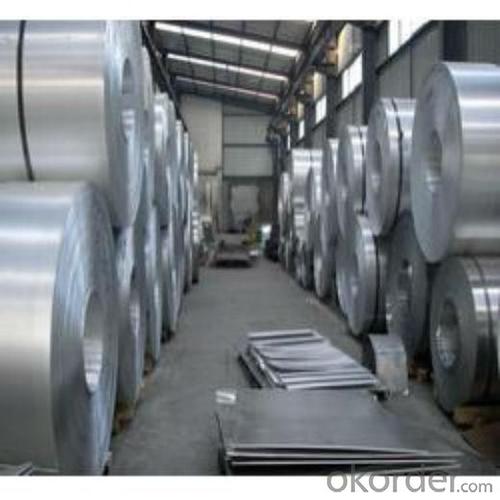
Aluminum Pharmaceutical Foilstock
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 MT / Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details of Aluminium Foil Stock for Pharmaceutical Foil
Alloy: 8011
Temper: H14 / H16 / H24 / H26
Specifications of Aluminium Foil Stock for Pharmaceutical Foil
Thickness & Tolerance: 0.28 mm - 0.3 mm (+/-0.01%)
Width & Tolerance: 1000 - 2020 mm (+/-1 mm)
Core I.D.: 405/505/508 mm
Surface Quality: Good appearance with no-crack and well distribute grain
Build Up: Tight slit edges free from cracks, layer to layer shift not more then 2 mm
Flatness: Mill flatnesscoil having slight edge waviness rather than center buckles shall be acceptable
Rolling Performance: Re-rollable to the final desired gauges
Standard: GB/T3198 / ASTM-B209
Usage/Application of Aluminium Foil Stock for Pharmaceutical Foil
To produce aluminium foil for Pharmaceutical application
Packaging & Delivery of Aluminium Foil Stock for Pharmaceutical Foil


- Q: Is aluminum a suitable material for construction purposes?
- <p>Yes, aluminum is widely used in building materials due to its lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance. It is common in window frames, roofing, facades, and structural components. Aluminum's malleability allows for versatile design, and its recyclability makes it an environmentally friendly choice.</p>
- Q: What characteristics distinguish pure aluminum from its alloyed forms?
- <p>Pure aluminum is a soft, lightweight, and highly malleable metal with good electrical and thermal conductivity. It is often used for its corrosion resistance and is relatively inexpensive. Aluminum alloys, on the other hand, are made by combining aluminum with other elements like copper, magnesium, silicon, or zinc to enhance its properties. These alloys are stronger, more durable, and can be tailored for specific applications, such as in aerospace, automotive, or construction. They offer improved strength-to-weight ratios, better resistance to heat and wear, and can be anodized for enhanced surface properties. While pure aluminum is more ductile and easier to weld, aluminum alloys provide greater versatility in terms of mechanical properties and performance.</p>
- Q: This question asks for a comparison between aluminum and other metals, highlighting their distinct properties and characteristics.
- <p>Aluminum is a lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal with a low density, making it ideal for applications requiring strength without excessive weight. It is also a good conductor of heat and electricity. Unlike other metals like iron or copper, aluminum is not magnetic and has a lower melting point. It is also more abundant and cheaper to produce than many other metals, which makes it widely used in industries such as construction, transportation, and packaging. Aluminum's reactivity means it forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to air, which prevents further corrosion. In contrast, metals like stainless steel offer greater strength and resistance to corrosion, while copper has superior electrical conductivity. Each metal has its unique properties that make it suitable for specific applications.</p>
- Q: Exploring the impact of reducing aluminum usage on global warming.
- <p>Using less aluminum in our daily lives can contribute to reducing global warming, albeit marginally. Aluminum production is energy-intensive, requiring significant amounts of electricity, often from fossil fuels. This process generates greenhouse gas emissions. By reducing demand for aluminum, we can potentially lower the energy consumption and emissions associated with its production. However, aluminum's impact on global warming is relatively small compared to other industries like transportation, energy production, and agriculture. Thus, while reducing aluminum use is beneficial, it should be part of a broader strategy to combat climate change that includes transitioning to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable agricultural practices.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to construct vehicles using aluminum?
- <p>Yes, aluminum can be used to make cars. It is known for its lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, which are desirable properties in automotive manufacturing. Aluminum alloys are commonly used in car bodies, engines, and other components to reduce weight, improve fuel efficiency, and enhance performance. Additionally, its recyclability makes it an environmentally friendly choice for vehicle production.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to use aluminum as a treatment for diseases?
- <p>Aluminum is not typically used to treat diseases directly. It is a common element found in the Earth's crust and is used in various industries, such as manufacturing and construction. However, aluminum compounds can have medicinal uses in specific contexts. For example, aluminum hydroxide is used as an antacid to neutralize stomach acid and treat conditions like heartburn. It's important to note that aluminum should not be ingested in large amounts, as it can be harmful. Always consult a healthcare professional for proper treatment and medication advice.</p>
- Q: What are some important safety measures to take when handling or working with aluminum?
- <p>When working with aluminum, it's crucial to take several safety precautions. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses, gloves, and a dust mask to prevent inhalation of aluminum dust. Ensure good ventilation to avoid build-up of fumes, especially during welding or cutting processes. Use proper tools designed for aluminum to prevent sparks and overheating. Be aware of the fire hazard; aluminum can burn at high temperatures, so have fire extinguishers readily available. Finally, be cautious with chemicals used in aluminum processing, as they can be harmful; always follow the manufacturer's safety instructions.</p>
- Q: What measures should be taken to ensure safety while working with aluminum?
- <p>When working with aluminum, it's important to follow safety precautions. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, safety glasses, and a dust mask to prevent inhalation of aluminum dust. Ensure good ventilation to avoid the buildup of fumes. Use proper tools and equipment to handle aluminum, as it can become sharp and cause cuts. Be cautious of the heat generated during cutting or welding, as aluminum conducts heat quickly and can cause burns. Store aluminum in a dry place to prevent it from reacting with moisture, which can cause it to corrode. Lastly, be aware of the fire hazard associated with aluminum dust and take necessary fire prevention measures.</p>
- Q: Is it possible to develop allergies from exposure to aluminum found in food packaging materials?
- <p>While aluminum is commonly used in food packaging materials, the risk of allergic reactions to aluminum is generally low for most people. Aluminum is not a known allergen, and exposure through packaging is typically minimal. However, individuals with a rare condition called contact dermatitis may experience skin irritation from aluminum. For the general population, the risk of allergic reactions due to aluminum in food packaging is negligible. It's always important to monitor any unusual reactions and consult a healthcare professional if concerned.</p>
- Q: This question asks about the various applications and purposes of aluminum in different industries and everyday life.
- <p>Aluminum is widely used due to its lightweight, corrosion resistance, and high thermal and electrical conductivity. It's extensively used in the transportation industry for manufacturing vehicles, airplanes, and ships. In construction, it's used for window frames, roofing, and structural components. Aluminum is also prevalent in packaging, particularly for food and beverages, and in electrical components like wiring and capacitors. Additionally, it's used in everyday items such as cans, foil, and cookware, and in industrial machinery and tools. Its versatility and recyclability make it a valuable material across many sectors.</p>
Send your message to us
Aluminum Pharmaceutical Foilstock
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 MT / Month m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords