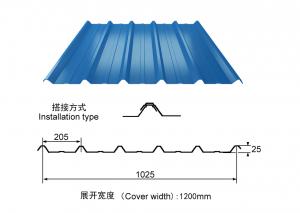
CORRIGATED SHEET
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like
Product Name:corrugated steel roofing sheet
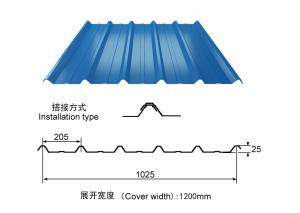
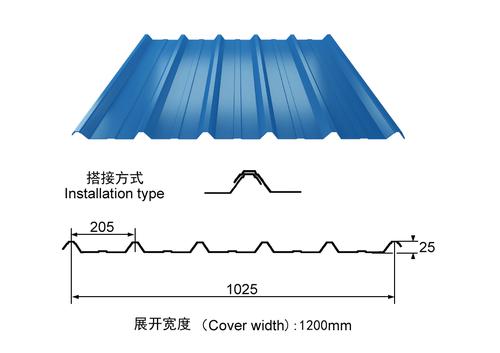
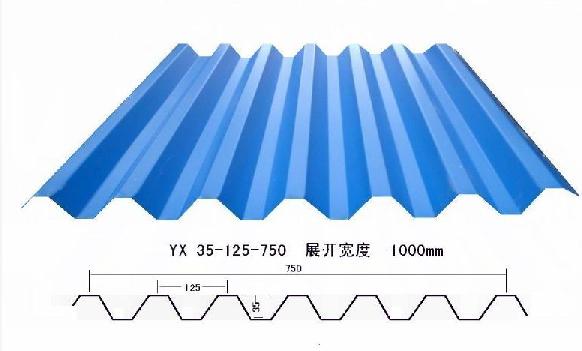
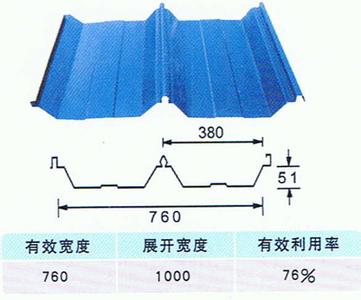
Effective Width:650mm to 1250mm
Thickness:0.13mm-0.8mm
Material PPGI/PPGL steel coil
Coating:Z30-Z275,AZ30-AZ180
Color:white,blue or any RAL colors
length:1m-11.8m according to the container
top color coating:12um-25um
Back color coating:7um-10um
HRB:50-95
Base plate:PRE-PAINTED ALUZINC STEEL COIL,PRE-PAINTED GALVANIZED STEEL COIL
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for elevator panels or interiors?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for elevator panels or interiors. Steel is a durable and versatile material that is commonly used in elevator construction. It can provide a sleek and modern look while also offering strength and stability to the elevator panels and interiors.
- Q: How long do steel sheets typically last?
- Steel sheets can typically last for several decades, depending on various factors such as the quality of the steel, the environment it is exposed to, and proper maintenance.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for manufacturing agricultural equipment?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for manufacturing agricultural equipment. Steel is a durable and strong material that can withstand the rigors of agricultural activities and provide the necessary strength and stability required for equipment such as plows, cultivators, and trailers. Steel sheets can be shaped, welded, and fabricated into various components, making them suitable for manufacturing a wide range of agricultural equipment.
- Q: What is the specific heat capacity of steel sheets?
- The specific heat capacity of steel sheets is approximately 0.45 J/g°C.
- Q: What is the average moisture resistance of steel sheets?
- The average moisture resistance of steel sheets can vary depending on the specific type of steel and the protective coatings applied. Generally, steel sheets exhibit good moisture resistance due to their inherent ability to resist corrosion. However, additional surface treatments like galvanization can further improve their resistance by adding a layer of zinc to protect against moisture and corrosion. Providing an exact average moisture resistance value is challenging as it depends on factors such as the steel grade, thickness, and coating. Steel sheets with galvanized coatings typically offer excellent moisture resistance, with some studies reporting corrosion rates as low as 0.1-0.5 micrometers per year in highly corrosive environments. It is important to consider that the performance of steel sheets in resisting moisture can also be affected by factors like scratches, cuts, or exposure to chemicals. Proper maintenance, regular inspection, and careful handling of steel sheets are crucial to ensure their optimal moisture resistance over time.
- Q: What are the different surface treatments for color-coated steel sheets?
- Some common surface treatments for color-coated steel sheets include galvanized coating, galvalume coating, and organic coating.
- Q: What is the typical yield strength of stainless steel sheets?
- The yield strength of stainless steel sheets can vary based on factors such as the grade and thickness of the material. On average, stainless steel sheets possess a yield strength within the range of 30,000 to 80,000 psi. It should be noted that the yield strength differs among various grades of stainless steel, such as 304, 316, or 430. Moreover, the thickness of the sheet also impacts the yield strength, with thinner sheets generally exhibiting lower yield strengths when compared to thicker sheets. Therefore, it is advisable to refer to the manufacturer or supplier's specific grade and thickness specifications to ascertain the precise yield strength of a given stainless steel sheet.
- Q: Can steel sheets be used for electrical transformers?
- Yes, steel sheets can be used for electrical transformers. Steel is often used as the core material in transformers due to its magnetic properties and ability to efficiently conduct magnetic flux.
- Q: What are the common thicknesses for cold-rolled steel sheets?
- The common thicknesses for cold-rolled steel sheets typically range from 0.4mm to 3mm.
- Q: What is the typical composition of stainless steel sheets?
- Stainless steel sheets are primarily made up of iron, chromium, and nickel. These three elements are the main components that give stainless steel its unique properties. The amount of each element can vary depending on the specific grade of stainless steel being used, but generally, stainless steel sheets contain around 10-30% chromium and 8-20% nickel. Additionally, small amounts of other elements such as carbon, manganese, and molybdenum may be present to further enhance the strength, corrosion resistance, and other desired characteristics of the stainless steel. The composition of stainless steel sheets is carefully balanced to achieve the desired combination of strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, making it a popular choice for various applications in industries such as construction, automotive, and manufacturing.
Send your message to us
CORRIGATED SHEET
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords