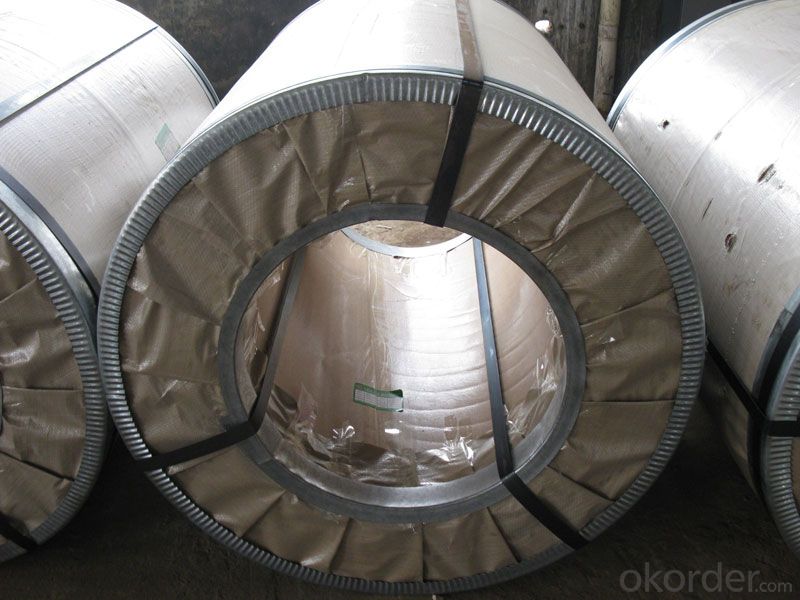
Cold Rolled Steel Coil JIS G3141 -in Low Price
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Cold Rolled Steel Coil JIS G3141 -in Low Price
1.Structure of Cold Rolled Steel Coil JIS G3141 Description:
The raw material of cold rolled steel coil/sheet is high quality hot rolled product, and after pickling continuous rolling, degreasing, annealing,skin pass,slitting and cut to length line etc. Along with it many kinds of new technology and new process of global cold rolling production have been applied.
2.Main Features of the Cold Rolled Steel:
• Excellent process capability
• Smooth and flat surface
• High strength
3. Cold Rolled Steel Images:


4.
Cold Rolled Steel Coil JIS G3141 Specification:
Standard:AISI,ASTM,DIN,GB,JIS,JIS G3302 ASTM 653M EN10142
Grade: Q195~Q345
Thickness: 0.16mm~2.0mm
Width: 1250mm MAX
Coil weight:3-12 MT
Coil ID:508/610mm
FAQ :
1.How to guarantee the quality of the products?
We have established the international advanced quality management system,every link from raw material to final product we have strict quality test.
2. How long can we receive the product after purchase?
Usually within thirty working days after receiving buyer’s advance payment or LC. We will arrange the factory manufacturing as soon as possible. The cargo readiness usually takes 15-25 days, but the shipment will depend on the vessel situation.
- Q: Can steel coils be coated with organic materials?
- Yes, steel coils can be coated with organic materials. Organic coatings such as paints or varnishes can be applied to steel coils to provide protection against corrosion, improve aesthetics, or add other desired properties.
- Q: How do steel coils contribute to the marine vessel construction industry?
- The marine vessel construction industry heavily relies on steel coils as vital components. These coils, typically made of high-quality steel, are crucial for fabricating various structural elements of ships and boats. They are utilized in multiple ways to contribute to the construction and functionality of marine vessels. To begin with, steel coils are essential for constructing the hull, which serves as the main body of the ship. Given the harsh conditions at sea, such as waves, corrosion, and impacts, the hull requires strong and durable materials. Steel coils provide the necessary strength and integrity to ensure the structural stability and safety of the vessel. Furthermore, steel coils are utilized in fabricating decks, bulkheads, and other internal structures of marine vessels. These components are vital for dividing the ship into compartments, providing stability, and supporting various equipment and machinery. Steel coils, known for their excellent tensile strength, can bear heavy loads and resist deformation, making them ideal for constructing these crucial elements. In addition, steel coils are employed in the construction of propulsion systems and other mechanical parts of marine vessels. These coils are often shaped and formed into specific components, such as shafts, gears, and propellers, which are essential for the vessel's propulsion and maneuverability. The high strength and durability of steel coils ensure the reliability and efficiency of these mechanical systems, enabling smooth navigation and operation of the vessel. Moreover, steel coils contribute to the marine vessel construction industry by enhancing safety and longevity. Steel is highly resistant to corrosion, a major concern in marine environments due to saltwater exposure. By utilizing steel coils, marine vessels can withstand the corrosive effects of seawater, reducing the need for frequent maintenance and repair. This, in turn, improves the vessel's lifespan and minimizes the risk of accidents or failures at sea. In conclusion, steel coils are indispensable in the marine vessel construction industry. They provide the necessary strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion, ensuring the safety, performance, and longevity of ships and boats. Whether it is the construction of the hull, fabrication of internal structures, or creation of mechanical components, steel coils play a vital role in every aspect of marine vessel construction.
- Q: How are steel coils used in the manufacturing of HVAC ductwork?
- Steel coils are used in the manufacturing of HVAC ductwork to form the main structure of the ducts. The steel coils are processed and shaped into specific sizes and dimensions, allowing them to be easily fabricated into duct sections. These coils provide strength and durability to the ductwork, ensuring it can withstand the high pressures and temperatures involved in HVAC systems.
- Q: What are the dimensions of steel coils used in the industrial machinery industry?
- In the industrial machinery industry, the dimensions of steel coils can vary depending on the specific application and requirements. However, it is generally observed that steel coils used in this industry typically have a width ranging from 600 to 2,000 millimeters (24 to 79 inches) and a weight ranging from 2 to 25 metric tons (4,400 to 55,100 pounds). The core, or inner diameter, of the coil can range from 508 to 762 millimeters (20 to 30 inches). Furthermore, the thickness of the steel coil can range from 0.4 to 25 millimeters (0.016 to 0.98 inches). These dimensions may experience variations according to the specific needs and specifications of the machinery being manufactured or used in the industrial machinery industry.
- Q: Why people prefer prefabricated buildings these days? Recently my friend has told me that he is going to owe a steel house so I was just thinking are these steel structures really durable and cheaper than concrete structures?
- It really depends upon the environment and the construction techniques used. Steel that is painted or coated will without maintenance eventually rust. I would expect this tendency to be exacerbated in a humid or shore environment. Heat may tend to cook a steel house and the structure does not add much thermal mass. Construction techniques tend to be fairly quick a part of the construction is essentially prefabricated. Work done in a factory will almost always be cheaper than work done in the field, all things being equal. Concrete can be fairly hi tech with lots of equipment or as seen in many parts of the world fairly low tech with lots of laborers. It is easy to change the characteristics of concrete depending upon how it is mixed, reinforced, and treated during the curing process. Because it is applied in a relatively fluid state it can flow around obstructions like bedrock and be formed up into interesting shapes. A concrete structure can be cooler as it provides thermal mass, and a heat sink. It's resulting rigidity may make it more subject to earthquakes than steel. We do really need to be smarter in constructing our homes to make them fit the land and not only the general environment but our particular micro environment.
- Q: What is the role of steel coils in the production of storage tanks?
- Steel coils play a crucial role in the production of storage tanks as they are used to construct the cylindrical body of the tank. These coils are cut and shaped into the desired dimensions and then welded together to create a strong and durable structure. The high strength and corrosion resistance properties of steel make it an ideal material for storage tanks, ensuring the safety and longevity of the tanks in various industries such as oil and gas, chemical, and water storage.
- Q: I want to know what to my wash stainless fridge door with before applying the stainless steel polish.
- Tips For Cleaning Your Stainless Steel No matter if you are in an industrial kitchen or just your household kitchen, maintaining the look and the cleanliness of your stainless is essential. There are plenty of products on the market that claim to be able to help you, but you can also do just as good with just knowing how to handle it. Stainless steel is difficult to clean because streaks and fingerprints show up easily. It is easier to see grime, grease and fingertips on stainless than on windows. To help you to keep your stainless steal countertops, utensils and appliances clean, follow these basic rules of thumb. Much more at web page!!
- Q: What is the purpose of coating steel coils?
- The purpose of coating steel coils is to provide a protective layer that prevents corrosion and enhances the durability and lifespan of the steel.
- Q: I'm going to see Man Of Steel this weekend, and the reviews that I've been hearing aren't that good. I've been hearing that it's this depressing, dark, dramatic film with no humor, loud noises, and action on top of action (which is kind of what I expected from this movie). With that said, I was quite positive that this was what the fans wanted, a more serious Super Man interpretation. I'm ultimately going to judge the movie when I see it, but for now, I have 3 short questions for you:1) What did you think of Man Of Steel?2) Superman Returns got somewhat better reviews than Man Of Steel. Does it seem logical?3) There is a huge fan battle between Man Of Steel and Christopher Reeve's version of Super Man. Which one do you favor?
- I know nothing about Superman nor have I watched the other films or read the comics. Man Of Steel was a CGI-fest, maybe a little bit too much, though it is Zack Synder's style. I actually fell asleep for most of the movie, seeing only the first 30 minutes and last 45 minutes? So that might be a good indication or it could just be me. There were loads of action scenes but overall, the movie wasn't that impressionable to me. The storyline was quite standard and had nothing outstanding, not even humour. Lois Lane and Superman barely had much screen time together to establish any chemistry. The other characters were pretty flat as well. I did like the dark psychological themes of Superman's struggles and coming to terms with his abilities though.
Send your message to us
Cold Rolled Steel Coil JIS G3141 -in Low Price
- Loading Port:
- China main port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 50 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords