Currugated Galvanized Steel Sheet in High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Hot-dip Zinc Coating Steel Building Roof Walls
1.Structure of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Description:
Hot-dip galvanized steel coils are available with a pure zinc coating through the hot-dip galvanizing process. It offers the economy, strength and formability of steel combined with the corrosion resistance of zinc. The hot-dip process is the process by which steel gets coated in layers of zinc to protect against rust. It is especially useful for countless outdoor and industrial applications. Production of cold formed corrugated sheets and profiles for roofing, cladding, decking, tiles, sandwich walls, rainwater protective systems, air conditioning duct as well as electrical appliances and engineering.
2.Main Features of the Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
• Excellent process capability
• Smooth and flat surface
• Workability, durability
• Excellent anticorrosive property
• High strength
• Good formability
• Good visual effect
3.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Images:
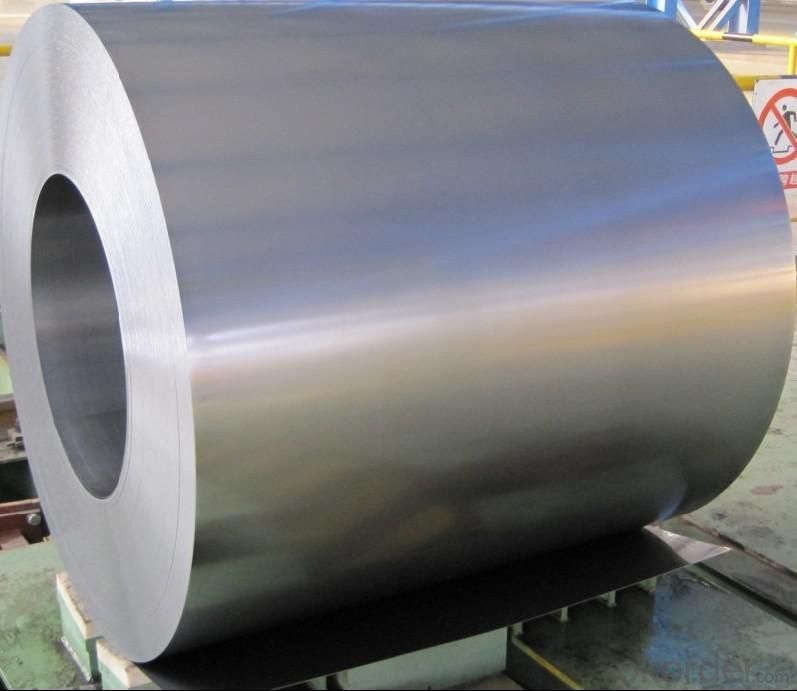


4.Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet Specification:
Standard: ASTM, JIS,EN
Grade: CS, DX51D+Z,SGCC, SS 230~550,S220GD+Z~S550GD+Z, SGC340~SGC570
Thickness: 0.1mm~5mm
Width: max 2000mm
Coil weight:3-12 MT
Coil ID:508/610mm
Surface structure: zero spangle, regular spangle or minimum spangle
Surface treatment: Chromate treatment, Oiled/dry, skinpassed/non-skinpassed
Packing: Standard seaworthy export package
Technology test results:
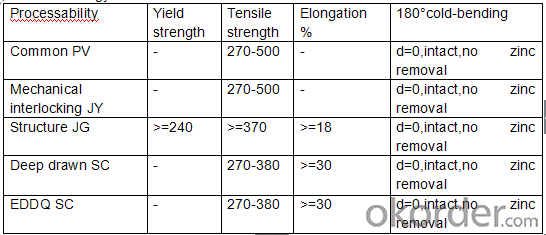
5.FAQ of Hot-Dip Galvanized Steel Sheet:
We have organized several common questions for our clients,may help you sincerely:
1.How about your company?
A world class manufacturer & supplier of castings forging in carbon steel and alloy steel,is one of the large-scale professional investment casting production bases in China,consisting of both casting foundry forging and machining factory. Annually more than 8000 tons Precision casting and forging parts are exported to markets in Europe,America and Japan. OEM casting and forging service available according to customer’s requirements.
2.How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test;We resolutely put an end to unqualified products flowing into the market. At the same time, we will provide necessary follow-up service assurance.
3. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-30 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for elevator shafts?
- Indeed, elevator shafts can utilize steel sheets. Steel, renowned for its durability, strength, and fire-resistant qualities, finds widespread application in the construction of elevator shafts. Typically, steel sheets are employed to form the walls and floors of these shafts, furnishing them with structural reinforcement and ensuring the safety of the entire elevator system. These sheets can be easily fabricated, allowing for precise tailoring to accommodate the specific dimensions and design prerequisites of the shaft. Moreover, various coatings can be applied to steel sheets to impede corrosion and bolster their longevity. Consequently, steel sheets represent a fitting choice for the construction of elevator shafts, providing a dependable and sturdy solution for vertical transportation systems.
- Q: Do the steel sheets have any specific certifications?
- The quality and compliance of the steel sheets are ensured through specific certifications. These certifications are typically granted by reputable organizations like the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) or specific regulatory bodies based on the country or region. The common certifications for steel sheets include ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ISO 14001 for environmental management systems, and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety management systems. Furthermore, there might be industry-specific certifications, such as the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) standards or the European Committee for Standardization (EN) certifications. These certifications guarantee that the steel sheets meet specific criteria for various attributes, including material composition, mechanical properties, and manufacturing processes.
- Q: What is the typical lifespan of painted steel sheets?
- The typical lifespan of painted steel sheets can vary depending on several factors such as the quality of the paint used, the environmental conditions they are exposed to, and the maintenance and care given to the sheets. Generally, painted steel sheets can last anywhere from 20 to 40 years. However, if the paint is of high quality and the sheets are properly maintained, their lifespan can be extended even further. Regular cleaning, inspection for any signs of damage or corrosion, and appropriate touch-ups or repainting can help prolong the lifespan of painted steel sheets. Additionally, factors such as exposure to harsh weather conditions, chemicals, or corrosive environments can also impact the longevity of painted steel sheets. It is worth considering these factors and conducting regular maintenance to ensure the extended lifespan of painted steel sheets.
- Q: Are steel sheets suitable for magnetic shielding?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for magnetic shielding as they have high magnetic permeability which helps in redirecting and absorbing magnetic fields, effectively reducing their strength.
- Q: How do steel sheets perform in terms of air permeability?
- Steel sheets are not permeable to air, meaning they do not allow air to pass through them easily.
- Q: How are steel sheets protected during welding?
- Steel sheets are protected during welding through the use of various methods such as shielding gases, fluxes, and coatings. Shielding gases, like argon or carbon dioxide, create a protective atmosphere around the welding arc, preventing oxidation and contamination of the molten metal. Fluxes can be applied to the surface of the steel sheets, which react with the impurities and form a protective slag layer. Additionally, coatings such as anti-spatter sprays or heat-resistant tapes can be used to protect the steel sheets from weld spatter and heat damage.
- Q: What are the benefits of using pre-painted steel sheets?
- There are several benefits to using pre-painted steel sheets in various applications. Firstly, pre-painted steel sheets offer enhanced durability and longevity compared to other materials. The paint coating on these sheets provides a protective barrier against corrosion, rust, and weathering, ensuring that the steel remains in excellent condition for an extended period of time. This makes pre-painted steel sheets ideal for outdoor use, where they are continuously exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Secondly, pre-painted steel sheets offer a wide range of color options and finishes, allowing for greater design flexibility. Whether it's for architectural purposes, interior decoration, or industrial applications, the availability of different colors and finishes enables the creation of aesthetically pleasing and visually appealing structures or products. Additionally, pre-painted steel sheets are easy to maintain and clean. The paint coating makes them resistant to stains, dirt, and grime, making them easier to keep clean and requiring less maintenance over time. This makes them an attractive choice for applications where cleanliness and hygiene are essential, such as in the food and beverage industry or healthcare facilities. Furthermore, pre-painted steel sheets are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of industries and applications. From roofing and cladding to automotive parts, appliances, and furniture, pre-painted steel sheets provide a reliable and cost-effective solution for various purposes. They can be easily fabricated, cut, and formed into desired shapes and sizes, making them suitable for diverse manufacturing processes. Lastly, pre-painted steel sheets are environmentally friendly. The paint coatings used on these sheets are typically formulated to be low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs), reducing their impact on air quality and human health. Additionally, the durability and longevity of pre-painted steel sheets contribute to a longer lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing waste. In conclusion, the benefits of using pre-painted steel sheets include enhanced durability, a wide range of design options, easy maintenance, versatility, and environmental friendliness. These advantages make pre-painted steel sheets a preferred choice for many industries and applications.
- Q: Are steel sheets resistant to mold and mildew?
- No, steel sheets are not resistant to mold and mildew.
- Q: Are steel sheets easy to clean and maintain?
- Yes, steel sheets are easy to clean and maintain. They have a smooth surface that can be wiped clean with a damp cloth or cleaned using mild soap and water. Additionally, steel sheets are resistant to staining, rusting, and corrosion, making them low-maintenance and durable.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for soundproofing purposes?
- Steel sheets are indeed suitable for soundproofing purposes. Due to its density and rigidity, steel effectively blocks the transmission of sound waves. When utilized in soundproofing applications, steel sheets aid in reducing the amount of sound that penetrates through walls, floors, or ceilings. They can be installed as a barrier or added as an extra layer to existing structures, thus enhancing their soundproofing capabilities. However, it is essential to acknowledge that relying solely on steel sheets may not guarantee complete soundproofing, as sound can still travel through alternate pathways like windows or doors. Therefore, a comprehensive soundproofing approach may entail combining steel sheets with other sound-absorbing materials, such as acoustic foam or insulation, to achieve optimal outcomes.
Send your message to us
Currugated Galvanized Steel Sheet in High Quality
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























