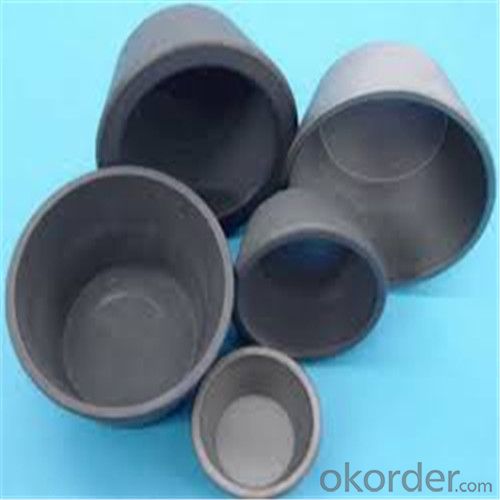
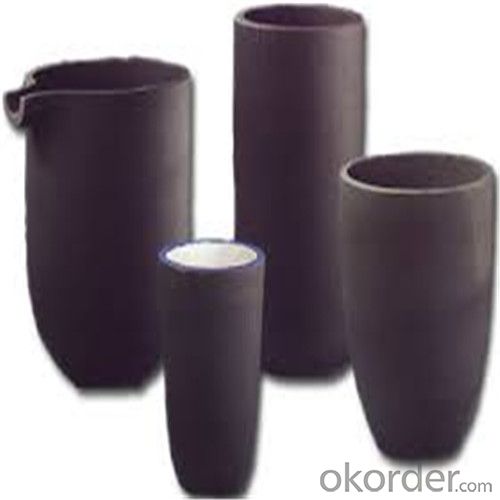
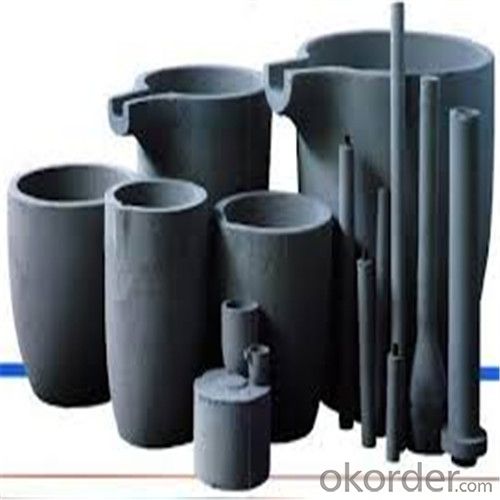
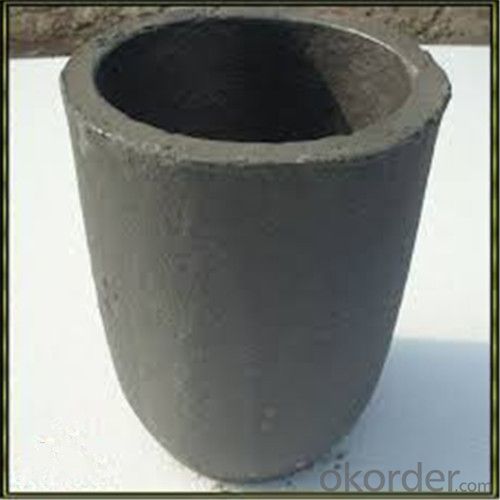
Borax Graphite Crucible for High Heat Resistance Copper Melting
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details for SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium,Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
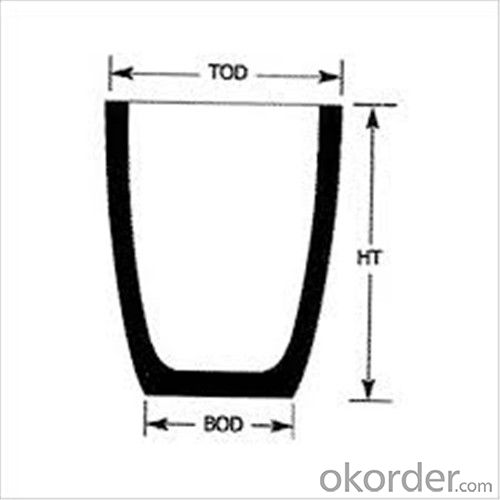
| Type: | High Strength, graphite crucible crucible | Application: | melting metal | Height: | as your requirements |
| Composition: | High Pure | Top Diameter: | 10-600mm | Bottom Diameter: | 10-1000mm |
| Place of Origin: | China (Mainland) | Brand Name: | Model Number: | ||
| Color: | Black grey | Si3N4%: | 5min | Fe2O3%: | 0.7max |
| C%: | 30-45 | Apparent porosity: | 30max | Refractoriness: | 1680 |
| Bulk Density: | 1.71min | Using life: | >5000 hours | MAX temperature: | 1600c |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Details: | Seaworty packing or as per customer's detail requirement of graphite crucible. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 20-30 days after confirm order of graphite cru |
SiC Crucibles For Melting Aluminium,Copper, Brass with High Heat Resistance
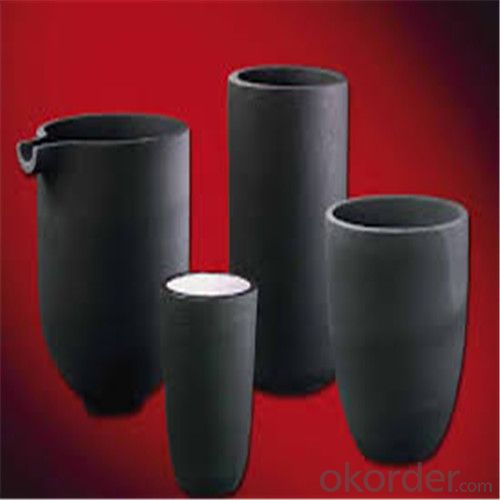

Features of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
1. resistance to deformation at high temperature,
2. thermal shock resistance, wear resistance, corrosion resistance.
3. anti-oxidation, anti- erosion.
Usage of SiC 95% silicon carbide sic crucible
electricity and steel slag trench,
coal chemical and mining transport pipeline.

FAQ
1.What's your MOQ?
We will indicate the MOQ for each item in the quotation list. We accept the sample and trail order.
2.Can I negotiate the Prices?
Sure, we may consider discounts for bulk order of products.
3.How long will it take to complete my order?
For the stock items, we can arrange the shippment within 2~3days after received your payment. For the customized items, we will indicate the delivery time in the quotation list.
4.Can you give warranty of your products?
Yes, we extend a 100% satifisfaction guarantee on all items. Please feel free to provide timely feedback if you're not satisfied with N&D's Quality and Service. For the overseas orders, if there is a quality problem, please kindly to provide the picturers to show the problem by e-mail. We will provide the replacements to you at our cost according to actual conditions.
5.Can I visit you?
Sure. If you're a volume buyer and would like to visit our in-house products and production line, please contact us to make an appointment.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used with gas burners or torches?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used with gas burners or torches. Graphite crucibles are known for their high heat resistance and durability, making them suitable for use with gas burners or torches. They can withstand extremely high temperatures and are often used in applications such as melting metals, glass, or other materials. The high thermal conductivity of graphite allows for efficient heat transfer, making it an ideal choice for such high-temperature applications. However, it is important to ensure that the crucible is properly sized and designed for the specific gas burner or torch being used to prevent any potential damage or safety hazards.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for metal powder atomization?
- Metal powder atomization can utilize graphite crucibles. These crucibles are widely employed in metallurgical procedures because of their impressive thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and resistance to extreme temperatures. During metal powder atomization, the crucible is subjected to high temperatures, causing the metal feedstock to melt and subsequently be atomized into fine powder particles through the use of a gas or water jet. The graphite crucible is instrumental in maintaining a stable temperature throughout the atomization process, as well as facilitating efficient heat transfer, leading to the production of consistent and high-quality metal powder. Moreover, graphite crucibles possess the ability to withstand the corrosive properties of molten metals, thereby making them suitable for a wide range of metal powder atomization applications.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for gold or silver melting?
- Yes, a graphite crucible can be used for gold or silver melting. Graphite crucibles have high heat resistance and excellent thermal conductivity, making them suitable for melting precious metals like gold and silver. They also have good chemical resistance, which prevents contamination during the melting process.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for rapid thermal cycling?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for rapid thermal cycling. Graphite has excellent thermal conductivity and high heat resistance, making it suitable for rapid temperature changes. This means that graphite crucibles can withstand the rapid heating and cooling required for thermal cycling processes. Additionally, graphite has a low coefficient of thermal expansion, which means it has minimal dimensional changes during temperature variations, making it ideal for repetitive thermal cycling.
- Q: Can a graphite crucible be used for ceramic molding?
- No, a graphite crucible is not suitable for ceramic molding as it is primarily used for melting and casting metals due to its high melting point and heat resistance. Ceramic molding requires materials that can withstand high temperatures and provide proper insulation, such as refractory crucibles made from materials like alumina or silica.
- Q: Is it possible to cast or mold materials using a graphite crucible?
- Yes, it is possible to cast or mold materials using a graphite crucible. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in various industries, such as metal casting, jewelry making, and foundries, due to their high melting point and excellent thermal conductivity. Graphite crucibles can withstand extreme temperatures, making them ideal for melting and casting materials like metals and alloys. Graphite crucibles also have good chemical resistance, which prevents contamination of the molten material. Additionally, graphite crucibles have low thermal expansion and are non-wetting, meaning they do not adhere to the melted material, making it easier to remove the cast or molded material once it has solidified. Overall, graphite crucibles are widely used and highly effective for casting and molding various materials.
- Q: Can graphite crucibles be used for metal powder atomization?
- Yes, graphite crucibles can be used for metal powder atomization. Graphite crucibles are commonly used in metallurgical processes due to their high thermal conductivity, chemical inertness, and resistance to high temperatures. In metal powder atomization, the crucible is heated to a high temperature, and the metal feedstock is melted and then atomized into fine powder particles using a gas or water jet. The graphite crucible helps to maintain a stable temperature during the atomization process and allows for efficient heat transfer, resulting in consistent and high-quality metal powder production. Additionally, graphite crucibles can withstand the corrosive nature of molten metals, making them suitable for various metal powder atomization applications.
- Q: Is it possible to achieve a controlled atmosphere inside a graphite crucible?
- Achieving a controlled atmosphere inside a graphite crucible is indeed possible. Graphite crucibles find common usage in high-temperature applications, particularly for melting metals and alloys. Various methods can be employed to achieve a controlled atmosphere. One approach involves the use of a gas purging system. This entails introducing a specific gas into the crucible to create the desired atmosphere. For instance, if an inert atmosphere is necessary, gases like argon or nitrogen can be used to displace any oxygen or other reactive gases present. The gas flow rate and pressure can be adjusted to maintain the desired atmosphere. Another method involves creating a sealed environment around the crucible. This can be accomplished by utilizing a furnace or an induction heating system equipped with a gas-tight enclosure. By controlling the gas composition and pressure within this enclosure, a specific atmosphere can be maintained surrounding the crucible. Moreover, the choice of crucible material is crucial to consider. Graphite possesses high thermal conductivity, allowing for rapid heat transfer. However, it can also react with certain gases or metals at elevated temperatures. Hence, selecting the appropriate grade of graphite and ensuring proper crucible conditioning are essential in maintaining a controlled atmosphere. Ultimately, by utilizing suitable equipment and employing effective techniques, it is feasible to establish a controlled atmosphere inside a graphite crucible, thereby enabling precise control of the environment during high-temperature processes.
- Q: What is the difference between the indirect method Zinc Oxide and the direct law Zinc Oxide?
- Zinc Oxide direct method generally used for ceramics, glaze, glass frit, and pigment industry.Zinc Oxide: the indirect method can be used in rubber, varistors, paint, phosphating solution, film, conductive materials and other industries. The direct effect of heavy metal impurity content of the products of the heavy metal content of zinc or zinc, low heavy metal content of the products, but also can be used for livestock feed, medicine, health care and other industries.
- Q: Will a graphite crucible conduct electricity?Soluble aluminum material with electric iron stove appearance
- Thermal conductivity, conductive graphite is one hundred times higher than the general non metallic minerals. Its thermal conductivity is better than steel, iron and lead metal materials. The thermal conductivity decreases with the increase of temperature, even in high temperature, graphite as adiabatic. Because graphite conductive graphite to each carbon atom and other carbon only 3 atoms formed covalent bond, each carbon atom retains 1 free electrons to transfer charge.
Send your message to us
Borax Graphite Crucible for High Heat Resistance Copper Melting
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords




























