Schedule 40 Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe 12Cr2Mo CNBM
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 30 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Quick Details
| Thickness: | 1.73 - 59.54 mm | Section Shape: | Round | Outer Diameter: | 10.3 - 914.4 mm |
| Secondary Or Not: | Non-secondary | Application: | Fluid Pipe | ||
| Technique: | Hot Rolled | Certification: | API | Surface Treatment: | Galvanized,vanish covering, black painting, galvenized ect. |
| Special Pipe: | API Pipe | Alloy Or Not: | Non-alloy | Length: | 5-12m as per customer's requirements |
| SCH: | SCH10~160, STD, XS & XXS | Payment Terms: | L/C T/T | Supply Ability: | 5000 Ton/Tons per Week |
| Product: | pipe prices | Grade: | 10#,20#,45#,A106(B,C),A53(A,B),12Cr1MoV,12Cr1MoVG,12Cr2Mo,13CrMo44,13CrMo45,15CrMo,15CrMoG,St52,St52.4,10#-45#,A53-A369,Cr-Mo alloy,ST35-ST52 | Standard: | API 5CT,API 5L,ASTM A106-2006,ASTM A53-2007,DIN 17175,GB 3087-1999,GB 5130,GB 6479-2000,GB 9948-2006,GB/T 17396-1998,GB/T 5312-1999,GB/T 8162-1999,GB/T 8163-1999,API,ASTM,DIN,GB |
Packaging & Delivery
| Packaging Detail: | By bundles, seaworthy wooden cases, steel framed cases, and simple packaging or according to the demand of the customers. |
| Delivery Detail: | within 5-15 days |
Specifications
1.pipe prices
2.Supply Ability:5000 Tons per Week
3.Payment Terms:L/C T/T
High quality Carbon steel pipe, Best pipe prices
1) Application: Overheat pipe for low and mediumpressure boiler,boiling water pipe, locomotive smoke pipe(big and small),Carry gas ,water or oil in the industries of petroleum and natural gas etc
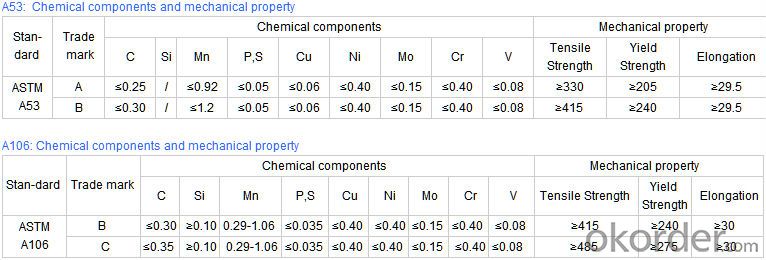
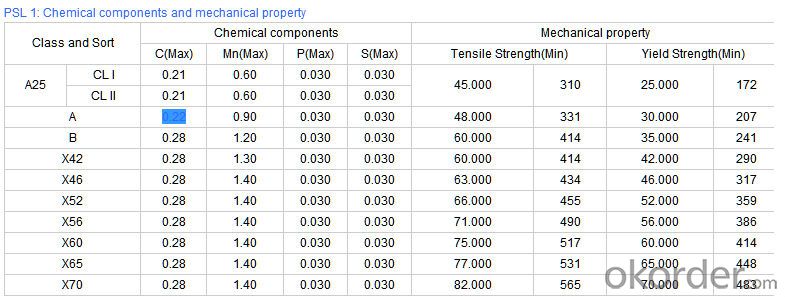
2) Materials: 10#, 20#, 45#, 15CrMo, 12Cr1MoV, 13CrMo44, 12Cr2Mo, 13CrMo45, 12Cr1MoVG, 15CrMoG, API J55, API K55, API N80, API L80, API P110
3)Pipe according to standard: GB 3087-1999, GB/T 8163-1999, GB/T 8162-1999, GB 9948-2006, GB/T 17396-1998, GB/T 5312-1999, GB 6479-2000, GB 5130, DIN 17175, API 5CT, API 5L .
4)Packing: By bundles, seaworthy wooden cases, steel framed cases, and simple packaging or according to the demand of the customers.
Technical Parameters of Seamless Steel Pipe
- Q: What is the maximum diameter of steel pipes?
- The maximum diameter of steel pipes can vary depending on various factors such as manufacturing capabilities, industry standards, and specific project requirements. However, steel pipes can typically range from a few millimeters in diameter for small-scale applications to several meters in diameter for large-scale industrial projects.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the construction of highways?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in the construction of highways for various purposes, such as drainage systems, culverts, and sign supports. They provide a durable and efficient solution for transporting stormwater and preventing damage to the road surface. Additionally, steel pipes are utilized to support highway signs and traffic signals, ensuring their stability and longevity.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used in the oil and gas industry?
- Yes, steel pipes are commonly used in the oil and gas industry. They are known for their high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion and high pressure, making them suitable for transporting oil and gas.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for underground gas distribution?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for underground gas distribution. Steel pipes are commonly utilized in the gas industry due to their high strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. They are capable of withstanding the pressure and stress associated with gas distribution systems. Additionally, steel pipes have been proven to be reliable and safe for transporting natural gas underground. However, it is essential to ensure that the steel pipes are properly coated and protected against corrosion to maintain their integrity and longevity. Regular inspections and maintenance are also necessary to identify and address any potential issues that may arise.
- Q: How are steel pipes used in the construction of chemical plants?
- Steel pipes are commonly used in the construction of chemical plants due to their excellent durability, strength, and resistance to corrosion. They are used to transport various chemicals, gases, and fluids throughout the plant, ensuring a safe and efficient flow. These pipes are also used for structural support, providing stability to the plant's infrastructure. Additionally, steel pipes are often used for the installation of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, as well as for the construction of process equipment and storage tanks within the chemical plant.
- Q: What are the different grades of steel pipes?
- The different grades of steel pipes vary based on their chemical composition and physical properties. Some commonly used grades include carbon steel pipes (grades A, B, and C), alloy steel pipes (grades P1, P5, P9, and P11), stainless steel pipes (grades 304, 316, and 321), and duplex steel pipes (grades 2205 and 2507). Each grade offers specific characteristics suited for different applications and industries.
- Q: What are the advantages of using steel pipes in the manufacturing of appliances?
- There are several advantages of using steel pipes in the manufacturing of appliances. Firstly, steel pipes offer high strength and durability, making them ideal for handling heavy loads and withstanding harsh conditions. Secondly, steel pipes have excellent corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity and preventing damage from exposure to moisture or chemicals. Furthermore, steel pipes provide a smooth interior surface, promoting efficient flow of liquids or gases within the appliances. Lastly, steel pipes are recyclable, making them a sustainable choice and contributing to environmental conservation.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used in high-pressure applications?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used in high-pressure applications. Steel pipes are known for their strength and durability, making them suitable for handling high pressures in various industries such as oil and gas, water distribution, and chemical processing.
- Q: How do steel pipes connect to other components?
- Steel pipes can be connected to other components using various methods, including welding, threading, flanges, and couplings. These connections ensure a secure and leak-proof joint between the steel pipe and other components, allowing for efficient fluid or gas transfer in various industries.
- Q: Can steel pipes be used for underground drainage?
- Yes, steel pipes can be used for underground drainage. Steel pipes are commonly used for underground drainage systems due to their durability, strength, and resistance to various elements, such as soil erosion, chemical corrosion, and high pressure. However, it is important to consider factors like the type of soil, environmental conditions, and the specific requirements of the drainage system before deciding on the material for underground drainage pipes.
Send your message to us
Schedule 40 Seamless Carbon Steel Pipe 12Cr2Mo CNBM
- Loading Port:
- Qingdao
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 pc
- Supply Capability:
- 30 pc/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords



























