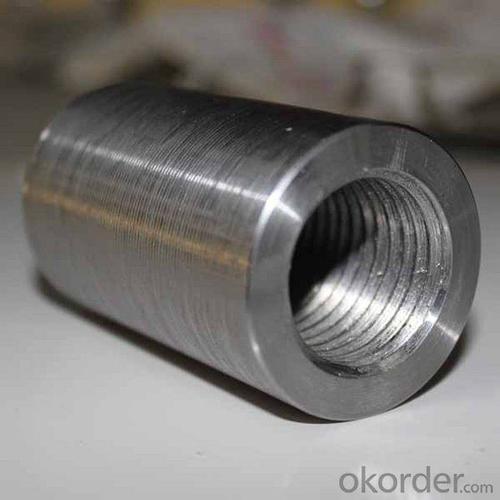
Steel Coupler Rebar Scaffolding Wire Layer Scaffolding with New Design
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Steel Coupler Rebar Scaffolding Wire Layer Scaffolding with New Design
1.Description:
Lapped joints are not always an appropriate means of connecting rebar. The use of Steel Rebar Couplers can simplify the design and construction of reinforced concrete and reduce the amount of reinforcement required.
The threaded steel coupler system is designed as a threaded reinforcement connection with 100% load transmission. The steel coupler rebar connection system is suitable for both static and dynamic load transmission in construction joints.
The coupler is designed as a threaded reinforcement connection for formed construction joints. Reinforcement work is normally carried out on both sides of the construction joint using lap joints or one side is anchored. The bar lengths are based on the structural analysis requirements of the building component and are calculated from anchorage and lap lengths.
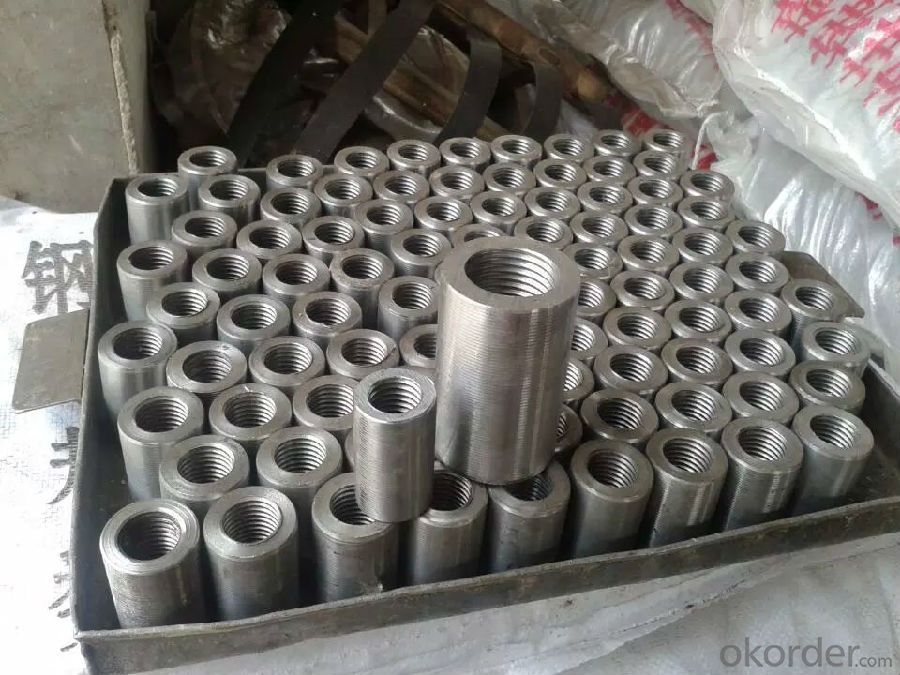


2.Advantages of Steel Coupler Rebar Lift Scaffolding Galvanized Scaffolding Tube with Low Price:
The coupler system provides the opportunity to connect rebars quickly, easily and cost effectively, even when large rebar diameters are used. This makes the steel coupler rebar range a logical extension to our rebendable CNBM reinforcement continuity system for rebars over 12 mm.
3.Available sizes of Steel Coupler Rebar Lift Scaffolding Galvanized Scaffolding Tube with Low Price:
14mm,16mm,18mm,20mm,22mmm,25mm,28mm,32mm,36mm,40mm
4.Delivery:
Delivery Term: FOB / CFR / CIF available.
Delivery Time: 15 days or less after order confirmed.
5.Why choose us?
Technical Expertise
Experienced Management
Stringent Quality Control
Exemplary Service
On-Time Delivery
Wide Product Range
Competitive Pricing
Huge branch network capable of catering worldwide
- Q: Can steel formwork be used in areas with extreme temperature variations?
- Steel formwork is indeed capable of being utilized in regions with significant temperature fluctuations. Thanks to its high strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to thermal changes, steel is well-suited for diverse conditions. It can endure both high and low temperatures without experiencing structural deformity or deterioration. Moreover, steel formwork delivers exceptional stability and durability, guaranteeing its ability to withstand the strain caused by extreme temperature fluctuations. However, it is crucial to take into account the effects of thermal expansion and contraction when employing steel formwork in areas with substantial temperature variations, as these factors may influence the precision of the formwork and the ultimate concrete structure. By considering proper design aspects and employing appropriate installation techniques, any potential issues arising from temperature variations can be effectively managed.
- Q: Can steel formwork be used for both new construction and renovation projects?
- Absolutely, steel formwork is applicable in both new construction and renovation projects. It boasts remarkable versatility, effortlessly accommodating diverse project demands. With exceptional sturdiness and resilience, it proves suitable for projects of any scale, whether they are minor or massive. Steel formwork serves the purpose of erecting new structures and revamping existing ones alike. Moreover, it presents the added benefit of reusability, effectively diminishing expenses and waste in the long term. Furthermore, steel formwork guarantees meticulous and precise construction, ensuring top-notch outcomes in both fresh construction endeavors and renovation undertakings.
- Q: What are the different types of joints used with steel formwork?
- There are several types of joints that are commonly used with steel formwork in construction projects. These joints are designed to ensure stability, strength, and ease of assembly and disassembly. Some of the most commonly used joints include: 1. Butt joint: This is a simple joint where two steel formwork sections are connected by placing their edges together. It is commonly used for straight sections of formwork. 2. Lap joint: In a lap joint, one formwork section overlaps another, creating a strong connection. This joint is often used for longer sections of formwork to provide additional strength. 3. Clamped joint: A clamped joint involves using clamps or bolts to secure the formwork sections together. This type of joint allows for easy adjustment and repositioning of the formwork. 4. Wedge joint: A wedge joint is commonly used to connect vertical and horizontal formwork sections. It involves inserting a wedge-shaped piece into a slot to create a secure connection. 5. Flanged joint: A flanged joint is created by using flanges or plates on the formwork sections that overlap and are bolted together. This joint provides a strong connection and is often used for large and heavy formwork components. 6. Pin joint: A pin joint involves using pins or dowels to connect formwork sections together. This type of joint allows for quick and easy assembly and disassembly of the formwork. It is important to select the appropriate joint type based on the specific requirements of the construction project. The choice of joint will depend on factors such as the formwork design, load-bearing capacity, ease of assembly, and required reusability.
- Q: How does steel formwork contribute to the sustainability of a construction project?
- Steel formwork contributes to the sustainability of a construction project in several ways. Firstly, steel formwork is highly durable and has a long lifespan. This means that it can be used for multiple construction projects, reducing the need for new formwork and minimizing waste. Additionally, the durability of steel formwork reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements, saving both time and resources. Secondly, steel formwork is a reusable material. It can be easily disassembled and reassembled for use in different projects, reducing the demand for new formwork and minimizing the amount of waste generated. This significantly reduces the environmental impact of construction projects, as it reduces the need for new materials and decreases the amount of waste sent to landfills. Furthermore, steel formwork is highly efficient and allows for faster construction times. Its strength and stability enable the construction process to progress more quickly, reducing the overall duration of the project. This not only saves time but also reduces the energy consumption associated with construction activities, contributing to the overall sustainability of the project. Moreover, steel formwork is a recyclable material. At the end of its lifespan, the steel formwork can be recycled, further reducing its environmental impact. Recycling steel requires less energy and resources compared to manufacturing new steel, thus reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving natural resources. In summary, steel formwork contributes to the sustainability of a construction project by being durable, reusable, efficient, and recyclable. It reduces the need for new formwork, minimizes waste generation, saves construction time, and conserves resources. By incorporating steel formwork into construction projects, builders can significantly reduce the environmental impact while ensuring long-term durability and efficiency.
- Q: What are the different types of lifting systems used in steel formwork?
- There are several types of lifting systems used in steel formwork, including manual lifting systems, mechanical lifting systems, and hydraulic lifting systems. Manual lifting systems involve the use of manual labor and equipment, such as cranes or hoists, to lift and move the steel formwork. Mechanical lifting systems utilize mechanical devices, such as electric winches or chain blocks, to lift and transport the formwork. Hydraulic lifting systems utilize hydraulic power to lift and lower the steel formwork, providing greater control and precision in the lifting process.
- Q: How does steel formwork contribute to the accuracy of concrete placements?
- There are several ways in which steel formwork contributes to the accuracy of concrete placements. To begin with, the high level of dimensional accuracy associated with steel formwork ensures that the concrete structures being formed have the correct dimensions and shape. This is because the steel panels and components used in the formwork system are manufactured with precise measurements and tolerances. In addition, steel formwork provides excellent stability and rigidity, preventing any movement or deformation during the concrete pouring and curing process. This stability is crucial for maintaining the accuracy of the concrete placement, as any shifting or warping of the formwork can result in inconsistencies in the final product. Moreover, steel formwork is highly durable and capable of withstanding the pressure exerted by the fresh concrete. This durability ensures that the formwork remains intact and maintains its shape throughout the entire placement process. It also eliminates the risk of bulging or sagging, which can compromise the accuracy of the concrete placement. Furthermore, steel formwork allows for precise control of the concrete's surface finish. With steel formwork, it is easy to mold and shape the concrete to achieve the desired surface texture and quality. This is particularly important in architectural applications where aesthetics play a significant role. Lastly, steel formwork is reusable and can be easily assembled and disassembled, allowing for multiple uses. This reusability factor contributes to cost-effectiveness and ensures that the formwork remains in optimal condition for accurate concrete placements over time. In conclusion, the dimensional accuracy, stability, durability, surface finish control, and reusability of steel formwork make it an invaluable tool for achieving accurate and high-quality concrete placements.
- Q: Can steel formwork be used for both horizontal and vertical structures?
- Yes, steel formwork can be used for both horizontal and vertical structures. Steel formwork is a versatile construction material that can be easily adjusted and reused, making it suitable for various types of structures. It provides excellent strength and stability, making it ideal for supporting heavy concrete loads in both horizontal and vertical applications. Steel formwork systems can be customized and assembled to meet the specific requirements of different construction projects, allowing for efficient and precise construction of both horizontal slabs and vertical walls. Its durability and resistance to wear and tear make it a reliable choice for long-term use in various construction applications.
- Q: How does steel formwork compare to timber formwork?
- Steel formwork is generally considered to be superior to timber formwork in terms of durability, strength, and reusability. Steel formwork has a longer lifespan, can withstand higher pressures and loads, and requires less maintenance compared to timber formwork. Additionally, steel formwork provides better dimensional accuracy and consistency, resulting in smoother and more uniform concrete surfaces. While timber formwork may be less expensive and easier to handle, steel formwork offers numerous advantages that make it a preferred choice in many construction projects.
- Q: How does steel formwork contribute to better site organization?
- Steel formwork contributes to better site organization in several ways. Firstly, steel formwork is highly durable and reusable, which means it can be used multiple times on different construction projects. This eliminates the need for frequent replacement and reduces waste on site. The ability to reuse steel formwork also reduces storage space requirements, as it can be easily stacked and stored when not in use. Secondly, steel formwork is adjustable and customizable, allowing it to be easily modified to fit different shapes and sizes of concrete structures. This flexibility enables efficient use of space on site, as the formwork can be tailored to the specific requirements of each project. This ensures that the construction process is organized and streamlined, minimizing the need for additional materials or adjustments. Furthermore, steel formwork is known for its high strength and stability, which enhances site safety. Its robust structure provides a secure platform for workers to carry out their tasks, reducing the risk of accidents or injuries. This promotes a safer working environment and improves overall site organization. Steel formwork also contributes to better site organization by facilitating faster construction cycles. Its quick assembly and disassembly process allows for efficient and smooth workflow, enabling construction projects to be completed in a timely manner. This helps to minimize delays and ensures that the site is well-organized and productive. Lastly, steel formwork can be easily integrated with other construction systems and technologies. This compatibility allows for seamless coordination between different components of the project, promoting better site organization. Whether it is integrating with scaffolding systems or connecting to other structural elements, steel formwork ensures a cohesive and well-organized construction site. In conclusion, steel formwork contributes to better site organization through its durability, adjustability, strength, and compatibility with other construction systems. Its ability to be reused, customized, and integrated with other components enhances efficiency, safety, and productivity on construction sites.
- Q: What are the common safety training requirements for steel formwork installation?
- The common safety training requirements for steel formwork installation involve several key aspects to ensure the safety of workers and the successful completion of the project. These requirements may vary depending on the specific regulations and standards set by the local authorities and the company's policies. However, some of the common safety training requirements for steel formwork installation include: 1. General Construction Safety Training: All workers involved in steel formwork installation should receive general construction safety training, which covers topics such as hazard identification, personal protective equipment (PPE) usage, emergency procedures, and safe work practices. This training ensures that workers have a basic understanding of construction site safety. 2. Fall Protection Training: Given that steel formwork installation often involves working at heights, fall protection training is crucial. Workers should be trained on the proper use and inspection of fall protection equipment, such as harnesses, lanyards, and anchor points. They should also learn how to set up and dismantle temporary fall protection systems like guardrails and safety nets. 3. Material Handling and Lifting Training: Steel formwork components can be heavy and require proper lifting techniques to avoid injuries. Workers should receive training in safe lifting practices, including correct body mechanics, proper use of lifting equipment such as cranes or forklifts, and understanding load capacities. 4. Scaffold Safety Training: Steel formwork installation often involves the use of scaffolding to access higher areas. Workers should be trained on safe scaffold erection, inspection, and usage. This includes knowledge of scaffold components, stability, fall protection on scaffolds, and safe practices for working on scaffolds. 5. Electrical Safety Training: Steel formwork installation may involve working near electrical systems or equipment. Workers should receive training on electrical safety, including identifying electrical hazards, using lockout/tagout procedures, and understanding safe distances from power lines. 6. Hazard Communication Training: Workers should undergo training on hazard communication protocols, including the identification and understanding of safety data sheets (SDS) and proper handling of hazardous materials commonly used in steel formwork installation. 7. First Aid and CPR Training: In the event of an accident or injury on the job site, workers should be trained in basic first aid and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) techniques. This training can help stabilize an injured worker until professional medical help arrives. It is important for employers to ensure that all workers receive comprehensive safety training before commencing steel formwork installation. Regular refresher courses and ongoing safety awareness programs should also be conducted to reinforce safe work practices and maintain a high level of safety on the job site.
Send your message to us
Steel Coupler Rebar Scaffolding Wire Layer Scaffolding with New Design
- Loading Port:
- Shanghai
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1000 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 10000000 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches