Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF)
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF)

Top Blown Process (BOP)
In the top blown process a water cooled oxygen lance is lowered from the top of the furnace and blows oxygen at supersonic speed into the melt. The majority steelmakers utilize top-blown oxygen steelmaking.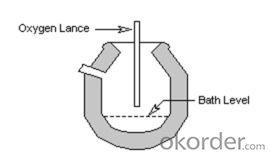
Bottom Blown Furnace (Q-BOP)
In the bottom-blown processes, oxygen is introduced through a number of tuyeres in the bottom of the furnace. In the Q-BOP process, the oxygen tuyeres are cooled by injecting hydrocarbon gas through an outer pipe surrounding the oxygen pipe. Most bottom-blown processes use methane or propane as the hydrocarbon coolant, but fuel oil is also used. A principle advantage of the Q-BOP process is that it reduces the height requirements of the process allowing a lower profile building to be constructed.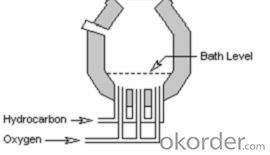
Combination Processes
One class of combination blown process uses top-blown oxygen with inert gas (argon and Nitrogen) injection through the bottom by means of tuyeres or permeable elements. In the second class of combination furnaces, there are both top and bottom oxygen lances; the bottom lances can also be used for inert gas injection during stirring.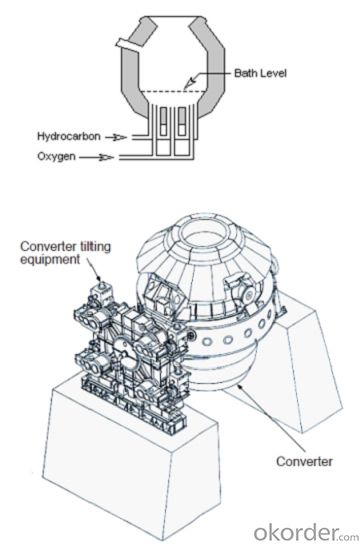
The basic oxygen furnace (BOF), whose profile is shown in the figure, is a tiltable vessel lined with refractories such as magnesia carbon brick. Auxiliary equipment includes a chute for scrap charging, hoppers for alloys and fluxes, a lance for injecting pure oxygen gas, a sublance for measuring the temperature and carbon concentration of the molten steel, lifting devices for the lance and sublance, equipment for tilting the vessel, and equipment for recovering and cleaning the exhaust gas. The BOF capacity is expressed as the weight of crude steel that can be decarburized per heat. Most BOFs in China have a capacity of 150-300 tons.
The main function of the BOF is to decarburize the hot metal using pure oxygen gas. In the top-blown BOF, pure oxygen is injected as a high-velocity jet against the surface of the hot metal, allowing penetration of the impinging jet to some depth into the metal bath. Under these conditions, the oxygen reacts directly with carbon in the hot metal to produce carbon monoxide. The pure oxygen top-blown BOF can decarburize 200 tons of hot metal from 4.3% C to 0.04% C during 20 minutes. As a result of this high productivity, the BOF replaced the open hearth furnace, which was a much slower process.
The injected pure oxygen gas first oxidizes silicon and then carbon in hot metal. When the carbon concentration of the hot metal is decreased to about 1%, the oxidation of Iron begins in parallel with that of carbon. The oxidation of Iron becomes marked at carbon concentrations of less than 0.1%, decreasing both the oxygen efficiency for decarburization and the decarburization rate, while increasing Iron loss into the slag. The problem with the top-blown BOF is thus the oxidation of Iron when a low carbon concentration is reached, and the resulting decrease in the decarburization rate. When the Iron oxide content of the slag increases excessively, it can react too quickly with carbon in the molten Steel and cause sudden gas evolution, forming a mix of slag and molten Steel that sometimes erupts from the vessel in a phenomenon called "slopping" or "spitting".
The use of an oxygen lance with multiple holes at the tip has proven very effective in delocalizing the oxygen supply and increasing the decarburization rate while restraining excessive oxidation of the molten Steel and preventing slopping and spitting. However, the effectiveness of this lance was still inadequate, and the bottom-blown oxygen process was developed, in which pure oxygen gas is injected into the molten Steel from the bottom of the BOF. The bottom blowing enhances the stirring of the hot metal and thereby shortens the average mixing time in the molten Steel bath, and promotes transport of solute carbon in the bath, preventing the over-oxidation of slag, which is the cause of slopping and spitting. Consequently, the bottom blowing enhances decarburization efficiency, especially at low carbon concentrations. The bottom-blowing is performed with bottom tuyeres of concentric double-wall pipe. The inner pipe is used to blow pure oxygen gas along with pulverized limestone as a slag-forming agent, while propane gas is blown through the outer pipe as a coolant to prevent tuyere burn back, since propane undergoes an endothermic reaction during decomposition, which results in cooling and reduced burning of the tuyeres. These improvements have made the production of low-carbon steels much easier.
The top-and-bottom blown BOF, which combines the advantages of both types of BOF, has recently become prominent in oxygen steel making. The combined blowing BOF mostly uses bottom-blown inert gases in place of oxygen gas for stirring. Various methods of bottom-blowing have been adopted. As one example, a ceramic plug with embedded multiple small pipes or multiple slits is used in the bottom tuyeres. Irrespective of the type of the BOF, the exhaust gas, which is high in CO content, is either combusted in the throat of the BOF and passes through a waste-heat boiler installed in the upper part of the throat to recover the sensible heat and the heat of combustion, or is recovered through exhaust-gas recovery equipment and stored in a gas tank for later use as fuel.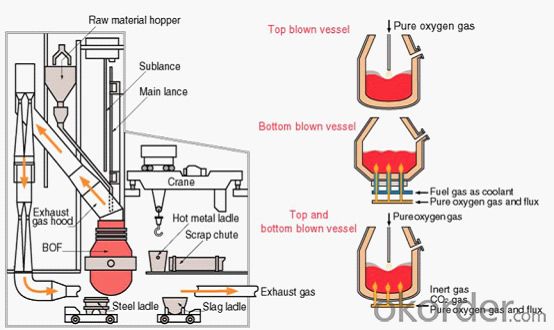
- Q: What is the difference between industrial furnaces and boilers?
- A boiler is a mechanical device for heating water into hot water or steam by the use of heat from fuel or other sources of energy. The original meaning of a pot is a water container heated by fire. The furnace is the place where the fuel is burned. The boiler includes two parts, the cooker and the furnace.
- Q: Should the industrial furnace shell cool down?
- The function of furnace shell is beautiful, protective lining, fixed function accessories and so on.
- Q: Heat treatment equipment (industrial furnace), which products generally contain what kind of, which industries need to use heat treatment industrial furnace equipment.
- The general metal die casting plant and the metal smelting plant need process melting and dissolving furnace, usually there are reverberatory furnace, cupola, rotary furnace, etc. I do the melting furnace of aluminium alloy.
- Q: What are the companies in the world that are currently engaged in metallurgical furnaces?
- Basically, no industrial furnace manufacturer can do all types of stoves.Often associated with the industry is very large,so your ranking is basically meaningless.
- Q: What is industrial furnace masonry?
- Masonry industrial furnaces refers to complete materials such as brick kilns in construction process.
- Q: How many kinds of industrial electric furnaces are there?
- Electric furnace is divided into four categories: resistance furnace, induction furnace, arc furnace and special electric furnace according to the different ways of electric heating.
- Q: What is the difference between industrial furnace masonry and ordinary masonry?
- Industrial furnace masonry requirements are relatively high, industrial furnaces of different uses, whether material or masonry process, have strict requirements.
- Q: How to use industrial furnace equipment?
- If it is water cooling furnace door, but also to ensure the smooth flow of pipes, winter pipes are not frozen. When the boiler is in a limited position, the interlocking device for cutting off the power supply shall be provided when the furnace is in and out, and the number of broken wires in the pitch of the steel wire shall not exceed 10%, and the counterweight of the furnace door shall be reliably hung.
- Q: Brief introduction to repair of industrial furnace
- The industrial furnace is the main production equipment in the machinery industry. The repair of industrial furnace directly affects the quality, high yield, long life, low consumption and safe production of the furnace.
- Q: What is an industrial furnace pit?
- Later, a chamber kiln with a semi closed or fully enclosed kiln made of refractory bricks can be used as fuel for coal, gas or oil, and electricity can be used as heat source. The workpiece will be heated in the kiln hearth.
Send your message to us
Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF)
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- -
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords























