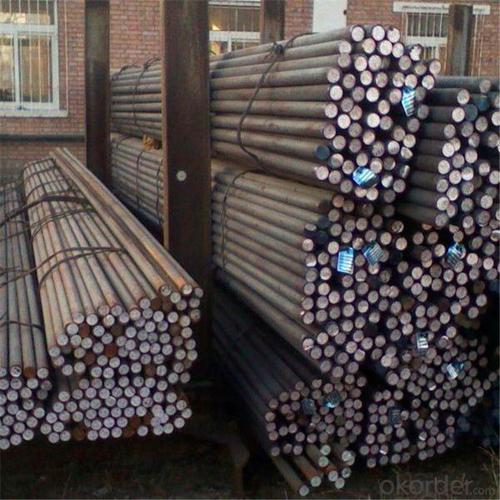
SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
Specification
SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
Product Description of SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
1. Steel grade: SAE1045, 45#, C45, S45C
2. Length: 6M-12M
3. Diameter: 16mm-300mm
4. Product range: round bar, flat bar, square bar
5. Technique: Hot rolled, forged, cold drawn
Specification of SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
Material | SAE1045 | Round bar | Dia(mm) | 16-300mm |
Process | EAF + LF + VD + Forged + Heat Treatment (optional) | Length (mm) | Max 12m | |
Heat treatment | Normalized / Annealed / Quenched / tempered | Flat bar | Thickness(mm) | 8-500mm |
Delivery condition | Hot forged +Rough machined (black surface after Q/T)+ Turned (optional) | Width(mm) | 70-200mm | |
Test | Ultrasonic test according to SEP 1921-84 D/d | Length (mm) | Max 12m |
Chemical Composition of SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Cu |
0.42~0.47 | 0.17~0.37 | 0.35~0.65 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.30 | ≤0.25 |
Photo Show of SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
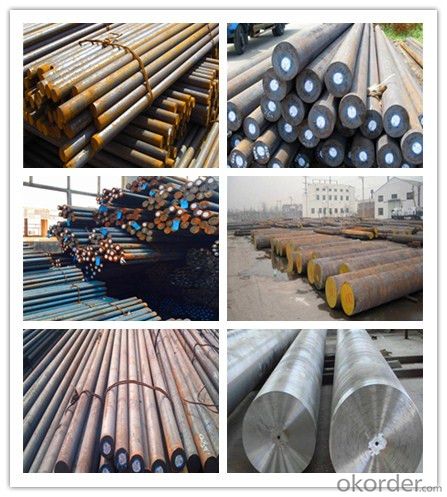

Packing and Delivery:
Packing in bundle package, or as customer's requirements.
Delivery Detail: 45 days after receiving the deposit.
Usage and Applications of SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
1. Steel round bar is used in a large number of architectural and engineering structures. Or it can be used in construction of plants for the production of steel house frames, high-voltage transmission towers, bridges, vehicles, boilers, containers, ships, etc.
2. And we can use this kind of product on the performance of the mechanical parts if the demand is not very high.
3. Some special material steel round bar can be used for main shaft of steamer, hummer shank, with big section and supper force.
Company Information
CNBM International Corporation is the most important trading platform of CNBM group.
Whith its advantages, CNBM International are mainly concentrate on Cement, Glass, Iron and Steel, Ceramics industries and devotes herself for supplying high qulity series of refractories as well as technical consultancies and logistics solutions.
F A Q
1, Your advantages?
professional products inquiry, products knowledge train (for agents), smooth goods delivery, excellent customer solution proposale
2, Test & Certificate?
SGS test is available, customer inspection before shipping is welcome, third party inspection is no problem
3, Factory or Trading Company?
CNBM is a trading company but we have so many protocol factories and CNBM works as a trading department of these factories. Also CNBM is the holding company of many factories.
4, Payment Terms?
30% TT as deposit and 70% before delivery.
Irrevocable L/C at sight.
5, Trading Terms?
EXW, FOB, CIF, FFR, CNF
6, After-sale Service?
CNBM provides the services and support you need for every step of our cooperation. We're the business partner you can trust.
For any problem, please kindly contact us at any your convenient time.
We'll reply you in our first priority within 24 hours.
- Q: Can steel round bars be used in the manufacturing of office furniture?
- Yes, steel round bars can be used in the manufacturing of office furniture. Steel is a versatile and durable material that can be shaped into various forms, including round bars. These round bars can be used as structural components in office furniture, such as table legs, chair frames, or support beams. Steel round bars provide strength and stability to the furniture, making it suitable for heavy use in office environments. Additionally, steel can be finished in different ways, such as powder coating or chrome plating, to enhance its appearance and match the aesthetic of the office space. Overall, using steel round bars in the manufacturing of office furniture offers durability, stability, and a modern look.
- Q: Can steel round bars be used in the manufacturing of appliances?
- Yes, steel round bars can be used in the manufacturing of appliances. Steel is a durable and versatile material that can be shaped into different forms, including round bars, which can be used for various purposes in appliance manufacturing such as structural support, handles, or components.
- Q: Can steel round bars be used for making bicycle frames?
- Yes, steel round bars can be used for making bicycle frames. Steel is a commonly used material for bicycle frames due to its strength, durability, and relatively low cost. Steel round bars can be shaped and welded together to create a sturdy and rigid frame that provides stability and support for the rider.
- Q: What are the different types of surface defects that can occur in steel round bars?
- Steel round bars can experience multiple types of surface defects. Some of the most frequently encountered defects include the following: 1. Scratches: These shallow grooves or marks on the round bar's surface occur due to friction or contact with sharp objects during handling or transportation. 2. Pitting: Small, localized cavities or depressions on the surface are caused by corrosion or exposure to harsh environments. If left unaddressed, pitting can lead to further corrosion. 3. Scale: During the manufacturing process, a thin layer of oxide or impurities, known as scale, can form on the surface of steel round bars. Although it affects appearance and quality, scale is often removed during subsequent processing or cleaning. 4. Scabs: Irregularly shaped protrusions or raised areas on the surface result from solidification or cooling issues during the casting process. Proper attention is required to ensure the strength and integrity of the bar. 5. Roll marks: Elongated depressions or ridges on the surface are caused by uneven or improper rolling during manufacturing. Roll marks can impact the dimensional accuracy of the bar and may necessitate additional processing or grinding for removal. 6. Laminations: Sometimes visible on the surface, laminations are internal defects resulting from improper bonding or separation of layers during the steelmaking process. They can weaken the bar and reduce its load-bearing capacity. 7. Inclusions: Non-metallic particles or impurities can become trapped in the steel during manufacturing, appearing as dark spots or irregularities on the round bar's surface. Inclusions can affect the bar's mechanical properties. It is essential to recognize that the severity and impact of these surface defects may vary. Manufacturers and quality control personnel employ diverse inspection techniques to identify and mitigate these defects, ensuring the quality and reliability of the final product.
- Q: Can steel round bars be used in the hospitality industry?
- Yes, steel round bars can be used in the hospitality industry. Steel round bars are versatile and durable, making them suitable for various applications within the industry. They can be used for constructing furniture, such as chairs, tables, and bar stools, as well as for creating decorative elements like railings, light fixtures, and signage. Steel round bars also provide excellent strength and stability, ensuring the safety of guests and staff. Moreover, they can be easily customized to match the desired aesthetic and design preferences of different hospitality establishments. Overall, steel round bars are a reliable and practical choice for the hospitality industry due to their durability, versatility, and aesthetic appeal.
- Q: What are the different machining processes used for steel round bars?
- Some of the different machining processes used for steel round bars include turning, milling, drilling, and grinding. Turning involves rotating the bar against a cutting tool to remove material and create a desired shape. Milling uses a rotating cutter to remove material from the surface of the bar. Drilling involves creating holes in the bar using a rotating drill bit. Grinding uses an abrasive wheel to remove material and achieve a smooth surface finish on the bar. These processes are commonly used in metalworking industries to shape and refine steel round bars for various applications.
- Q: Are steel round bars available in different shapes other than round?
- No, steel round bars are specifically designed and manufactured in a cylindrical shape.
- Q: Can steel round bars be coated or plated?
- Yes, steel round bars can be coated or plated using a variety of methods such as electroplating, hot-dip galvanizing, or powder coating. Coating or plating steel round bars helps to enhance their corrosion resistance, improve their appearance, and provide additional durability and protection.
- Q: What are the different types of steel round bar coatings used in the automotive industry?
- There are several different types of steel round bar coatings that are commonly used in the automotive industry. These coatings are applied to the steel bars to enhance their durability, corrosion resistance, and overall performance. 1. Galvanized Coating: This is one of the most widely used coatings for steel round bars in the automotive industry. Galvanized coating involves applying a layer of zinc to the surface of the steel bar. This coating provides excellent corrosion resistance, protecting the steel from rust and other forms of degradation. 2. Epoxy Coating: Epoxy coatings are often used in automotive applications that require high chemical resistance. This type of coating provides a protective barrier against chemicals, moisture, and other corrosive substances. Epoxy coatings also have excellent adhesion properties, ensuring long-lasting performance. 3. Powder Coating: Powder coating is a popular choice for steel round bars in the automotive industry due to its durability and aesthetic appeal. This coating involves applying a dry powder to the surface of the steel bar, which is then heated to create a tough, protective layer. Powder coatings come in a wide range of colors and finishes, allowing for customization and branding opportunities. 4. Ceramic Coating: Ceramic coatings offer exceptional heat resistance, making them ideal for automotive applications that involve high temperatures. This type of coating provides a protective barrier that prevents heat damage and improves the overall lifespan of the steel round bars. 5. Phosphate Coating: Phosphate coatings are often used as a pre-treatment before applying other types of coatings. This coating improves the adhesion of subsequent coatings and provides additional corrosion resistance. Phosphate coatings also enhance the lubricity of the steel bar, reducing friction and wear. These are just a few examples of the different types of steel round bar coatings used in the automotive industry. Each coating offers unique benefits and is chosen based on the specific requirements of the application. Overall, these coatings play a crucial role in improving the performance and longevity of steel round bars in automotive applications.
- Q: What are the different types of steel round bar surface finishes for improved lubricity?
- To enhance lubricity, there exists a variety of surface finishes for steel round bars. 1. Achieving a smooth finish involves employing grinding or polishing techniques to create a sleek surface. This reduces friction and serves as a solid foundation for applying lubricants. 2. Chrome plating entails electroplating a layer of chromium onto the round bar's surface. This results in a hard, smooth, and corrosion-resistant coat that offers exceptional lubricity. Chrome plating is frequently employed in applications necessitating low friction and wear resistance. 3. Nitriding, a surface hardening process, involves diffusing nitrogen into the round bar's surface. This generates a robust layer that amplifies the steel's lubricity. Nitriding is commonly utilized when high wear resistance and improved lubrication are imperative. 4. Black oxide, a chemical conversion coating, forms a black surface on the steel round bar. This finish provides a thin layer of protection against corrosion along with enhanced lubricity. Black oxide is frequently favored in applications that require lubricity without a decorative appearance. 5. Teflon coating, also known as PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) coating, involves applying a thin layer of Teflon onto the round bar's surface. This coating offers exceptional lubricity and low friction properties. Teflon coating is often employed in industries like food processing or packaging that necessitate non-stick properties. These examples showcase the various steel round bar surface finishes that can be utilized to enhance lubricity. The choice of finish depends on specific application requirements and the desired level of lubrication and wear resistance.
Send your message to us
SAE1045 C45 Cold Drawn Steel Round Bar
- Loading Port:
- Tianjin
- Payment Terms:
- TT OR LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 100 m.t.
- Supply Capability:
- 50000 m.t./month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords


































