve the desired appearance and functionality. Overall, the process of installing steel rebars in slabs and beams involves careful planning, precise cutting and bending, accurate placement, proper securing, and thorough inspection to ensure a reinforced structure that meets design requirements and provides long-lasting strength and durability.
- Q: Can steel rebars be bent or shaped on-site?
- Yes, steel rebars can be bent or shaped on-site using specialized equipment or tools such as rebar benders or hydraulic benders. This allows for flexibility in adjusting the rebars to fit specific construction requirements or designs.
- Q: What are the safety precautions to take when working with steel rebars?
- When working with steel rebars, it is crucial to follow various safety precautions to ensure the well-being of yourself and those around you. Here are some safety measures to consider: 1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate PPE such as safety goggles, gloves, hard hats, and steel-toed boots to protect yourself from potential hazards like falling objects, cuts, and burns. 2. Training and Awareness: Obtain proper training and be aware of the potential risks associated with working with steel rebars. Educate yourself and your team about the correct procedures and safe handling techniques. 3. Secure Storage: Store steel rebars in a designated area to prevent them from falling or causing accidents. Stack them systematically, ensuring stability and avoiding areas with heavy foot traffic. 4. Lifting Techniques: When lifting steel rebars, use proper lifting techniques such as bending your knees and using your legs to lift rather than your back. Avoid overloading yourself and seek assistance when needed. 5. Handling Tools: Use suitable tools like wire mesh gloves or pliers to handle steel rebars. This prevents injuries caused by sharp edges or splinters. 6. Inspection: Regularly inspect steel rebars for any defects, such as rust or sharp edges, before using them. Damaged or defective rebars should be discarded and replaced. 7. Clear Work Area: Keep the work area organized and free from clutter, ensuring that there are no tripping hazards or obstacles that could cause accidents. 8. Communication: Maintain clear communication with your team members, signaling when moving or handling steel rebars. This helps prevent accidental collisions or injuries. 9. Fire Safety: Be mindful of fire hazards when working with steel rebars. Keep flammable materials away from the work area and have fire extinguishers readily accessible. 10. First Aid: Ensure that a first aid kit is available nearby, and be familiar with basic first aid procedures in case of any accidents or injuries. By following these safety precautions, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and injuries while working with steel rebars. Remember, safety should always be a top priority in any work environment.
- Q: What are the potential risks of using steel rebars in construction?
- Some potential risks of using steel rebars in construction include corrosion, inadequate bonding with concrete, and potential for structural failure if not properly installed or maintained. Additionally, steel rebars can conduct electricity, posing a risk in areas with electrical currents or lightning storms.
Send your message to us
Hot Rolled Deformed Steel Rebars for Constrution
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 200000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























