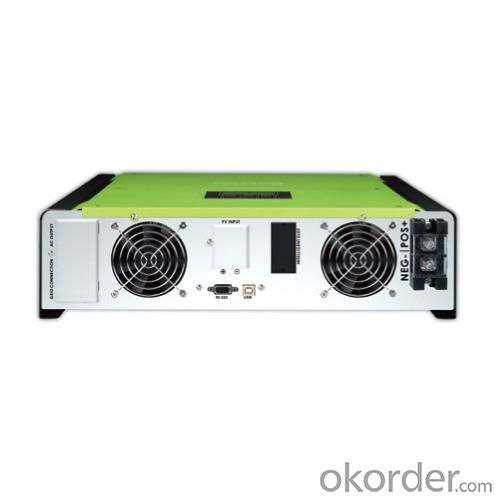
Solar Inverter Fan - On-grid Inverter with Energy Storage 2000W
- Loading Port:
- Shenzhen
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 Unit pc
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 Units/month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Description of On-Grid Inverter With Energy Storage 2000W
1.Pure sine wave output
2.Microprocessor controlled to guarantee stable charging system
3.Multiple operations: Grid tie, Off grid, and grid tie with backup
4.Built-in MPPT solar charger
5.LCD display panel for comprehensive information
6.Multiple communication
7.Green substitution for generators
8.User adjustable charging current up to 25A
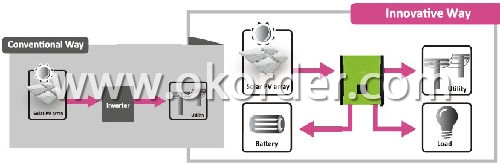
Feed-in is not only choice
In comparison with conventional grid-tie inverter, CNBM hybrid inverter is able to not only feed-in power to grid but also store solar power to battery for future usage and directly power to the loads.
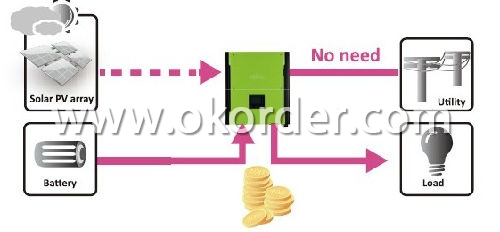
Save money by discharging battery for self-consumption first
CNBM hybrid inverter can save money by using battery energy first when PV energy is low. Until battery energy is low, CNBM will extract AC power from the grid.
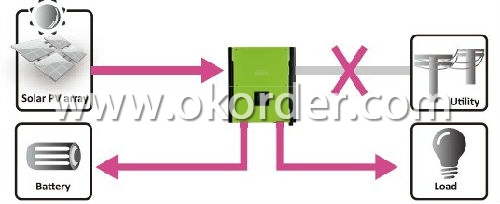
Power backup when AC failed
CNBM hybrid inverter can operate as an off-grid inverter to provide continuous power even without the grid.
It's perfect power solution for remote regions or temporary AC power source such as camping or flea market.
Datasheet of On-Grid Inverter With Energy Storage 2000W
MODEL | CNBM-H 2KW | CNBM-H 3KW |
RATED POWER | 2000W | 3000W |
GRID-TIE OPERATION | ||
PV INPUT (DC) | ||
Maximum DC power | 2250W | 3200W |
Nominal DC voltage / Maximum DC voltage | 300 VDC / 350VDC | 360 VDC / 500VDC |
Start voltage / Initial Feeding Voltage | 80 VDC / 120VDC | 116 VDC / 150 VDC |
MPP voltage range | 150 VDC ~ 320 VDC | 250 VDC ~ 450 VDC |
Number of MPP Trackers / Max. input current | 1 / 1×15A | 1 / 1×13A |
GRID OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Output Voltage Range | 88 - 127 VAC | 184 – 264.5 VAC |
Nominal Output Current | 18 A | 13.1 A |
Power Factor | > 0.99 | |
EFFICIENCY | ||
Maximum Conversion Efficiency (DC/AC) | 95% | 96% |
European Efficiency@ Vnominal | 94% | 95% |
OFF-GRID OPERATION | ||
AC INPUT | ||
AC Startup Voltage / Auto Restart Voltage | 60 - 70 VAC / 85VAC | 120 - 140 VAC / 180VAC |
Acceptable Input Voltage Range | 85 - 130 VAC | 170 - 280 VAC |
Maximum AC Input Current | 30A | 25A |
PV INPUT (DC) | ||
Maximum DC voltage | 350 VAC | 500 VAC |
MPP Voltage Range | 150 VAC ~ 320 VDC | 250 VAC ~ 450 VDC |
Maximum Input Current | 1 / 1×15A | 1 / 1×13A |
BATTERY MODE OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Output Frequency | 50 Hz / 60 Hz (auto sensing) | |
Output Waveform | Pure sine wave | |
Efficiency (DC to AC) | 90% | 93% |
HYBRID OPERATION | ||
PV INPUT (DC) | ||
Nominal DC voltage / Maximum DC voltage | 300 VDC / 350VDC | 360 VDC / 500VDC |
Start voltage / Initial Feeding Voltage | 80 VDC / 120VDC | 116 VDC / 150 VDC |
MPP voltage range | 150 VDC ~ 320 VDC | 250 VDC ~ 450 VDC |
Maximum Input Current | 1 / 1×15A | 1 / 1×13A |
GRID OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Output Voltage Range | 88 - 127 VAC | 184 – 264.5 VAC |
Nominal Output Current | 18 A | 13.1 A |
AC INPUT | ||
AC Startup Voltage / Auto Restart Voltage | 60 - 70 VAC / 85VAC | 120 - 140 VAC / 180VAC |
Acceptable Input Voltage Range | 85 - 130 VAC | 170 - 280 VAC |
Maximum AC Input Current | 30A | 25A |
BATTERY MODE OUTPUT (AC) | ||
Nominal Output Voltage | 101/110/120/127 VAC | 208/220/230/240 VAC |
Efficiency (DC to AC) | 90% | 93% |
BATTERY & CHARGER | ||
Nominal DC Voltage | 48 VDC | |
Maximum Charging Current | 25A | |
GENERAL | ||
PHYSICAL | ||
Dimension, D X W X H (mm) | 420 x 415 x 170 | |
Net Weight (kgs) | 15.5 | |
INTERFACE | ||
Communication Port | RS-232 / USB | |
Intelligent Slot | Optional SNMP, Modbus, and AS400 cards available | |
ENVIRONMENT | ||
Humidity | 0 ~ 90% RH (No condensing) | |
Operating Temperature | 0 to 40°C | |
Altitude | 0 ~ 1000 m | |
COMPLIANCE | ||
Standard | CE, VDE 0126-1-1,VDE-AR-N 4105 | |
- Q: What is the role of a solar inverter in a utility-scale system?
- The role of a solar inverter in a utility-scale system is to convert the direct current (DC) electricity produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used by the utility grid. In addition to this basic function, a solar inverter also monitors and controls the performance of the solar panels, ensures maximum power generation, and provides safety features such as grid synchronization and protection against voltage fluctuations.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a generator?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a generator. In fact, it can be a useful combination in situations where solar power is not sufficient or unavailable. The generator can provide backup power to charge the batteries or directly power the inverter, which then converts the DC power from the generator into AC power for use in electrical appliances and systems.
- Q: What is the role of an isolation transformer in a solar inverter?
- The role of an isolation transformer in a solar inverter is to provide electrical isolation between the solar panels and the grid. It helps protect the solar panels and the inverter from electrical disturbances, such as voltage spikes or surges, that may occur in the grid. Additionally, the isolation transformer helps mitigate ground fault currents and provides a safety barrier between the grid and the solar system.
- Q: Are there any government incentives for installing a solar inverter?
- Yes, there are government incentives available for installing a solar inverter. Many countries offer tax credits, grants, or subsidies to promote the use of renewable energy sources like solar power. These incentives aim to encourage homeowners and businesses to adopt solar energy systems, including solar inverters, by offsetting the initial installation costs and promoting sustainability. It is advisable to check with local authorities or consult renewable energy organizations to understand the specific incentives available in your region.
- Q: How do you choose the right size solar inverter for a specific solar power system?
- Choosing the right size solar inverter for a specific solar power system requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some steps to help you make the right choice: 1. Determine your solar power system's capacity: Start by calculating the total capacity of your solar power system. This involves determining the total wattage of all your solar panels combined. This information can usually be found on the product specifications or by consulting with your solar panel manufacturer. 2. Consider your average energy consumption: Assess your average energy consumption to determine the size of the solar inverter needed to meet your requirements. Consider your peak power usage and any potential future increase in energy demands. 3. Evaluate the inverter's capacity: Match the capacity of the solar inverter with your solar power system's capacity. The inverter's capacity should be equal to or slightly higher than your system's total capacity to ensure optimal performance. 4. Consider the inverter's efficiency: Look for an inverter with high efficiency ratings. A higher efficiency rating means that it can convert a larger percentage of the solar energy into usable electricity, minimizing power losses. 5. Determine the inverter type: Decide on the type of solar inverter suitable for your system. There are three main types: string inverters, microinverters, and power optimizers. String inverters are the most common and cost-effective option for small to medium-sized systems, while microinverters and power optimizers are better suited for complex installations or systems with shading issues. 6. Assess the inverter's features: Consider additional features that the solar inverter may offer. Look for features such as monitoring capabilities, grid integration capabilities, and built-in safety features like arc fault protection or rapid shutdown. 7. Consult with professionals: If you are uncertain about the right size solar inverter for your specific solar power system, it is advisable to consult with a professional solar installer or an electrical engineer. They can help assess your energy needs, system requirements, and provide expert guidance on selecting the appropriate inverter size. Remember, choosing the right size solar inverter is crucial for the overall performance and efficiency of your solar power system. Taking the time to evaluate your system's requirements and seeking expert advice will help ensure you make an informed decision.
- Q: Does a solar inverter require any additional cooling or ventilation?
- Yes, a solar inverter typically requires additional cooling or ventilation. This is because the inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power household appliances. During this conversion process, the inverter generates heat, and to maintain optimal performance and prevent overheating, it requires proper cooling or ventilation mechanisms.
- Q: What is the PV inverter starting voltage
- sine wave becomes narrower and the voltage width in the center of the sine wave is widened and the switching element is always operated in a direction at a certain frequency in a half cycle, A pulse wave train (pseudo sine wave). Then let the pulse wave form a sine wave through a simple filter
- Q: What is the warranty period for a solar inverter?
- The warranty period for a solar inverter typically varies depending on the manufacturer and model, but it commonly ranges from 5 to 10 years.
- Q: What is the role of a solar inverter in a solar-powered telecommunications system?
- The role of a solar inverter in a solar-powered telecommunications system is to convert the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power the telecommunications equipment. It is responsible for ensuring that the energy generated by the solar panels is compatible with the electrical requirements of the system, allowing for efficient and reliable operation of the telecommunications equipment.
- Q: What is the role of a solar inverter in maintaining system stability?
- The role of a solar inverter in maintaining system stability is to convert the direct current (DC) produced by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used by household appliances and fed back into the electrical grid. By regulating the voltage and frequency of the AC output, the inverter ensures that the solar system operates within the acceptable range, preventing overloading or damaging the connected devices. Additionally, solar inverters also help to synchronize the solar system with the grid, allowing for smooth integration and optimal energy flow. Overall, the solar inverter plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and efficiency of the solar power system.
Send your message to us
Solar Inverter Fan - On-grid Inverter with Energy Storage 2000W
- Loading Port:
- Shenzhen
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 1 Unit pc
- Supply Capability:
- 8000 Units/month pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords






























