Aluminum AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles for Cookware
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 3 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1.Structure of AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles used for Cookware Description
AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles used for Cookware is made from aluminum coils 1xxx. AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles used for Cookware are widely used for kitchen wares including fried pans, non-sticky pans, cooking pots,hard anodized cookware, pressure cooker and house hold utensils.
2.Main Features of AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles used for Cookware
• Superior quality of raw material
• Reasonable and stable chemical composition
• Accurate tolerance
3.AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles used for Cookware Images
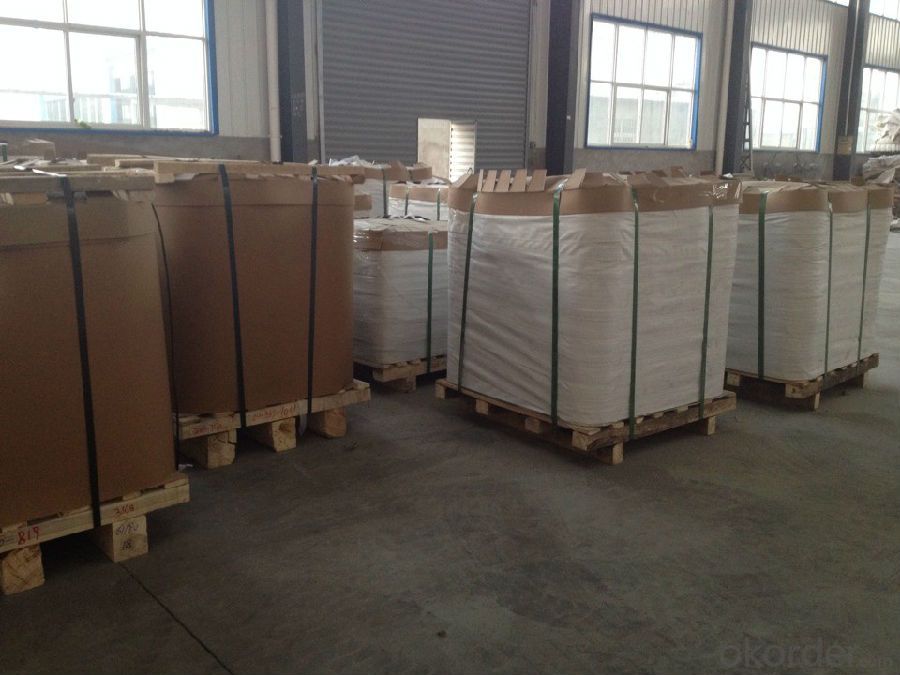
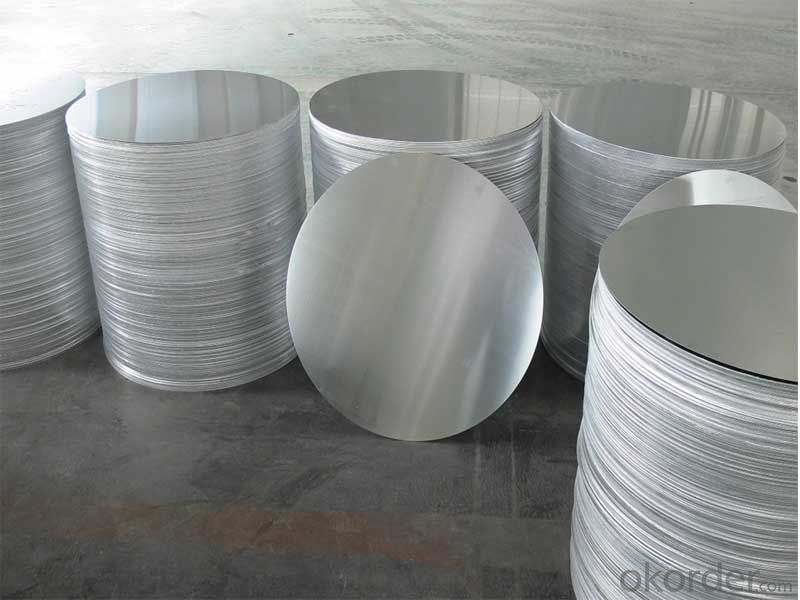
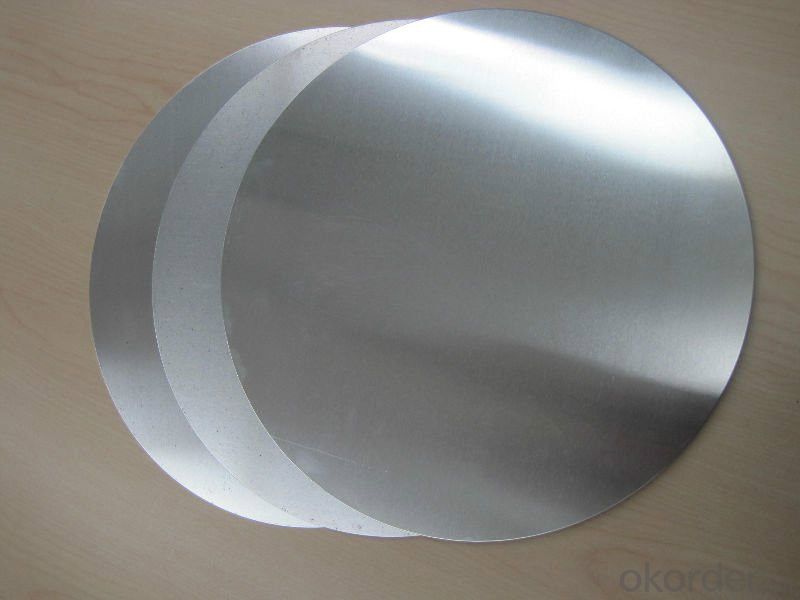



4.AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles used for Cookware Specification
Alloy | AA3003 |
Temper | H14, H16, H18, O/F |
Thickness | 0.5mm -- 4mm |
Diameter | 200mm -- 1200mm |
Standard | GB/T 3880-2006 |
5. FAQ of AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles used for Cookware
A. Now which countries do you export your goods?
Now we export to South East Asia,Africa, North America,South America ect.
B. What is the MOQ for each size?
The MOQ for each size is 3 tons.
- Q: This question asks about the impact of aluminum on human health.
- <p>Aluminum is a naturally occurring element that can be found in small amounts in various foods, water, and air. While it's not considered an essential nutrient, it's also not inherently harmful in small quantities. However, excessive exposure to aluminum has been linked to potential health concerns. Some studies suggest that high levels of aluminum might contribute to neurological disorders, particularly Alzheimer's disease, although the evidence is not conclusive. Aluminum can also cause digestive issues and bone disorders if ingested in large amounts. It's important to note that the human body does not absorb aluminum efficiently, and most ingested aluminum is excreted without issue. However, it's always advisable to minimize exposure to high levels of aluminum, especially for vulnerable populations such as infants and those with kidney issues.</p>
- Q: This question asks for typical applications of aluminum foil in everyday life.
- <p>Aluminum foil is commonly used for food storage and preservation, as it can be wrapped around food to keep it fresh. It's also widely used in cooking, particularly for baking and roasting, to prevent food from sticking to pans or to seal in moisture and flavor. Beyond culinary uses, aluminum foil is employed in arts and crafts for creating 3D structures or as a reflective surface. It's also used in insulation, as a barrier in construction, and for packing and wrapping items to protect them during shipping. Additionally, aluminum foil is utilized in various industrial processes due to its heat resistance and malleability.</p>
- Q: This question asks for recent applications of aluminum in the transportation industry.
- <p>Aluminum has found new uses in transportation due to its lightweight and high strength properties. It's increasingly used in electric vehicles to reduce weight and extend battery life. Aluminum alloys are also utilized in the construction of high-speed trains and aircraft to improve fuel efficiency and performance. In addition, aluminum is employed in the manufacturing of automotive parts such as engine components, wheels, and body panels. Furthermore, it's used in the production of lightweight bicycles and other transportation infrastructure like bridges and road signs. The trend towards more sustainable and efficient transportation continues to drive innovative uses for aluminum.</p>
- Q: This question seeks to understand the impact of aluminum exposure on human health, including potential risks and consequences.
- <p>Aluminum is a common element found in the environment, and while it is generally considered safe, there are concerns about its health effects on humans. High levels of aluminum exposure have been linked to neurological disorders, particularly Alzheimer's disease, although the relationship is not definitively proven. Aluminum can also cause bone diseases and anemia, as it can interfere with the absorption of calcium and iron. Long-term exposure to high levels of aluminum may lead to cognitive dysfunction and memory loss. However, the everyday exposure to aluminum from food, water, and medications is considered safe by health authorities, and there is no need for alarm in normal circumstances.</p>
- Q: Describe the process of aluminum oxide formation in a few sentences.
- <p>Aluminum oxide forms through a process known as oxidation, where aluminum reacts with oxygen in the air. This reaction is typically exothermic and can occur at room temperature, especially in the presence of moisture. When aluminum is exposed to oxygen, it forms a thin, protective layer of aluminum oxide on its surface. This layer prevents further oxidation and is what gives aluminum its corrosion resistance. In industrial settings, aluminum oxide can also be produced through electrolysis of aluminum oxide dissolved in molten cryolite.</p>
- Q: Is it safe to use aluminum cookware for cooking food?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be used to make cookware that is safe for cooking food. Aluminum cookware is widely used due to its lightweight, durability, and good heat conductivity. While there were concerns about aluminum's potential health effects, current research indicates that the amount of aluminum leached into food during normal cooking is minimal and not harmful to health. However, it's important to avoid using abrasive cleaners or utensils on aluminum cookware to prevent scratching, as this could increase the amount of aluminum that might be released into food.</p>
- Q: This question asks for an explanation of the process involved in the production of aluminum foil.
- <p>Aluminum foil is made through a process that starts with the extraction of aluminum from its ore, bauxite. The bauxite is refined to produce aluminum oxide, which is then reduced to aluminum using the Hall-H茅roult process. The aluminum is then melted and cast into large ingots. These ingots are heated and rolled into thin sheets using large industrial rolling mills. The aluminum is rolled multiple times, each pass reducing its thickness until it reaches the desired foil thickness. The final thin sheets are then cut and packaged as aluminum foil. This process requires precision and control to ensure the foil is uniform and free of defects.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to utilize recycled plastic or paper for manufacturing new products instead of sourcing new materials?
- <p>Yes, recycled plastic and paper can be used to create new products, reducing the need for new materials. This process not only conserves natural resources but also decreases waste in landfills. Recycled paper can be used to make new paper products, packaging, and even some types of construction materials. Similarly, recycled plastics can be repurposed into various products such as clothing, furniture, and new plastic items. However, it's important to note that the quality of recycled materials may vary, and not all plastics or paper products can be recycled effectively. The recycling process also requires energy, so it's crucial to balance the environmental benefits with the energy costs and potential for contamination during recycling.</p>
- Q: This question asks for innovative applications of recycled aluminum in various industries or everyday life.
- <p>Recycled aluminum is finding new uses in various sectors due to its sustainability and strength. It's being used in the automotive industry to make lighter vehicles, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. In construction, it's used for building materials like window frames and roofing, known for durability and energy efficiency. Recycled aluminum is also employed in the aerospace industry for aircraft parts due to its lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio. Additionally, it's used in packaging, reducing waste and conserving resources. In electronics, recycled aluminum is used in the manufacturing of various components, contributing to the circular economy.</p>
- Q: This question inquires about the potential differences in cooking performance when using various types of aluminum foil.
- <p>Yes, there are differences in cooking performance between different types of aluminum foil. The thickness of the foil can affect heat distribution and cooking time; heavier gauges are more durable and better for roasting and baking, while thinner foils are suitable for lining pans or wrapping foods. The quality of the foil, such as whether it's non-stick or not, can impact food release and cleanup. Additionally, some aluminum foils are designed to be heat resistant up to higher temperatures, making them suitable for broiling or grilling, while others may not withstand such high heat. It's important to use the appropriate type of aluminum foil for the specific cooking method to ensure food safety and optimal results.</p>
Send your message to us
Aluminum AA3003 C.C Aluminum Circles for Cookware
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 3 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 10000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords