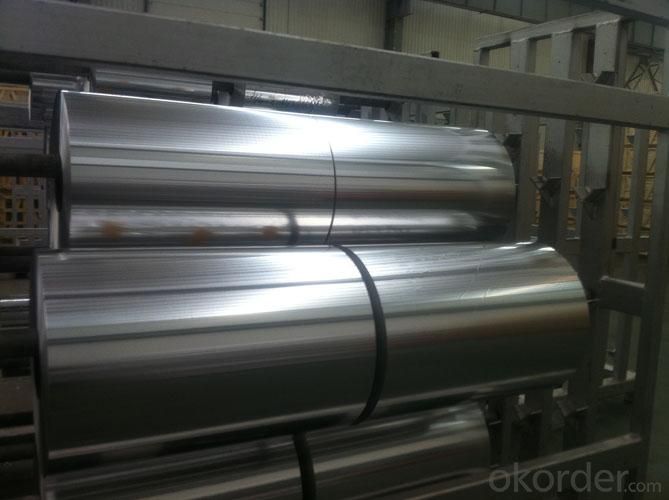
Aluminum foil for Container
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
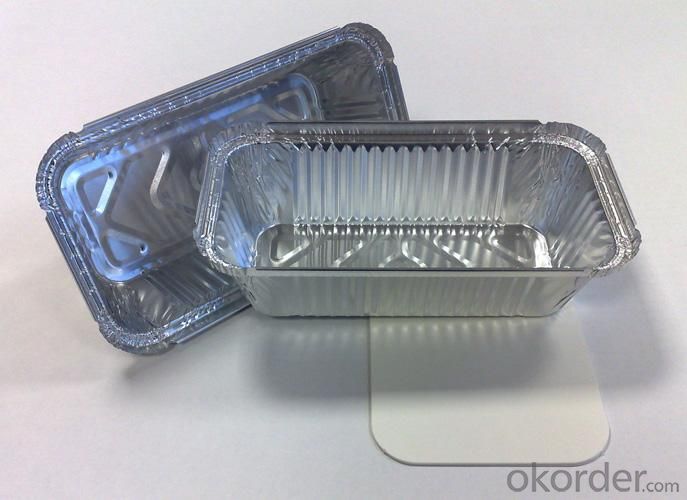
Quick details of Aluminum foil for Container
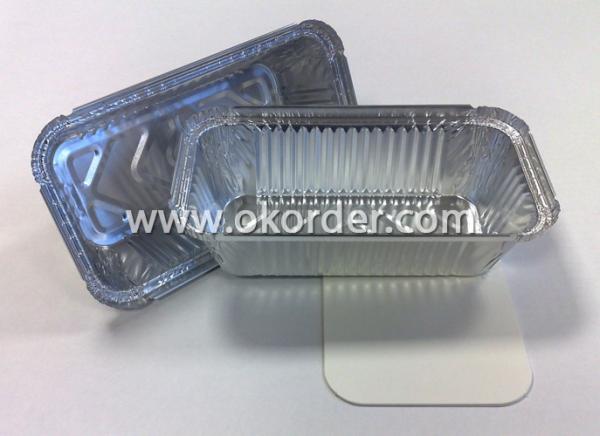
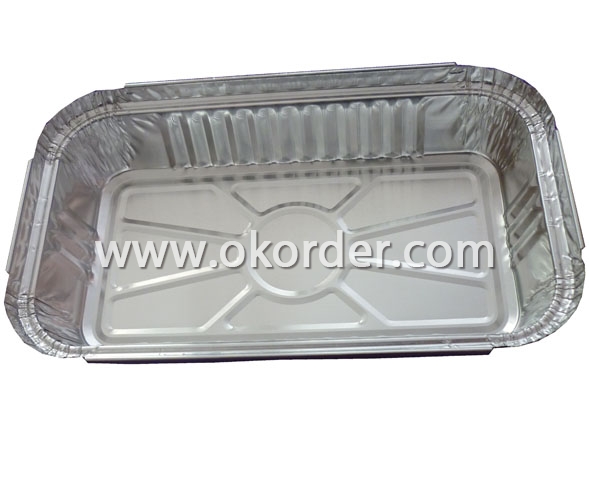
Application: | For different food container, such as dishes, plates, trays, etc |
Alloy: | 8011 /3003 |
Temper: | O/H22/H24 |
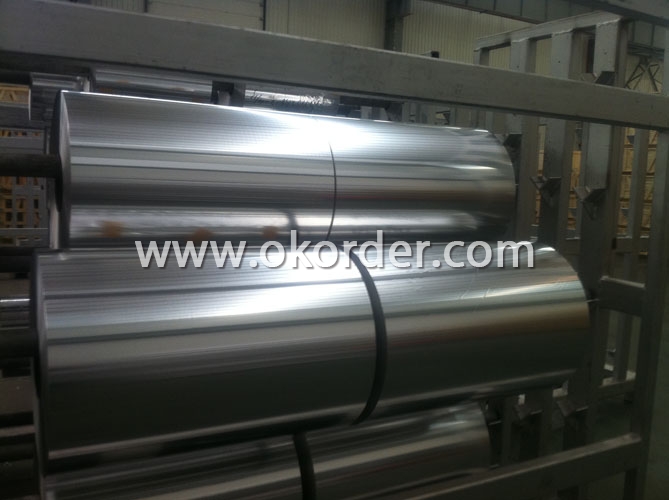
Thickness & Tolerance: | 0.05mm-0.20mm (±8%) |
Width & Tolerance: | 200mm-1650mm(±1mm) |
Mechanical Properties: | Tensile Strength(U.T.S)≥49Mpa, Elongation≥1% |
Standard: | GB/T3198 / ASTM-B209 / EN546 |
Usage/Application of Aluminum foil for Container
Use for different food container, such as dishes, plates, trays, etc
Packaging & Delivery of Aluminum foil for Container
Packing: seaworthy wooden box with pallet
Delivery: to be loaded by 1 x 20 feet container




- Q: Is it possible to utilize recycled aluminum for the production of cars or other types of vehicles?
- <p>Yes, recycled aluminum can be used to make cars and other vehicles. It is common practice in the automotive industry to use recycled aluminum in the manufacturing process due to its lightweight and strong properties. Recycled aluminum requires less energy to produce than new aluminum, making it more sustainable. It is used in various parts of vehicles, including engine components, body panels, and wheels. The use of recycled aluminum not only reduces waste but also contributes to energy savings and carbon emission reductions in vehicle production.</p>
- Q: Is it safe or permissible to use aluminum in food packaging materials?
- <p>Yes, aluminum is commonly used in food packaging due to its lightweight, durability, and excellent barrier properties against air, moisture, and light. It is used in various forms such as aluminum foil, cans, and flexible packaging materials. However, it's important to ensure that the aluminum packaging is food-grade and complies with safety regulations to prevent any potential health risks associated with aluminum exposure.</p>
- Q: This question asks for common applications of aluminum in everyday life.
- <p>Aluminum is widely used in daily life due to its lightweight, durability, and resistance to corrosion. It is commonly found in beverage cans, food packaging, and cookware. Aluminum is also used in construction for window frames, doors, and roofing. It is a key material in the manufacturing of vehicles, including cars, airplanes, and bicycles, due to its strength-to-weight ratio. In electronics, aluminum is used in heat sinks and wiring. Additionally, it is used in everyday items like foil, furniture, and sports equipment. Its versatility makes aluminum an essential material in many aspects of modern life.</p>
- Q: Explain the distinction between pure aluminum and aluminum alloys, focusing on their composition and properties.
- <p>Pure aluminum is composed of aluminum alone, with a high degree of purity, typically over 99%. It is soft, malleable, and has good thermal and electrical conductivity. Aluminum alloys, on the other hand, are made by combining aluminum with other elements such as copper, magnesium, or silicon to enhance their strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. These alloys are harder than pure aluminum and can be tailored for specific applications, making them more versatile for industrial use.</p>
- Q: Explain the impact of aluminum on manufacturing processes in a few sentences.
- <p>The use of aluminum significantly affects manufacturing processes by offering several advantages. It is lightweight, which reduces the weight of products and can lead to fuel efficiency in transportation sectors. Aluminum's high strength-to-weight ratio makes it ideal for structural components. Its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity allows for efficient heat dissipation and electrical transmission. Additionally, aluminum is non-magnetic and non-corrosive, which is beneficial for certain applications. The metal is also easily recyclable, contributing to sustainability in manufacturing. These properties make aluminum a popular choice in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and electronics, enhancing the efficiency and performance of manufacturing processes.</p>
- Q: Explain how the production process of recycled aluminum differs from that of new aluminum, focusing on energy consumption and environmental impact.
- <p>The production process for recycled aluminum is significantly less energy-intensive compared to the production of new aluminum. Producing new aluminum from bauxite ore requires high temperatures and substantial energy, often from fossil fuels, to smelt the ore and extract the metal. This process emits greenhouse gases and consumes large amounts of electricity. In contrast, recycling aluminum involves melting down existing aluminum products, which requires only about 5% of the energy needed to produce new aluminum. This process is more environmentally friendly, as it reduces energy consumption, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and conserves natural resources by decreasing the need for raw materials.</p>
- Q: Describe the steps involved in the manufacturing of aluminum sheets.
- <p>The process of manufacturing aluminum sheets involves several key steps. Initially, aluminum ore, typically bauxite, is mined and then processed to remove impurities. The purified aluminum oxide is then dissolved in a cryolite bath at high temperatures, a process known as the Hall-H茅roult process. This results in molten aluminum, which is then cast into ingots. These ingots are reheated and passed through rollers to gradually reduce their thickness, creating aluminum sheets. The sheets are then cooled, cut to size, and may undergo further treatments like annealing or coating, depending on their intended use. The final product is a flat, thin sheet of aluminum ready for various applications.</p>
- Q: This question asks for typical applications of aluminum foil in everyday life.
- <p>Aluminum foil is commonly used for food storage, as it helps preserve freshness and prevents freezer burn. It's also used in cooking, either to cover dishes to retain moisture or to create packets for steaming or baking. In the kitchen, it's often used to line baking sheets to prevent food from sticking. Beyond cooking, aluminum foil is used for insulation, in arts and crafts, and even for cleaning purposes, such as buffing glass or polishing silverware. It's a versatile material found in many households and commercial settings.</p>
- Q: What are some environmentally friendly options that can replace aluminum in various applications?
- <p>Sustainable alternatives to aluminum include biodegradable materials like bamboo and hemp, which can be used in construction and packaging. Stainless steel is a recyclable metal that can replace aluminum in many applications due to its durability and strength. Recycled aluminum itself is a sustainable option as it requires less energy to produce than new aluminum. Additionally, magnesium and titanium are lightweight metals that can be used in place of aluminum in certain industries. It's important to consider the specific application when choosing an alternative, as each material has its own set of properties and environmental impacts.</p>
- Q: This question asks for a brief overview of the characteristics or qualities of aluminum nitride, a chemical compound.
- <p>Aluminum nitride (AlN) is a covalent, ceramic material known for its exceptional properties. It has a high thermal conductivity, which is about two-thirds that of copper, making it useful in electronics for heat dissipation. It's also an electrical insulator, exhibiting high electrical resistivity. Aluminum nitride is characterized by its high thermal stability, resistance to thermal shock, and excellent mechanical strength. It's chemically inert, resistant to most acids and alkalis, and has a high melting point of approximately 2200掳C. These properties make it suitable for applications in high-temperature electronics, as a substrate for semiconductor devices, and in the automotive industry for heat sinks and other heat management components.</p>
Send your message to us
Aluminum foil for Container
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or L/C
- Min Order Qty:
- -
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 Tons Per Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords