Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverters SG630MX
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
You Might Also Like
1. Structure of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverters SG630MX Description
SG630KTL is using low-frequency isolation transformer for protective purpose.
Its wider input voltage range ensures more combinations of the PV arrays.
Moreover, optical fiber isolation technology has been adopted to increase its anti-interference ability under the circumstances
of multiple inverters installation.
In addition, optimized circuit and structural design has improved system thermal efficiency which enhancing
system reliability and stability.
Reinforced protection functions, including the DC ground fault protection, make it the best product for large
scale PV power plant.
2. Main Features of the Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverters SG630MX
• CE certification, CGC certification
• LVRT (Zero-voltage Ride-through)
• Active power continuously adjustable (0~100%)
• Reactive power control with power factor from 0.9 lagging to 0.9 leading
• DC input voltage up to 1000V
• Latest 32 bit DSP chip, advanced digital lock-in technique, more quickly and precisely
• -30℃~+55℃ continuously operating at rated power
• Continuously and stably working in high altitude environment
• Auxiliary heater (Optional)
3. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverters SG630MX Images


4. Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverters SG630MX Specification
MODEL | SG630MX-E |
DC SIDE DATA | |
Max. DC Voltage | 1000Vdc |
MPP Voltage Range | 615~850Vdc |
Max. DC Power | 7130kWp |
Max. Input Current | 1160A |
AC SIDE DATA | |
Rated Output Power | 630kW |
Rated Grid Voltage | 400Vac |
Grid Voltage Range | 250~362Vac |
Rated Grid Frequency | 50Hz/60Hz |
Grid Frequency Range | 47~52Hz/57~62Hz |
Output Current THD | <3% (at nominal power) |
DC Current Injection | <0.5% of rated inverter output current |
Power Factor | 0.9(lagging)~0.9(leading) |
SYSTEM | |
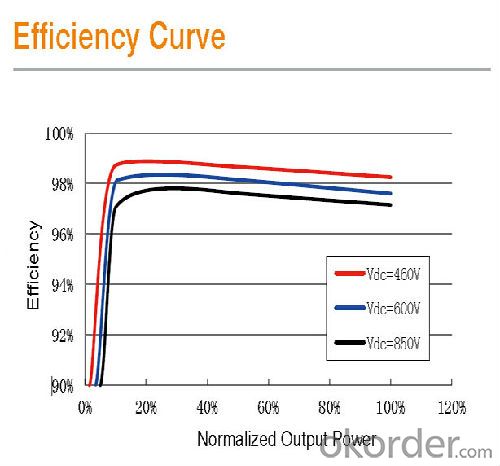
Max. Efficiency | 98.6% |
Euro Efficiency | 98.5% |
Protection Degree | IP21 |
Operating Temp. | -30~+65°C(> 55°C derating) |
Cooling Method | Temperature controlled forced-air cooling |
Relative Humidity | 0~95%, non-condensing |
Max. Working Altitude | 6000m (operation with derating above 3000m) |
Display AND COMMUNICATIONS | |
Display | touch screen LCD |
Standard Comm. Interfaces | RS485 |
Optional Comm. Interfaces | Ethernet |
MECHANICAL DATA | |
Dimensions(WxHxD) | 1606x2304x860mm |
Net Weight | 1700kg |
5. FAQ of Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverters SG630MX
Q1. What is the difference between inverter and solar inverter?
A1. Inverter only has AC inpput, but solar inverter both connect to AC input and solar panel, it saves more power.
Q2. What is the difference between MPPT&PWM?
A2. MPPT has higher efficiency, it can track the max power point and won't waste energy.
- Q: What is the role of a bypass switch in a solar inverter?
- The role of a bypass switch in a solar inverter is to provide a backup mechanism that allows the system to switch to the grid power in case of any issues or failures with the solar power generation. This ensures a continuous supply of electricity to the connected loads, even when the solar panels are not generating enough power or are experiencing problems.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in harsh weather conditions?
- Yes, solar inverters are designed to be used in harsh weather conditions. They are built to withstand extreme temperatures, high humidity, and heavy rain or snow. Additionally, they have protective features such as sealed enclosures and corrosion-resistant components to ensure reliable operation even in challenging weather environments.
- Q: What is the importance of insulation resistance measurement in a solar inverter?
- Insulation resistance measurement in a solar inverter is crucial as it helps ensure the safety and efficiency of the electrical system. By measuring the insulation resistance, any potential faults or deteriorations in the insulation can be detected, preventing electrical leakage or short circuits. This measurement also helps identify any insulation breakdowns that may compromise the performance and reliability of the solar inverter. Ultimately, insulation resistance measurement is essential for maintaining the integrity of the solar inverter and ensuring the safety of both the electrical system and the people using it.
- Q: How do you monitor the performance of a solar inverter?
- To monitor the performance of a solar inverter, several methods can be employed. Firstly, real-time monitoring systems can be installed that collect data on various parameters such as power output, voltage, current, and temperature. These systems often include data loggers or communication modules that transmit the information to a central monitoring station or cloud-based platform. Additionally, regular inspections and maintenance checks can be conducted to visually inspect the inverter for any signs of damage, loose connections, or overheating. Monitoring the inverter's efficiency over time, comparing the actual power output with the expected output based on solar irradiance and temperature, can also provide insights into its performance. Furthermore, some solar inverters come with built-in monitoring capabilities, allowing users to access performance data through a web-based interface or mobile app. This provides real-time and historical data, including energy production, system faults, and alerts, enabling users to identify and address any issues promptly. Overall, a combination of real-time monitoring systems, regular inspections, and utilizing inverter-specific monitoring features can effectively monitor the performance of a solar inverter.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used for residential applications?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used for residential applications. In fact, it is commonly used in residential solar power systems to convert the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power household appliances and electronics.
- Q: What is the role of frequency support in a solar inverter?
- The role of frequency support in a solar inverter is to ensure that the electricity generated by the solar panels is synchronized with the frequency of the electrical grid. This support is necessary to maintain grid stability and prevent any disruptions caused by fluctuations in frequency. The solar inverter monitors the grid frequency and adjusts the output of the solar panels accordingly, either by increasing or decreasing the power generation, to match the grid's frequency requirements.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a solar-powered pool heating system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a solar-powered pool heating system. The solar inverter is responsible for converting the direct current (DC) generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used to power various devices, including pool heating systems.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used in areas with unstable grid power?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used in areas with unstable grid power. Solar inverters are designed to convert the DC power generated by solar panels into AC power that can be used by household appliances or fed back into the grid. In areas with unstable grid power, solar inverters can provide a reliable and consistent power supply by utilizing the energy stored in the solar panels or batteries. This ensures a continuous power supply, even during grid power fluctuations or outages.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used with a solar-powered waste management system?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used with a solar-powered waste management system. A solar inverter is used to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity that can be used to power various appliances and systems. In the case of a solar-powered waste management system, the solar inverter would be an essential component to convert the DC power generated by the solar panels into the AC power required to operate the waste management equipment.
- Q: Can a solar inverter be used for both residential and commercial applications?
- Yes, a solar inverter can be used for both residential and commercial applications. Solar inverters are designed to convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is suitable for use in homes and businesses. They are versatile and can be scaled up or down depending on the size of the solar power system, making them suitable for both residential and commercial installations.
Send your message to us
Photovoltaic Grid-Connected Inverters SG630MX
- Loading Port:
- China Main Port
- Payment Terms:
- TT or LC
- Min Order Qty:
- 10 unit
- Supply Capability:
- 1000 unit/month
OKorder Service Pledge
OKorder Financial Service
Similar products
Hot products
Hot Searches
Related keywords
































