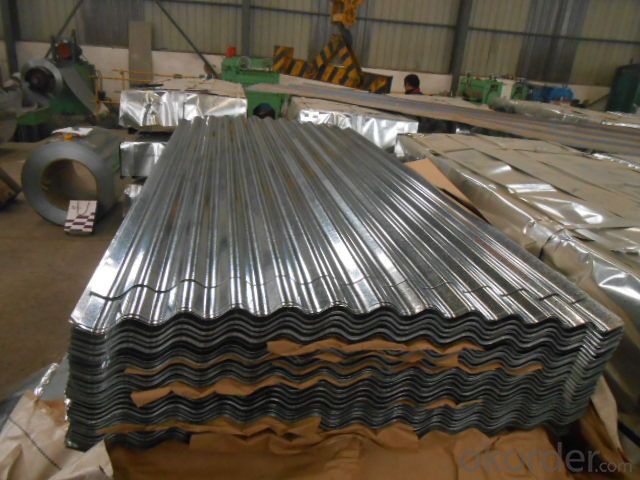
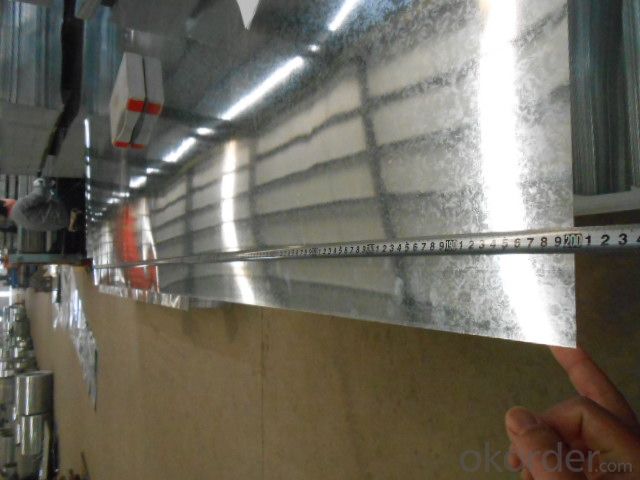
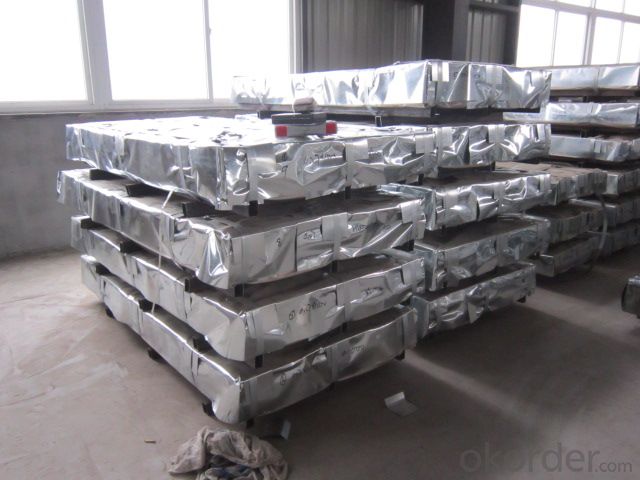
CORRUGATED HOT DIPPED GALVANIZED STEELSHEETS
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
CORRUGATED HOT DIPPED GALVANIZED STEEL SHEETS
THICKNESS TOLERANCE: (+/-0.01mm)
ZINC COATING: 50g/m2 (+/-10g/m2)
WIDTH: 900mm (0/+5mm; AFTER FORMING)
STANDARD:JIS G 3302, SGCH
SURFACE:REGULAR SPANGLE, CHROMATED, DRY
PACKAGE: 2- 3 TON/PALLET
SPECS: 0.18mm X 900mm X 2000mm
Specifications
1. Zinc coating :60-180g( as required)
2. thickness:0.14-0.80mm
3. width:700-1250mm( 750mm,900mm,1215mm,1250mm,1000mm the most common)
6. surface:regular/mini/zero spangle, chromated, skin pass, dry etc.
7.application: with excellent cold bending molded manufacturablity, good decoration effect, strong anti-corrosion ability, galvanized steel coils and sheets are also pollution-free and easily recycled. Accordingly, they can be used as final products and basic plates of color coated steel coils and widely applied in construction, home appliances, decoration, ect.
Package:Standard seaworthy export packing: 3 layers of packing, inside is
kraft paper, water plastic film is in the middle and outside GI steel
sheet to be covered by steel strips with lock.
- Q: How are steel sheets protected during welding?
- Shielding plays a crucial role in safeguarding steel sheets during welding. Its purpose is to shield the sheets from oxygen and other atmospheric contaminants that can lead to oxidation and impurities in the weld. Multiple methods are utilized to shield the steel sheets during welding. One commonly employed approach involves using a shielding gas, such as argon or carbon dioxide, which is directed towards the welding area to establish a protective atmosphere. This gas displaces the surrounding oxygen, effectively preventing it from reacting with the heated metal and causing oxidation. In addition to the use of shielding gas, another widely used method involves employing flux. Prior to welding, a substance known as flux is applied to the joint area of the steel sheets. Acting as a protective barrier, the flux creates a molten slag that covers the weld and provides shielding from the atmosphere. Flux can take the form of a powder, paste, or even a continuous wire feed during welding. Furthermore, certain welding techniques, like submerged arc welding, combine the use of both shielding gas and flux to offer optimal protection for the steel sheets. This technique involves the continuous feeding of granular flux along with the welding wire. As the flux melts, it forms a protective layer over the weld, while the shielding gas effectively prevents any atmospheric contamination. Overall, the safeguarding of steel sheets during welding is crucial for ensuring the weld's quality and integrity. Shielding methods, such as the use of shielding gas and flux, establish a protective environment that prevents the formation of oxidation, impurities, and other defects in the weld. Consequently, this results in a robust and long-lasting joint between the steel sheets.
- Q: What is the average thermal expansion coefficient of steel sheets?
- The average thermal expansion coefficient of steel sheets varies depending on the specific type of steel and its composition. However, a commonly accepted average value for the thermal expansion coefficient of steel sheets is around 12 x 10^-6 per degree Celsius (12 parts per million per degree Celsius). It is important to note that this value is an approximation and can vary slightly depending on the specific grade and composition of the steel being used.
- Q: Stainless steel plate and steel welding
- It is better to use argon arc welding or white steel welding rod, with electrode generally 3.2 or 2.5 can be, the color will change with some, wipe it will be good.
- Q: What is the process of laminating steel sheets?
- The process of laminating steel sheets involves bonding multiple layers of steel together to create a stronger and more durable material. This is typically done by applying heat and pressure to the sheets, which causes them to fuse together. The sheets are often coated with a layer of adhesive or resin before lamination to enhance the bonding process. The result is a laminated steel sheet that exhibits improved strength, resistance to corrosion, and other desirable properties.
- Q: What is the thickness of the steel sheets?
- The thickness of the steel sheets can vary depending on the specific application and requirements. Common thicknesses for steel sheets range from 0.4 millimeters to several inches, with standard measurements including 0.5 mm, 1.0 mm, 1.5 mm, 2.0 mm, 2.5 mm, and so on. However, it is important to note that the thickness can be customized based on the intended use, such as for construction, manufacturing, or automotive purposes. Therefore, it is essential to consult the specifications or inquire with the manufacturer or supplier to determine the exact thickness of the steel sheets in question.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for toolboxes and cabinets?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for toolboxes and cabinets. Steel is a durable and sturdy material that can withstand heavy loads, making it ideal for constructing toolboxes and cabinets that require strength and durability. Additionally, steel sheets can be easily welded or fastened together, allowing for customization and flexibility in design.
- Q: Are the steel sheets suitable for architectural cladding?
- Yes, steel sheets are suitable for architectural cladding. Steel is a strong and durable material that provides excellent protection against weather elements and other external factors. It can be easily shaped and fabricated into various designs, making it highly versatile for architectural applications. Steel cladding also offers a modern and sleek aesthetic, allowing for flexibility in creating visually appealing building façades. Additionally, steel sheets can be coated or painted to enhance their corrosion resistance and further customize their appearance. Overall, steel sheets are a popular choice for architectural cladding due to their strength, durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal.
- Q: What industries commonly use steel sheets?
- The industries that commonly use steel sheets include construction, automotive, manufacturing, aerospace, and shipbuilding.
- Q: What are the different grades of steel sheets available?
- There exists a variety of steel sheet grades, each possessing its own distinctive properties and applications. Among the commonly utilized grades are: 1. Carbon Steel: This grade of steel sheet is the most prevalent and extensively employed. It comprises varying carbon levels and is renowned for its robustness and durability. Carbon steel sheets find utility across diverse sectors, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing. 2. Stainless Steel: Distinguished by its elevated chromium content, this steel sheet grade showcases outstanding resistance to corrosion. Industries such as food processing, chemical, and medical frequently employ stainless steel sheets where corrosion resistance plays a pivotal role. 3. Galvanized Steel: To shield against corrosion, this type of steel sheet is coated with a layer of zinc. Galvanized steel sheets often serve in outdoor settings, such as roofing, fences, and gutters, where exposure to moisture and the elements is commonplace. 4. Alloy Steel: By incorporating additional elements like manganese, nickel, or chromium, this grade of steel sheet enhances its mechanical properties. Alloy steel sheets are extensively used in applications demanding heightened strength, such as construction equipment, aircraft components, and machinery. 5. Tool Steel: Designed with elevated hardness and wear resistance, this grade of steel sheet is ideal for tools and dies. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing frequently employ tool steel sheets. It's crucial to note that these represent only a fraction of the available steel sheet grades, as numerous specialized grades are tailored to specific applications. The choice of grade depends on factors such as desired strength, corrosion resistance, and specific application requirements.
- Q: What is the difference between a smooth and patterned steel sheet?
- A smooth steel sheet typically has a plain, uniform surface without any visible patterns or textures. It has a consistent and sleek appearance, making it suitable for applications where a clean, modern look is desired. On the other hand, a patterned steel sheet features various designs or textures that are embossed or etched onto the surface. These patterns can range from simple geometric shapes to intricate motifs. Patterned steel sheets are often chosen for their decorative appeal and ability to add visual interest to a space. They can be used in architectural elements, such as wall panels or ceiling tiles, to create a unique and artistic effect. In terms of functionality, smooth steel sheets may offer slightly better corrosion resistance due to their smoother surface, making them suitable for applications where protection against rust is important, such as in outdoor or marine environments. Conversely, patterned steel sheets may have reduced corrosion resistance due to the variation in surface texture, potentially offering less protection against rust. Overall, the choice between a smooth and patterned steel sheet depends on the desired aesthetic, functional requirements, and the intended application.
Send your message to us
CORRUGATED HOT DIPPED GALVANIZED STEELSHEETS
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords