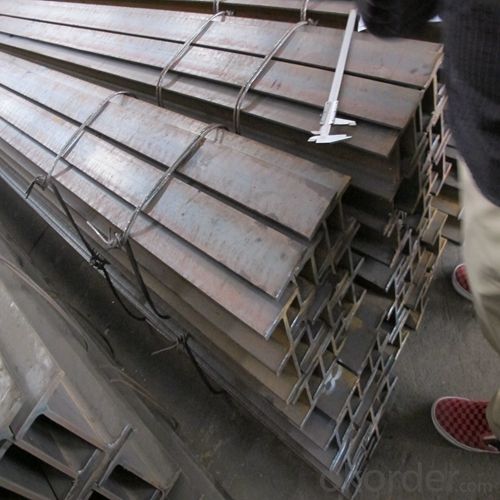
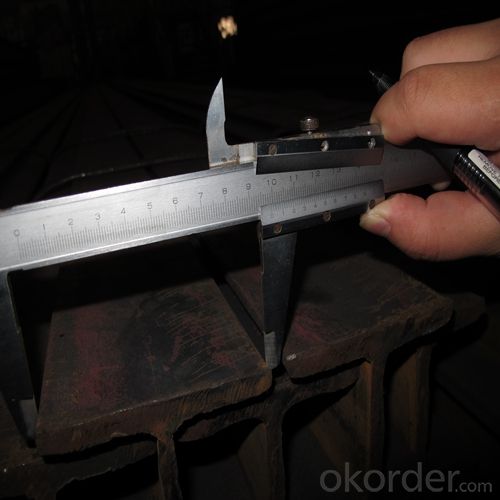
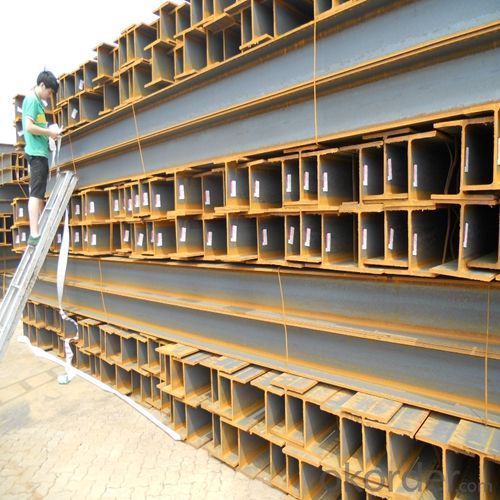
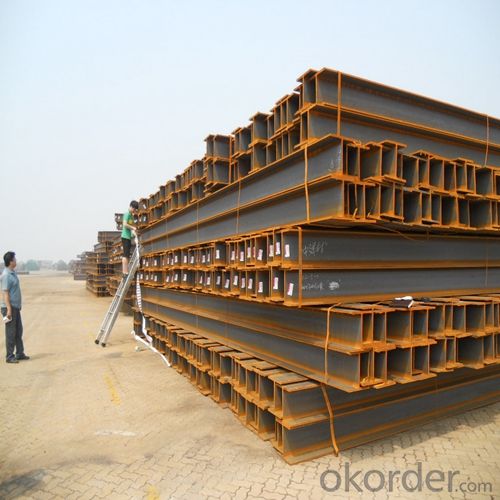
H-Beam Hot Rolled Structure Steel Made In China JIS Standard GB Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Product Description:
ecifications of Hot Rolled Steel H-beam
1. Standard: JIS 3192
2. Grade: SS400 or Equivalent
3. Length: 10m, 12m as following table
4. Invoicing on theoretical weight or actual weight as customer request
5.Payment: TT or L/C
6. Sizes:
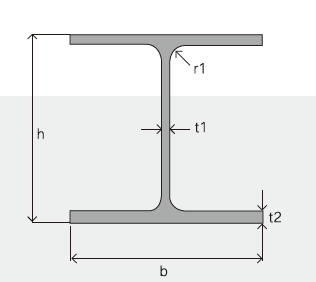
H x B (mm) | T1 | T2 | JIS Weight (kg/m) | GB Weight (kg/m) |
100*100 | 6 | 8 | 16.9 | 17.2 |
125*125 | 6.5 | 9 | 23.6 | 23.8 |
150*75 | 5 | 7 | 14 | 14.3 |
148*100 | 6 | 9 | 20.7 | 21.4 |
150*150 | 7 | 10 | 31.1 | 31.9 |
175*90 | 5 | 8 | 18 | 18.2 |
175*175 | 7.5 | 11 | 40.4 | 40.4 |
198*99 | 4.5 | 7 | 17.8 | 18.5 |
200*100 | 5.5 | 8 | 20.9 | 21.7 |
194*150 | 6 | 9 | 29.9 | 31.2 |
200*200 | 8 | 12 | 49.9 | 50.5 |
248*124 | 5 | 8 | 25.1 | 25.8 |
250*125 | 6 | 9 | 29 | 29.7 |
244*175 | 7 | 11 | 43.6 | 44.1 |
250*250 | 9 | 14 | 71.8 | 72.4 |
298*149 | 5.5 | 8 | 32 | 32.6 |
298*201 | 9 | 14 | 65.4 | |
300*150 | 6.5 | 9 | 36.7 | 37.3 |
294*200 | 8 | 12 | 55.8 | 57.3 |
300*300 | 10 | 15 | 93 | 94.5 |
346*174 | 6 | 9 | 41.2 | 41.8 |
350*175 | 7 | 11 | 49.4 | 50 |
340*250 | 9 | 14 | 78.1 | 79.7 |
350*350 | 12 | 19 | 135 | 137 |
400*200 | 8 | 13 | 65.4 | 66 |
390*300 | 10 | 16 | 105 | 107 |
400*400 | 13 | 21 | 172 | 172 |
446*199 | 8 | 12 | 65.1 | 66.7 |
450*200 | 9 | 14 | 77.9 | 79.5 |
440*300 | 11 | 18 | 121 | 124 |
496*199 | 9 | 14 | 77.9 | 79.5 |
500*200 | 10 | 16 | 88.2 | 89.6 |
488*300 | 11 | 18 | 125 | 129 |
596*199 | 10 | 15 | 92.5 | 95.1 |
600*200 | 11 | 17 | 103.4 | 106 |
588*300 | 12 | 20 | 147 | 151 |
700*300 | 13 | 24 | 182 | 185 |
800*300 | 14 | 26 | 207 | 210 |
900*300 | 16 | 28 | 240.1 | 243 |
Packaging & Delivery of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
1. Packing: it is nude packed in bundles by steel wire rod
2. Bundle weight: not more than 3.5MT for bulk vessel; less than 3 MT for container load
3. Marks:
Color marking: There will be color marking on both end of the bundle for the cargo delivered by bulk vessel. That makes it easily to distinguish at the destination port.
Tag mark: there will be tag mark tied up on the bundles. The information usually including supplier logo and name, product name, made in China, shipping marks and other information request by the customer.
If loading by container the marking is not needed, but we will prepare it as customer request.
4. Transportation: the goods are delivered by truck from mill to loading port, the maximum quantity can be loaded is around 40MTs by each truck. If the order quantity cannot reach the full truck loaded, the transportation cost per ton will be little higher than full load.
5. Delivered by container or bulk vessel
Production flow of Hot Rolled Structural Steel H Beam
Material prepare (billet) —heat up—rough rolling—precision rolling—cooling—packing—storage and transportation
- Q: How do steel angles contribute to the overall torsional stiffness of a structure?
- Steel angles can contribute to the overall torsional stiffness of a structure in several ways. Firstly, steel angles have a high moment of inertia, which means they are resistant to bending. This resistance to bending helps to distribute and resist the torsional forces acting on the structure, reducing any twisting or warping that may occur. Secondly, steel angles can be strategically placed and connected in a structure to form bracing or reinforcement systems. These systems help to transfer and distribute torsional forces throughout the structure, preventing localized areas from experiencing excessive twisting or distortion. Furthermore, steel angles can be used to create rigid connections between different structural members, such as beams or columns. These connections enhance the overall stiffness of the structure by effectively transmitting torsional forces between the connected members, minimizing any relative movement or deformation. Moreover, steel angles can also be utilized as diagonal members in truss structures or frames. By introducing diagonals, the angles help to resist and distribute torsional forces, maintaining the overall stability and rigidity of the structure. Overall, steel angles play a crucial role in enhancing the torsional stiffness of a structure by providing resistance to bending, forming bracing or reinforcement systems, creating rigid connections, and acting as diagonal members. By effectively managing and distributing torsional forces, steel angles contribute to the overall stability, durability, and performance of the structure.
- Q: How do steel angles compare to wooden or concrete structural elements?
- Steel angles have several advantages over wooden or concrete structural elements. Firstly, steel angles are known for their exceptional strength and durability. They can bear heavy loads and resist deformation, making them ideal for supporting large structures or bridges. In comparison, wooden elements are prone to rot, warping, and degradation over time, while concrete elements may develop cracks or suffer from corrosion. Additionally, steel angles offer a high level of versatility in terms of design and construction. They can be easily fabricated into various shapes and sizes, allowing for customized solutions for different structural needs. This flexibility is not easily achievable with wooden or concrete elements, which are limited by their natural properties and construction techniques. Moreover, steel angles provide excellent fire resistance compared to wooden elements, which are highly flammable. Steel does not burn, and its structural integrity remains intact even in high-temperature environments. Concrete also offers fire resistance, but steel angles have the advantage of being lightweight, reducing the overall load on the structure. Another significant advantage of steel angles is their resistance to pests, such as termites or rodents, which can severely damage wooden structures. Steel is impervious to these threats, ensuring long-term stability and reducing maintenance costs. However, there are some drawbacks to using steel angles as well. One of the main concerns is the potential for corrosion, especially in environments with high moisture or chemical exposure. Regular maintenance, including protective coatings or galvanization, is necessary to prevent rust formation and maintain the steel's structural integrity. Furthermore, steel angles tend to have a higher upfront cost compared to wooden elements. However, their long-term durability and reduced maintenance requirements often result in cost savings over time. In conclusion, steel angles offer numerous advantages over wooden or concrete structural elements, including superior strength, versatility, fire resistance, pest resistance, and long-term durability. However, considerations such as corrosion prevention and initial costs should be taken into account when deciding on the most suitable structural material for a specific project.
- Q: What are the cost considerations for using steel angles?
- The cost considerations for using steel angles primarily include the price of the raw material itself, transportation costs, and any additional processing or fabrication expenses. Other factors to consider are the required quantity, size, and complexity of the angles, as these can impact the overall cost. Additionally, market demand, availability, and fluctuations in steel prices can influence the cost of using steel angles. It is also important to account for any potential maintenance or corrosion protection expenses over the lifespan of the steel angles.
- Q: Are steel angles readily available in the market?
- Yes, steel angles are readily available in the market. They are commonly found in hardware stores, construction supply shops, and online platforms, making them easily accessible for various applications.
- Q: What are the different manufacturing processes for steel angles?
- Some of the different manufacturing processes for steel angles include hot rolling, cold rolling, and extrusion.
- Q: What is the minimum thickness for a steel angle?
- The specific application and requirements determine the minimum thickness for a steel angle. Typically, steel angles come in various thicknesses, beginning at approximately 1/8 inch (3.175 mm) and extending to multiple inches thick. Nevertheless, it is crucial to consider factors like the load it will support, the structural design, and any applicable building codes or industry standards when determining the minimum thickness for a steel angle. Seeking advice from a structural engineer or referring to relevant guidelines can offer more precise information on the minimum thickness necessary for a steel angle in a particular scenario.
- Q: Where does channel steel use more? Where does angle iron use more?
- Hot rolled stainless steel light channel steel (YB164-63) hot rolled light channel steel is a kind of steel with wide legs and thin wall, which has better economic effect than ordinary hot rolled channel steel. Its specifications range from 5-40#. In 1966, standard specifications ranged from 10-40#. Main applications: building and steel structure etc..
- Q: What are the fire resistance properties of steel angles?
- Steel angles have excellent fire resistance properties due to their high melting point and structural integrity. They can withstand high temperatures for an extended period without deformation or failure. Additionally, steel angles do not burn or contribute to the spread of fire, making them a reliable choice for fire-resistant construction and applications.
- Q: How do steel angles contribute to the stability of a structure?
- Steel angles contribute to the stability of a structure in several ways. First and foremost, steel angles are commonly used as structural members in various applications such as buildings, bridges, and towers. They provide strength and stability to the overall structure. The unique shape of steel angles, with one side longer than the other, allows them to resist both compression and tension forces, making them perfect for carrying heavy loads. Furthermore, steel angles are often used to create rigid connections between different structural components. By welding or bolting steel angles at critical joints, they help distribute the load evenly and prevent excessive movement or deformation. This enhances the overall stability and integrity of the structure, especially during dynamic loads such as wind or seismic forces. In addition, steel angles can also be utilized as bracing elements. Bracing is crucial for resisting lateral forces like wind or earthquake loads. By strategically placing steel angles diagonally between structural members, they create a triangulated system that improves the overall stability of the structure. This bracing helps prevent excessive sway or deflection, ensuring the structure remains rigid and secure. Moreover, steel angles are highly durable and resistant to corrosion, which is essential for the long-term stability of a structure. They can withstand harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to moisture, UV radiation, and temperature fluctuations. This durability ensures that steel angles maintain their structural integrity over time, providing ongoing stability and safety. Overall, steel angles play a vital role in ensuring the stability of a structure. Their ability to resist both compression and tension forces, create rigid connections, act as bracing elements, and their durability make them indispensable in various construction projects. By incorporating steel angles in the design and construction process, engineers can enhance the stability, strength, and safety of the structure, ultimately providing a reliable and long-lasting solution.
- Q: How do you determine the required number of fasteners for a steel angle connection?
- To determine the required number of fasteners for a steel angle connection, several factors need to be considered. These include the load being applied, the size and thickness of the angle, the type and strength of the fasteners being used, and any applicable building codes or engineering standards. Typically, calculations or guidelines provided by structural engineers or industry standards are used to determine the minimum number and spacing of fasteners needed to ensure the connection is strong and safe.
Send your message to us
H-Beam Hot Rolled Structure Steel Made In China JIS Standard GB Standard
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 5000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































