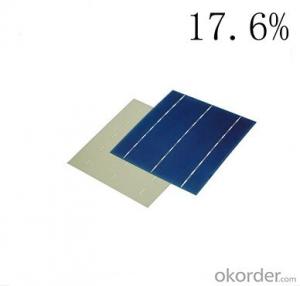
Si Solar Cells
Si Solar Cells Related Searches
C Si Solar Cells Cesi Solar Cells Solar Energy Cells Bio Solar Cells Cis Cigs Solar Cells Organic Solar Cells Free Solar Cells Photovoltaic Solar Cells Satellite Solar Cells Are Solar Cells Nano Solar Cells Chinese Solar Cells Chipped Solar Cells Electric Solar Cells Buy Solar Cells High Temperature Solar Cells Commercial Solar Cells High Power Solar Cells High Efficiency Solar Cells Large Solar Cells Solar Cell Module Biogenic Solar Cells Raw Solar Cells Residential Solar Cells Cigs Solar Cells High Performance Solar Cells Lightweight Solar Cells Hot Solar Cells Bacteria Solar Cells Loose Solar CellsSi Solar Cells Supplier & Manufacturer from China
Silicon-based solar cells, commonly known as Si Solar Cells, are a type of photovoltaic cell that harnesses sunlight to generate electricity. These cells are made from crystalline silicon, which is the most abundant material used in the production of solar panels. Si Solar Cells are highly efficient and reliable, making them a popular choice for residential, commercial, and utility-scale solar power applications.Si Solar Cells are widely used in various settings, from rooftop installations to large solar farms, due to their ability to convert sunlight into electricity with minimal energy loss. They are also known for their durability and long lifespan, which makes them a cost-effective solution for harnessing renewable energy. In addition to their use in power generation, Si Solar Cells are also utilized in a range of other applications, such as powering remote sensors, satellites, and portable electronic devices.
Okorder.com is a leading wholesale supplier of Si Solar Cells, offering a vast inventory of high-quality products to cater to the needs of various industries. With a commitment to providing top-tier products at competitive prices, Okorder.com has established itself as a trusted source for solar cell components. Their extensive inventory ensures that customers can find the exact Si Solar Cells they need for their specific projects, whether it's for a small-scale residential installation or a large-scale solar power plant.
Hot Products