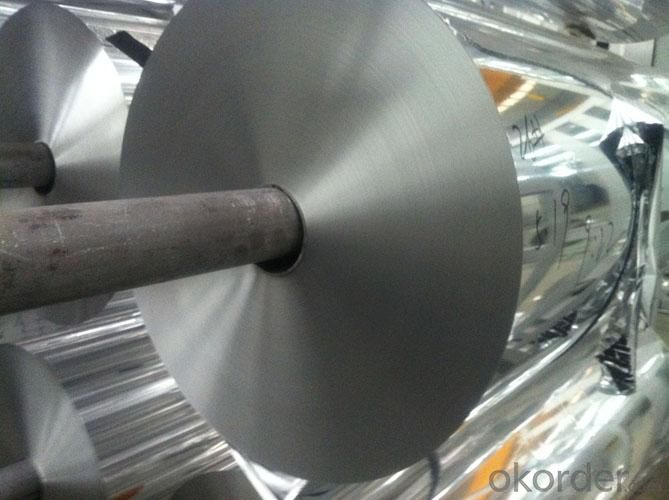
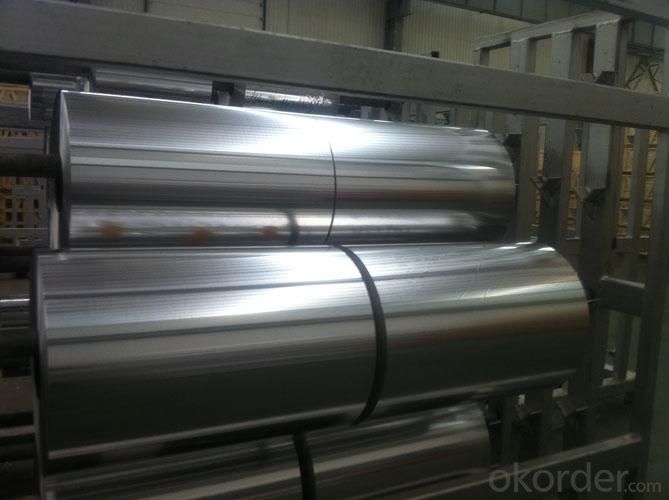
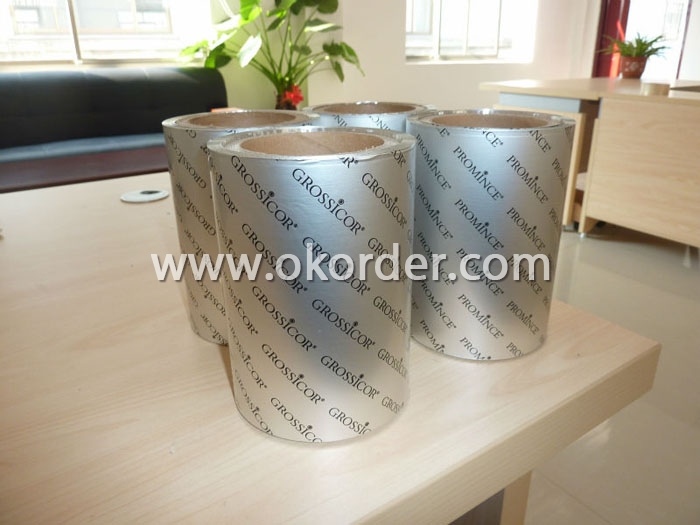
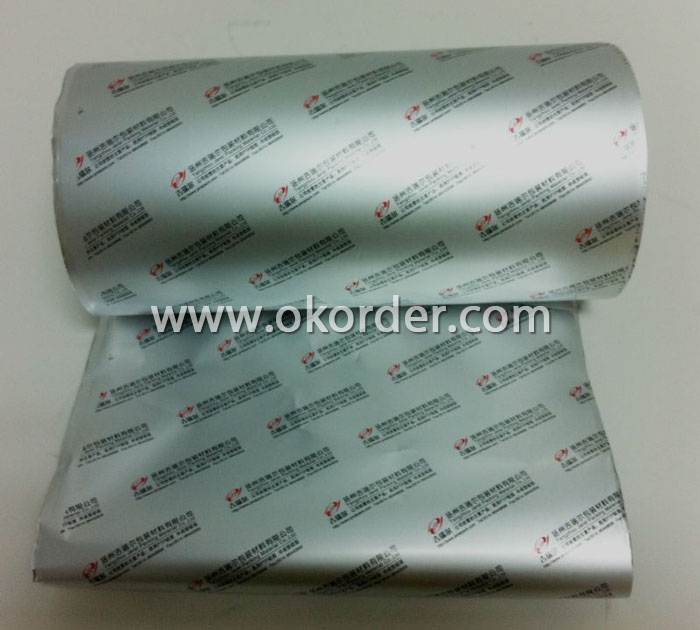
Aluminum Medicine Packaging Foil
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 3Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 2000Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick details of Aluminum Foil For Medicine Packaging
|
Application: |
PTP foil, cord-forming foil, alu-alu foil |
|
Alloy: |
8011/8006/8079 |
|
Temper: |
H18/O |
|
Thickness& Tolerance: |
0.02mm-0.09mm (±6%) |
|
Width& Tolerance: |
200mm-1650mm (±1mm) |
|
Mechanical Properties: |
Tensile Strength(U.T.S)≥160Mpa, Elongation≥1% |
|
Standard: |
GB/T3198 / ASTM-B209 / EN546 |
Usage/Application of Aluminum Foil For Medicine Packaging
Used for PTP foil, cord-forming foil, alu-alu foil
Packaging & Delivery of Aluminum Foil For Medicine Packaging
Packing: seaworthy wooden box with pallet
Delivery: to be loaded by 1 x 20 feet container



- Q: Is aluminum a suitable material for construction purposes?
- <p>Yes, aluminum is widely used in building materials due to its lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance. It is common in window frames, roofing, facades, and structural components. Aluminum's malleability allows for versatile design, and its recyclability makes it an environmentally friendly choice.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to utilize aluminum as a component in battery technology?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be used in batteries. Aluminum-air batteries are a type of metal-air battery that uses aluminum as the anode. These batteries have a high energy density and are lightweight, making them suitable for certain applications. However, they also have challenges such as the need for a specific electrolyte and issues with aluminum corrosion, which limit their practical use compared to more common battery technologies like lithium-ion batteries.</p>
- Q: What precautions should be taken when dealing with aluminum food containers to ensure safety?
- <p>When handling aluminum food containers, it's important to ensure they are food-grade and free from any damage or sharp edges. Always wash them thoroughly before use, and avoid using abrasive cleaners that could scratch the surface. Do not store acidic or alkaline foods in aluminum containers for extended periods as this can cause leaching of aluminum into the food. Also, avoid heating aluminum containers in a microwave as it can cause warping and potential chemical reactions. Use caution when disposing of aluminum containers to recycle them properly and minimize environmental impact.</p>
- Q: What limitations are there regarding the use of aluminum in food and beverage packaging?
- <p>Yes, there are restrictions on using aluminum in food and drink packaging. Aluminum can leach into food or beverages, potentially causing health issues. Regulations vary by country but generally aim to minimize exposure. For instance, the U.S. FDA has guidelines on the use of aluminum in food contact substances. In Europe, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) sets limits on aluminum migration into food. Manufacturers must comply with these regulations to ensure safety and avoid health risks associated with aluminum exposure.</p>
- Q: Explain how the strength of aluminum is affected by temperature changes.
- <p>The strength of aluminum decreases with increasing temperature. As temperature rises, aluminum undergoes thermal expansion, which can lead to a reduction in its yield strength and tensile strength. This is because the increased thermal energy causes the aluminum atoms to vibrate more, weakening the metallic bonds. At very high temperatures, aluminum can become ductile and may even lose its structural integrity. Conversely, at very low temperatures, aluminum can become brittle, which also affects its strength negatively. Therefore, the optimal temperature for maintaining the strength of aluminum is typically within its normal operating range.</p>
- Q: Is there any health risk associated with using pure aluminum cookware?
- <p>Using pure aluminum cooking utensils is generally considered safe for most people. However, there are some concerns regarding the potential for aluminum to leach into food, especially at high temperatures or with acidic foods. While the health risks are still a subject of debate, it's recommended to use aluminum cookware with a protective coating or opt for utensils made from other materials like stainless steel or cast iron for long-term health considerations.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to recycle aluminum from old products to create new ones?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be recycled to make new products from old ones. Recycling aluminum is a highly efficient process that requires only 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum from raw materials. This process is not only environmentally friendly but also economically viable. Recycled aluminum maintains its quality and can be used to create a wide range of new products, from cans and packaging to automotive parts and construction materials.</p>
- Q: This question asks about the typical applications of aluminum pipes in various industries and settings.
- <p>Aluminum pipes are commonly used in a variety of applications due to their lightweight, corrosion resistance, and high thermal conductivity. They are extensively used in the automotive industry for parts like radiators and heat exchangers. In construction, aluminum pipes are utilized for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. They are also used in the beverage industry for conveying and cooling liquids, as well as in the aerospace industry for fuel and hydraulic lines due to their strength-to-weight ratio. Additionally, aluminum pipes are found in industrial settings for compressed air and gas lines, and in marine applications for fuel and water systems.</p>
- Q: What are the negative aspects or drawbacks of using aluminum?
- <p>Aluminum has several disadvantages. It is a non-magnetic material, which limits its use in applications requiring magnetic properties. Aluminum is also less dense than many other metals, making it less suitable for heavy-duty applications. It can be toxic in certain forms, such as aluminum salts, and has been linked to health issues when ingested in large amounts. Additionally, aluminum's low melting point can be a disadvantage in high-temperature environments. Lastly, the production process of aluminum is energy-intensive and can contribute to environmental pollution.</p>
- Q: Exploring the possibility of using materials that are more eco-friendly than aluminum.
- <p>Yes, various alternative materials can be used that are more environmentally friendly than aluminum. These include biodegradable plastics, recycled materials, and natural fibers such as bamboo and hemp. For instance, bioplastics can be derived from renewable sources like corn starch or sugarcane, reducing the carbon footprint. Recycled materials not only reduce waste but also save energy compared to producing new materials. Natural fibers are sustainable and can be used in construction, packaging, and other applications traditionally served by aluminum. However, it's crucial to consider the specific application's requirements and the lifecycle impact of these alternatives.</p>
Send your message to us
Aluminum Medicine Packaging Foil
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 3Tons m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 2000Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords