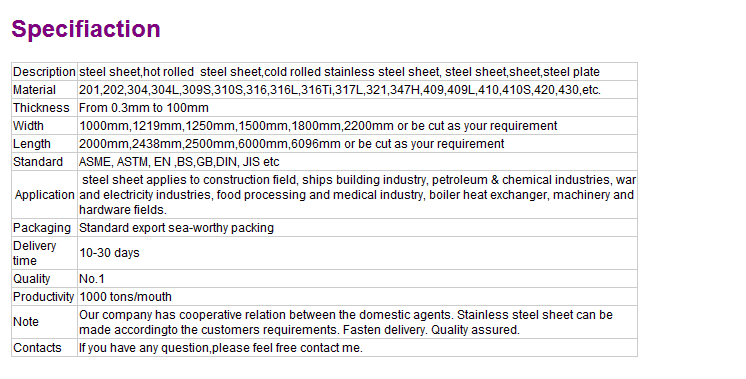
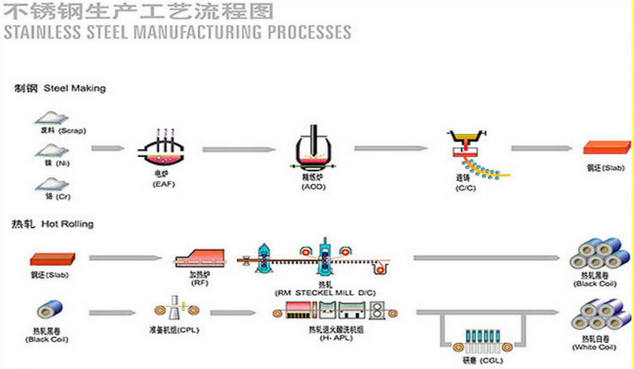
316 round stainless steel bar price for china
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
You Might Also Like

- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for underground drainage systems?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for underground drainage systems. Stainless steel is durable, corrosion-resistant, and can withstand the harsh underground conditions, making it a suitable choice for underground drainage systems.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be used for cryogenic applications?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be used for cryogenic applications. Stainless steel has excellent low temperature properties, such as good mechanical strength and resistance to embrittlement, making it suitable for handling cryogenic fluids and gases at extremely low temperatures.
- Q: What is the difference between 304N and 304LN stainless steel pipes?
- The chemical composition and presence of nitrogen are what distinguish 304N and 304LN stainless steel pipes. Comparatively, 304N stainless steel pipes contain a higher nitrogen concentration than 304LN stainless steel pipes. This nitrogen infusion enhances the stainless steel's durability and ability to withstand corrosion, rendering it more appropriate for use in demanding or corrosive environments. The heightened nitrogen levels in 304N stainless steel pipes result in improved overall performance in terms of strength, hardness, and resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion. Conversely, 304LN stainless steel pipes possess a lower nitrogen content but retain excellent corrosion resistance properties. These pipes are specifically engineered for use in low-temperature applications that require toughness. The reduced nitrogen content in 304LN stainless steel pipes ensures good weldability and formability, making them suitable for various fabrication processes. In conclusion, the disparity between 304N and 304LN stainless steel pipes lies in their nitrogen content, which impacts their strength, corrosion resistance, and suitability for diverse applications.
- Q: What is the difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel pipes?
- Both 304 and 316 stainless steel pipes are widely used in various industries for their exceptional resistance to corrosion and durability. Although they may appear similar, there are significant distinctions between the two grades: 1. Composition: The main difference lies in their composition. 304 stainless steel pipes contain 18-20% chromium and 8-10.5% nickel, whereas 316 stainless steel pipes contain 16-18% chromium, 10-14% nickel, and 2-3% molybdenum. The additional molybdenum in 316 stainless steel enhances its resistance to corrosion, particularly against aggressive chemicals like chlorides. 2. Corrosion resistance: In terms of corrosion resistance, 316 stainless steel pipes surpass 304 stainless steel pipes, especially in environments with high chloride exposure, such as coastal areas or industrial settings with corrosive chemicals. The molybdenum content in 316 stainless steel offers enhanced protection against pitting and crevice corrosion. 3. Temperature resistance: Both grades of stainless steel pipes exhibit good resistance to high and low temperatures, but 316 stainless steel pipes perform better under extreme temperature conditions. They can withstand higher temperatures and retain their strength better compared to 304 stainless steel pipes. 4. Applications: Due to its superior resistance to corrosion, 316 stainless steel pipes are commonly used in industries such as marine, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. On the other hand, 304 stainless steel pipes find applications in various industries, including automotive, construction, and appliances. 5. Cost: Generally, 304 stainless steel pipes are more affordable than 316 stainless steel pipes due to differences in composition and availability. However, the cost-effectiveness of each grade should be determined based on the specific application and required corrosion resistance. In conclusion, while both 304 and 316 stainless steel pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance and durability, the addition of molybdenum in 316 stainless steel provides superior resistance to chloride corrosion. The choice between the two grades depends on the specific application, budget, and level of corrosion resistance required.
- Q: What is the difference between electropolished and passivated stainless steel pipes?
- Electropolished and passivated stainless steel pipes are both surface treatments used to enhance the corrosion resistance and aesthetic appearance of stainless steel. However, there are some key differences between the two processes. Electropolishing is an electrochemical process that selectively removes a thin layer of material from the stainless steel surface. This process helps to remove impurities, contaminants, and embedded particles, resulting in a smooth and clean surface. Electropolishing also improves the microfinish of the stainless steel, reducing surface roughness and enhancing the overall appearance. This process can also improve the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by creating a passive chromium oxide layer on the surface. On the other hand, passivation is a chemical process that involves the application of an acid-based solution to the stainless steel surface. This solution helps to remove iron contaminants and other foreign substances from the surface, leaving behind a clean and passive layer of chromium oxide. Passivation helps to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel by promoting the formation of a stable and protective oxide layer. In summary, electropolishing is an electrochemical process that removes a thin layer of material to create a smooth and clean surface, while passivation is a chemical process that removes contaminants and promotes the formation of a protective oxide layer. Both processes contribute to improving the corrosion resistance and aesthetics of stainless steel pipes, but they differ in the method used to achieve these results.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes resistant to scaling?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes are highly resistant to scaling.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be insulated with foam?
- Yes, stainless steel pipes can be insulated with foam. Foam insulation is commonly used to improve energy efficiency and reduce heat or cold loss in various types of pipes, including stainless steel ones. The foam insulation helps to prevent condensation and provides thermal protection, making it an effective solution for insulating stainless steel pipes.
- Q: Can stainless steel pipes be insulated with polyethylene terephthalate?
- Indeed, it is possible to insulate stainless steel pipes with polyethylene terephthalate (PET). PET is widely employed as an insulating substance owing to its low thermal conductivity, elevated melting point, and commendable resistance against moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation. It can be administered as a safeguarding layer or encircling the stainless steel pipes in order to avert heat loss or gain. The installation of PET insulation is straightforward and it proves highly efficient in minimizing energy transfer, thus rendering it appropriate for a multitude of applications in industries like HVAC, plumbing, and oil and gas.
- Q: Are stainless steel pipes resistant to UV radiation?
- UV radiation does not affect stainless steel pipes as they are resistant to it. Stainless steel is renowned for its exceptional ability to resist corrosion, including the harmful impacts of UV radiation. When exposed to UV radiation, stainless steel develops a passive oxide layer on its surface, which acts as a shield to prevent further harm. This oxide layer effectively prevents degradation, discoloration, and loss of mechanical properties that can arise from exposure to UV radiation. Consequently, stainless steel pipes are an ideal option for outdoor or exposed uses where UV radiation is a concern.
- Q: How do you calculate the weight of a stainless steel pipe?
- To calculate the weight of a stainless steel pipe, you need to know its dimensions and the density of stainless steel. First, measure the outer diameter (OD) and wall thickness (WT) of the pipe. Use a caliper or ruler to get accurate measurements. Next, calculate the inner diameter (ID) by subtracting twice the wall thickness from the outer diameter. The formula to calculate the ID is: ID = OD - 2 * WT. Now, calculate the cross-sectional area (A) of the pipe using the formula: A = π * ((OD/2)^2 - (ID/2)^2), where π is approximately 3.14159. Next, find the density of stainless steel. The density can vary slightly depending on the specific grade of stainless steel, but an average value is around 7.9 grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³) or 7900 kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³). Finally, multiply the cross-sectional area (A) by the length of the pipe (L) and the density (D) to calculate the weight. The formula to calculate the weight (W) is: W = A * L * D. Make sure to use consistent units throughout the calculations. For example, if the length is in meters, the weight will be in kilograms. If the length is in inches, the weight will be in pounds.
Send your message to us
316 round stainless steel bar price for china
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 kg
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 kg/month
OKorder Service Pledge
Quality Product, Order Online Tracking, Timely Delivery
OKorder Financial Service
Credit Rating, Credit Services, Credit Purchasing
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords























