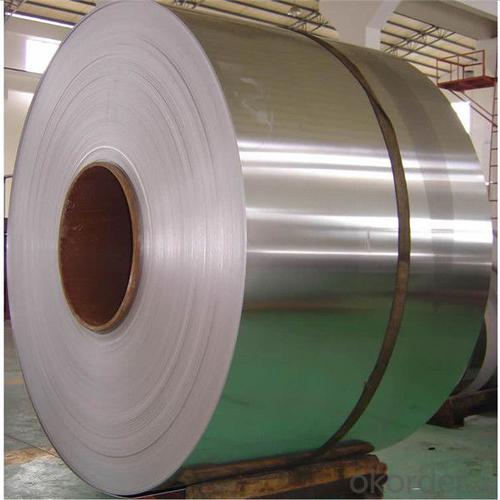
201 202 304 304L Stainless Steel Coil manufacturers
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 4 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
2MM thickness cold rolled baosteel aisi 201 202 304 304L stainless steel coil manufacturers
Stainless steel is a production which not easy rust,acid resistance and corrosion resistance,so it is widely used in light industry,heavy industry,daily necessities and the decoration industry.my company long-term supply stainless steel products including:stainless steel sheet,stainless steel coil and stainless steel tube.
Specification:
| Commodity | 2MM thickness cold rolled baosteel aisi 201 202 304 304L stainless steel coil manufacturers | |||||
| Width | 1000mm,1219mm,1240mm,1500mm,2000mm or as customer's demand | |||||
| Thickness | Cold Rolled:0.3-3.0mm Hot Rolled:3.0-150mm | |||||
| Length | 1000mm-6000mm or as customer's demand | |||||
| Surface | No.1,2B,8K,BA,2D,No.4,No.6,ect. | |||||
| Material | 201,202,301,302,303,304,304L,309S,316,316L,316N,410,420,ect. | |||||
| Grade | 200/300/400 series | |||||
| Certification | SGS ISO | |||||
| Application | Construction,Industry,Kitchenware,Building,etc | |||||
| Packing | Kraft Paper and Seaworthy Wooden Pallet or according to client's request | |||||
| Place of Origin | Shanxi China (MAINLAND) | |||||
| Payment terms | L/C & T/T | |||||
| Delivery Time | Up To Order | |||||
Surface:
| Surface | Definition | Application | |||
| No.1 | The surface finiyshed by heat treatment and pickling or processcorresponding there to after hot rolling. | Chemical tank,pipe | |||
| 2B | Those finished,after cold rolling,by heattreatment,pickling or otherequivalent treatment and lastly bycold rolling to given appropriate luster. | Medical equipment,Food industry,Construction material | |||
| No.3 | Those finished by polishing with No.100 to No.120 abrasives specified in JIS R6001. | Kitchen utensils,Building | |||
| No.4 | Those finished by polishing with No.150 to No.180 abrasive specified in JIS R6001 | Medical equipment | |||
| BA | Those processed with bright heat treatment after cold rolling. | Electric equipment, Building | |||
| HL | Those finished polishing so as to give continuous polishing streaks by use=ing abrasive of suitable grain size. | Kitchen utensils,Building | |||
Chemical Composition(in percentage):
| Grade | C | Mn(Max) | P(Max) | S(Max) | Si(Max) | Cr(Max) | Ni(Max) | Mo(Max) |
| 201 | 0.15 | 5.5-7.5 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 1 | 16.0-18.0 | 3.5-5.5 | |
| 202 | 0.15 | 7.5-10.5 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 1 | 17.0-19.0 | 4.0-6.0 | |
| 304 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-10.5 | |
| 304L | 0.03 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 18.0-20.0 | 8.0-12.0 | |
| 310S | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1.5 | 24.0-26.0 | 19.0-22.0 | |
| 316 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 |
| 316L | 0.03 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 1 | 16.0-18.0 | 10.0-14.0 | 2.0-3.0 |
| 317 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 18.0-20.0 | 11.0-14.0 | 3.0-4.0 |
| 317L | 0.03 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 18.0-20.0 | 11.0-15.0 | 3.0-4.0 |
| 321 | 0.08 | 2 | 0.045 | 0.03 | 0.75 | 17.0-19.0 | 9.0-12.0 | |
| 409 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 1 | 10.5-11.75 | 0.5 | |
| 410S | 0.08 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | 11.5-13.5 | 0.6 | |
| 410 | 0.15 | 1 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 1 | 11.5-13.5 | 0.75 | |
| 420 | 0.35 | 0.5 | 0.035 | 0.015 | 0.5 | 12.0-13.0 | 0.2-3.0 |
Application:

Packaging & Shipping
Packing :
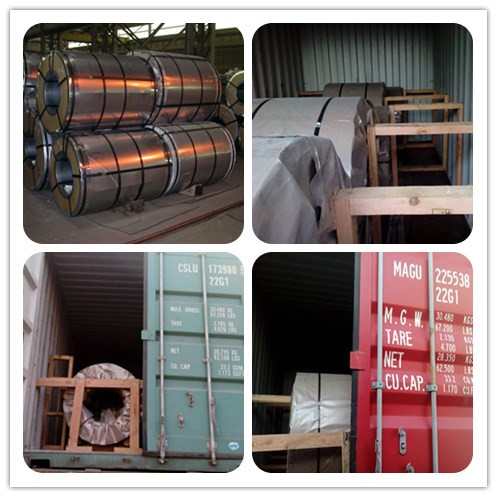

Our Factory:
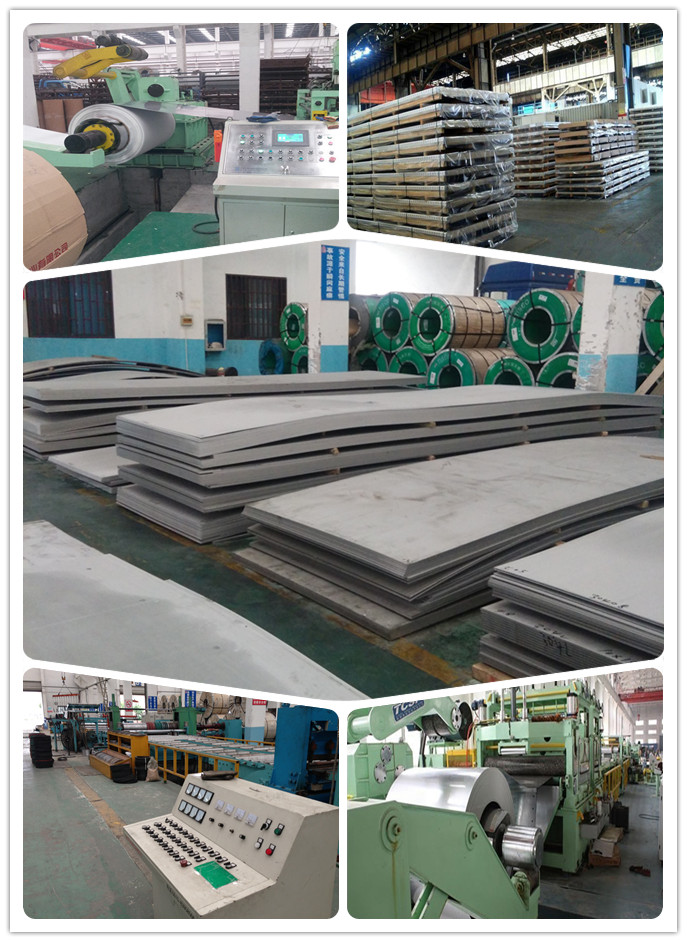

Process Flow:
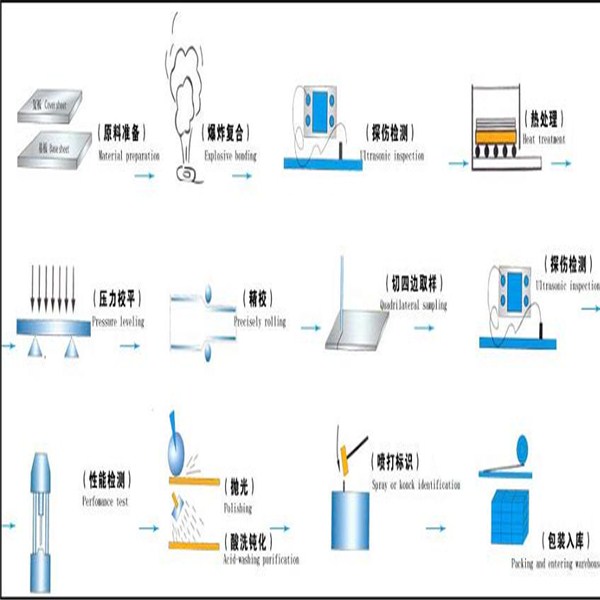


- Q: Are stainless steel strips magnetic?
- Yes, stainless steel strips can be magnetic depending on their composition and processing. Generally, austenitic stainless steels are non-magnetic, while ferritic and martensitic stainless steels can exhibit magnetic properties.
- Q: Can 111 stainless steel strips be laser cut for precise shapes?
- Indeed, it is possible to laser cut 111 stainless steel strips into precise shapes. Laser cutting proves to be an exceptionally precise and accurate technique suitable for cutting a wide range of materials, such as stainless steel. By harnessing a computer-controlled laser beam, intricate and detailed cuts can be effortlessly executed with utmost precision. By configuring the appropriate settings and parameters, laser cutting can effortlessly manipulate 111 stainless steel strips, crafting them into precise shapes that align with the desired specifications.
- Q: Are 111 stainless steel strips suitable for chemical reactors?
- Yes, 111 stainless steel strips are suitable for chemical reactors. They possess excellent corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, and good mechanical properties, making them suitable for handling various chemicals and operating conditions within a reactor.
- Q: Can 111 stainless steel strips be polished to a mirror-like finish?
- It is indeed possible to achieve a mirror-like finish on 111 stainless steel strips. However, the key factors that determine this outcome are the quality of the stainless steel strips and the polishing method employed. Stainless steel possesses inherent qualities such as a smooth surface and resistance to corrosion, which enable it to be polished to a high shine. Nevertheless, attaining a mirror-like finish necessitates a meticulous polishing process that involves several stages of abrasive materials and polishing compounds. By employing the appropriate equipment and technique, it becomes feasible to polish 111 stainless steel strips to a mirror-like finish, resulting in an exceptionally reflective and aesthetically pleasing surface.
- Q: How do stainless steel strips handle vibration and shock?
- Stainless steel strips are known for their exceptional strength and durability, making them highly capable of handling vibration and shock. Their inherent properties, such as high tensile strength and resistance to deformation, allow them to absorb and distribute the impact forces caused by vibrations and shocks. Additionally, stainless steel's excellent corrosion resistance ensures that the strips remain intact and unaffected even in harsh environments, further enhancing their ability to withstand vibration and shock.
- Q: Are stainless steel strips suitable for brewery piping?
- Yes, stainless steel strips are highly suitable for brewery piping. Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, durability, and hygiene properties, making it an ideal choice for brewery applications. It can withstand the aggressive and corrosive environment of breweries, ensuring the purity and integrity of the beer being produced. Stainless steel strips also offer easy maintenance and cleaning, making them a reliable and cost-effective option for brewery piping systems.
- Q: Are stainless steel strips suitable for architectural sculptures?
- Yes, stainless steel strips are suitable for architectural sculptures. Stainless steel is a highly versatile material that offers several advantages for creating architectural sculptures. Firstly, stainless steel is known for its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for outdoor sculptures that are exposed to various weather conditions. This ensures that the sculptures will maintain their aesthetic appeal and structural integrity over time. Additionally, stainless steel has a sleek and modern appearance, which can enhance the visual appeal of architectural sculptures. Its reflective surface can create interesting light and shadow effects, adding depth and dimension to the artwork. Stainless steel can also be easily manipulated and shaped into various forms, allowing artists to create intricate and complex designs. Moreover, stainless steel is a sustainable and eco-friendly material choice. It is 100% recyclable, meaning that it can be reused and repurposed, reducing waste and contributing to a greener environment. Overall, stainless steel strips are well-suited for architectural sculptures due to their durability, aesthetic appeal, versatility, and eco-friendliness.
- Q: Can stainless steel strips be etched or engraved?
- Yes, stainless steel strips can be etched or engraved using various techniques such as chemical etching, laser engraving, or mechanical engraving.
- Q: Are stainless steel strips affected by UV radiation?
- Stainless steel strips, in general, remain unaffected by UV radiation. The exceptional resistance of stainless steel to corrosion and oxidation, which encompasses resistance to UV radiation, is well known. This is attributed to the inclusion of chromium in the steel, resulting in the formation of a protective chromium oxide layer on the surface. Consequently, the steel is prevented from reacting with oxygen and other elements present in the surroundings. As a result, stainless steel strips can be employed in outdoor applications or environments exposed to sunlight without experiencing notable deterioration or harm.
- Q: Can stainless steel strips be used in the production of automotive parts?
- Yes, stainless steel strips can be used in the production of automotive parts. Stainless steel is a durable and corrosion-resistant material, making it suitable for various automotive applications such as exhaust systems, trim parts, brackets, and other components. Its strength, resistance to heat and chemicals, and aesthetic appeal make it a preferred choice in the automotive industry.
Send your message to us
201 202 304 304L Stainless Steel Coil manufacturers
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 4 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 100000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


























